Tanapol Kosolwattana
FCOM: A Federated Collaborative Online Monitoring Framework via Representation Learning
May 30, 2024Abstract:Online learning has demonstrated notable potential to dynamically allocate limited resources to monitor a large population of processes, effectively balancing the exploitation of processes yielding high rewards, and the exploration of uncertain processes. However, most online learning algorithms were designed under 1) a centralized setting that requires data sharing across processes to obtain an accurate prediction or 2) a homogeneity assumption that estimates a single global model from the decentralized data. To facilitate the online learning of heterogeneous processes from the decentralized data, we propose a federated collaborative online monitoring method, which captures the latent representative models inherent in the population through representation learning and designs a novel federated collaborative UCB algorithm to estimate the representative models from sequentially observed decentralized data. The efficiency of our method is illustrated through theoretical analysis, simulation studies, and decentralized cognitive degradation monitoring in Alzheimer's disease.
Online Modeling and Monitoring of Dependent Processes under Resource Constraints
Jul 26, 2023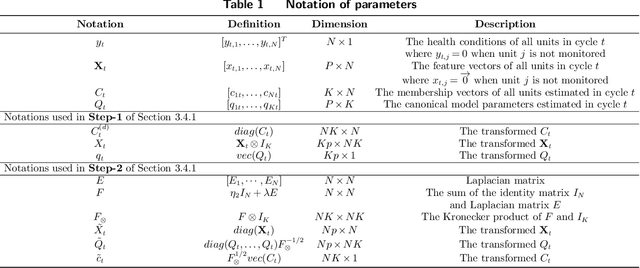
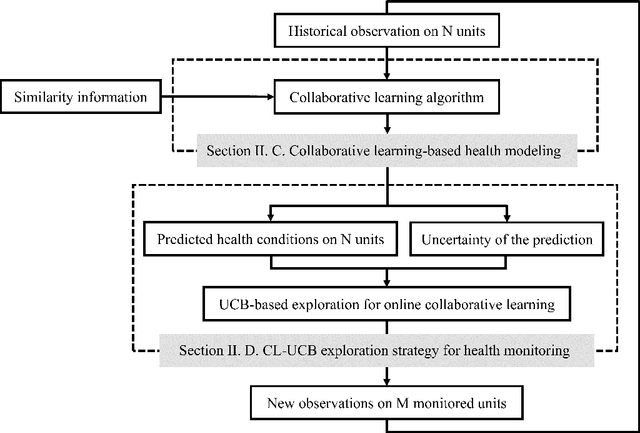
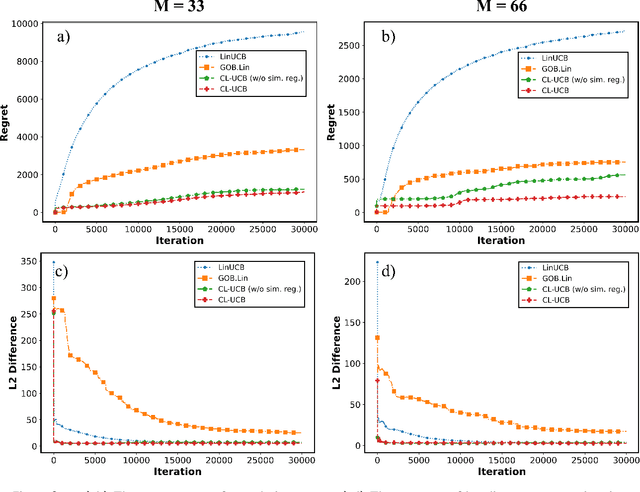
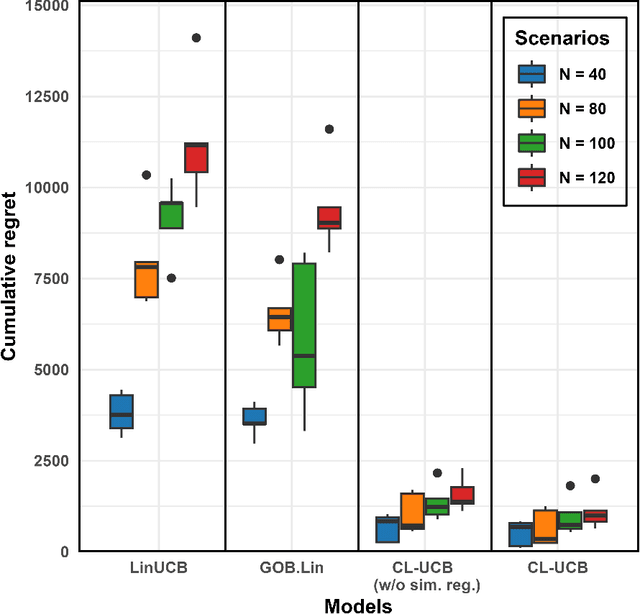
Abstract:Monitoring a population of dependent processes under limited resources is critical for abnormal events detection. A novel online collaborative learning method is proposed to adaptively allocate the resources for exploitation of high-risk processes and exploration of dependent dynamics. Efficiency of the proposed method is proved through theoretical analysis and experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge