Tamer Rabie
The Bulldozer Technique: Efficient Elimination of Local Minima Traps for APF-Based Robot Navigation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Path planning is a fundamental component in autonomous mobile robotics, enabling a robot to navigate from its current location to a desired goal while avoiding obstacles. Among the various techniques, Artificial Potential Field (APF) methods have gained popularity due to their simplicity, real-time responsiveness, and low computational requirements. However, a major limitation of conventional APF approaches is the local minima trap problem, where the robot becomes stuck in a position with no clear direction toward the goal. This paper proposes a novel path planning technique, termed the Bulldozer, which addresses the local minima issue while preserving the inherent advantages of APF. The Bulldozer technique introduces a backfilling mechanism that systematically identifies and eliminates local minima regions by increasing their potential values, analogous to a bulldozer filling potholes in a road. Additionally, a ramp-based enhancement is incorporated to assist the robot in escaping trap areas when starting within a local minimum. The proposed technique is experimentally validated using a physical mobile robot across various maps with increasing complexity. Comparative analyses are conducted against standard APF, adaptive APF, and well-established planning algorithms such as A*, PRM, and RRT. Results demonstrate that the Bulldozer technique effectively resolves the local minima problem while achieving superior execution speed and competitive path quality. Furthermore, a kinematic tracking controller is employed to assess the smoothness and traceability of the planned paths, confirming their suitability for real-world execution.
FaceBots: Steps Towards Enhanced Long-Term Human-Robot Interaction by Utilizing and Publishing Online Social Information
Apr 30, 2009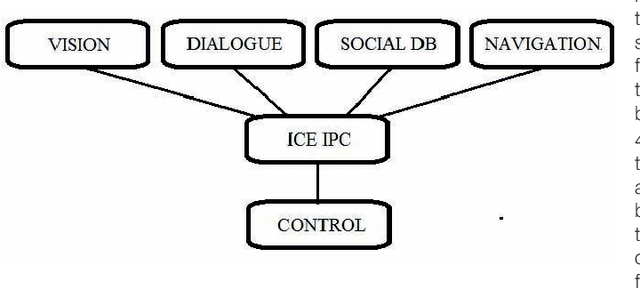

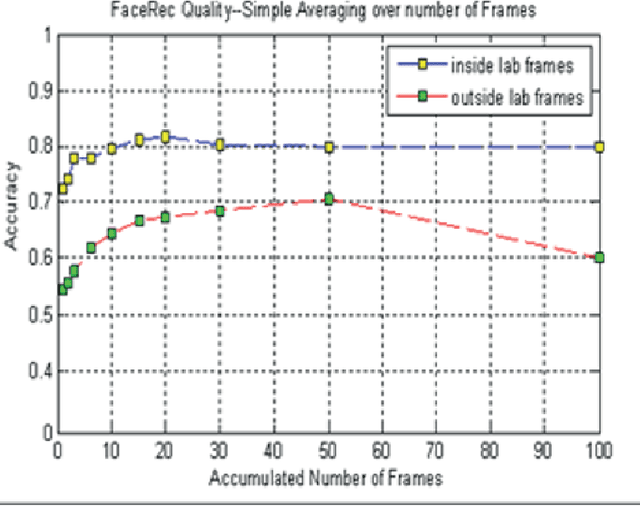
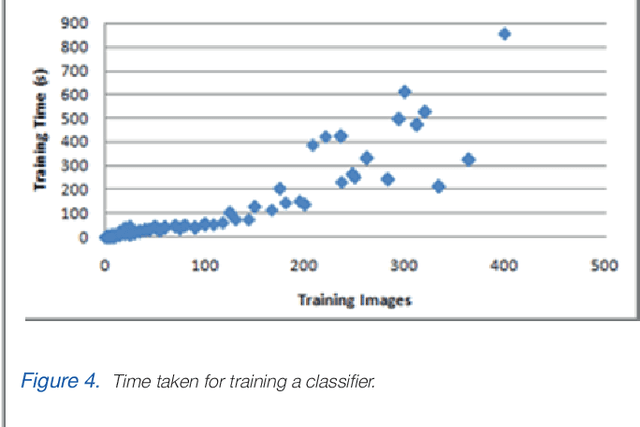
Abstract:Our project aims at supporting the creation of sustainable and meaningful longer-term human-robot relationships through the creation of embodied robots with face recognition and natural language dialogue capabilities, which exploit and publish social information available on the web (Facebook). Our main underlying experimental hypothesis is that such relationships can be significantly enhanced if the human and the robot are gradually creating a pool of shared episodic memories that they can co-refer to (shared memories), and if they are both embedded in a social web of other humans and robots they both know and encounter (shared friends). In this paper, we are presenting such a robot, which as we will see achieves two significant novelties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge