Taeuk Jang
A Unified Debiasing Approach for Vision-Language Models across Modalities and Tasks
Oct 10, 2024

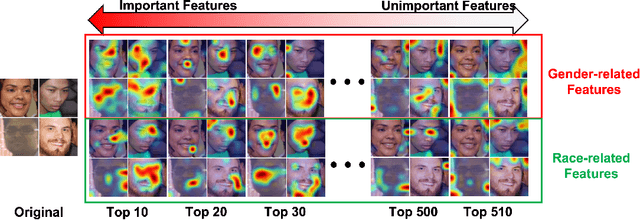

Abstract:Recent advancements in Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have enabled complex multimodal tasks by processing text and image data simultaneously, significantly enhancing the field of artificial intelligence. However, these models often exhibit biases that can skew outputs towards societal stereotypes, thus necessitating debiasing strategies. Existing debiasing methods focus narrowly on specific modalities or tasks, and require extensive retraining. To address these limitations, this paper introduces Selective Feature Imputation for Debiasing (SFID), a novel methodology that integrates feature pruning and low confidence imputation (LCI) to effectively reduce biases in VLMs. SFID is versatile, maintaining the semantic integrity of outputs and costly effective by eliminating the need for retraining. Our experimental results demonstrate SFID's effectiveness across various VLMs tasks including zero-shot classification, text-to-image retrieval, image captioning, and text-to-image generation, by significantly reducing gender biases without compromising performance. This approach not only enhances the fairness of VLMs applications but also preserves their efficiency and utility across diverse scenarios.
Group-Aware Threshold Adaptation for Fair Classification
Nov 08, 2021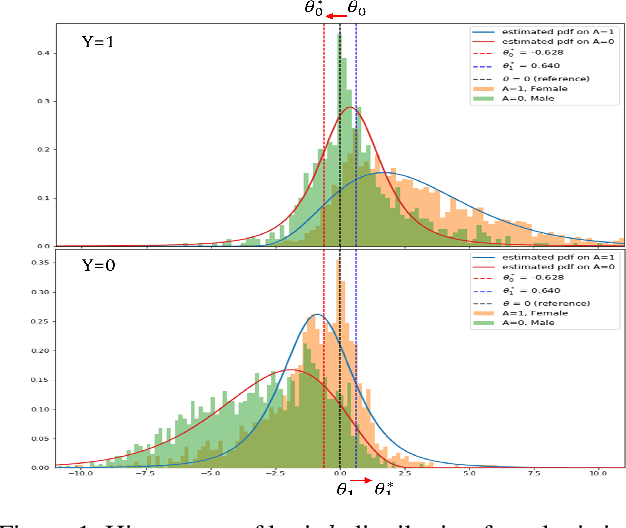
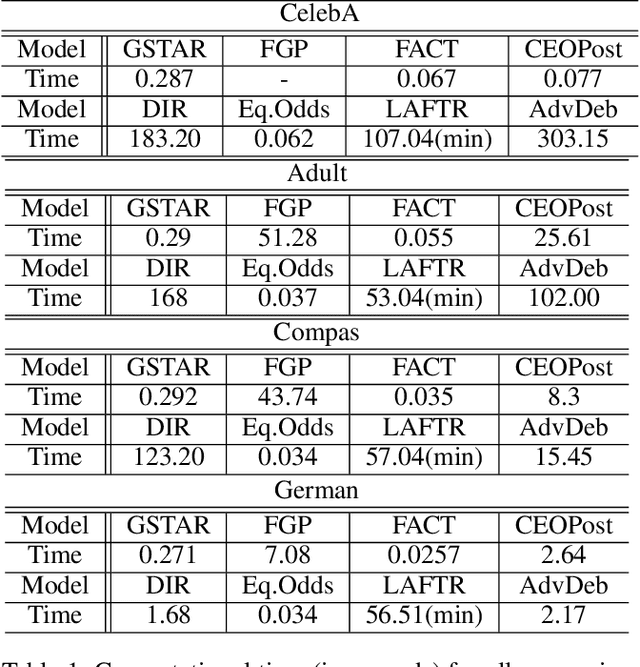
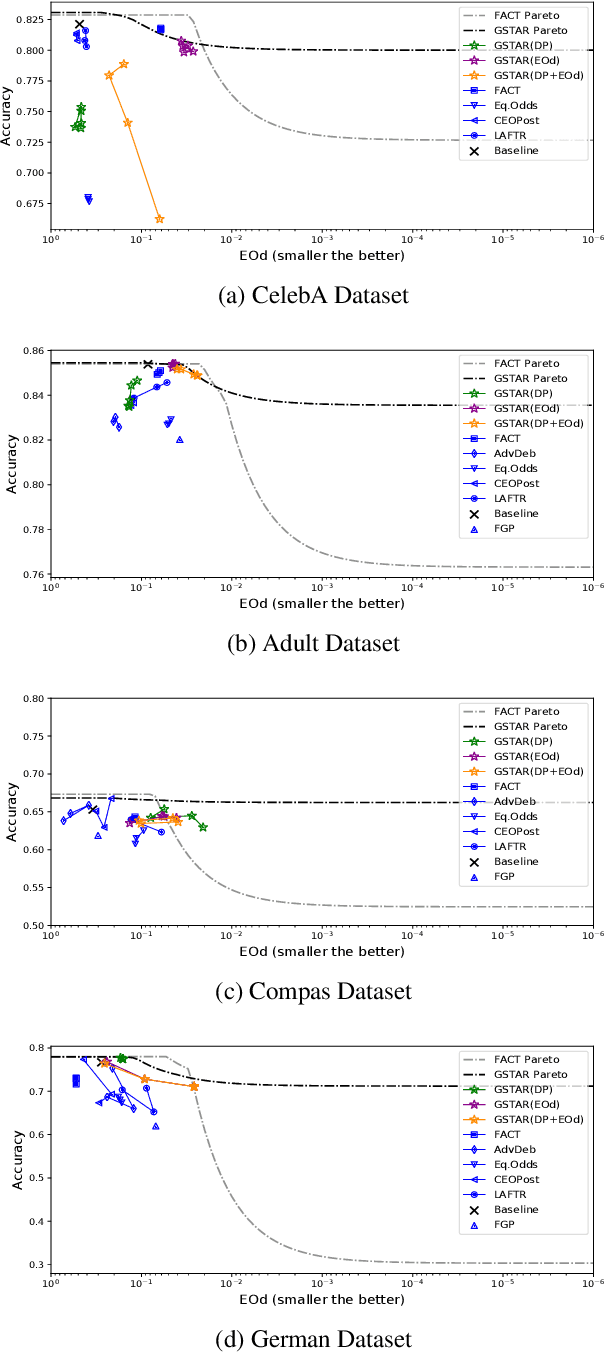
Abstract:The fairness in machine learning is getting increasing attention, as its applications in different fields continue to expand and diversify. To mitigate the discriminated model behaviors between different demographic groups, we introduce a novel post-processing method to optimize over multiple fairness constraints through group-aware threshold adaptation. We propose to learn adaptive classification thresholds for each demographic group by optimizing the confusion matrix estimated from the probability distribution of a classification model output. As we only need an estimated probability distribution of model output instead of the classification model structure, our post-processing model can be applied to a wide range of classification models and improve fairness in a model-agnostic manner and ensure privacy. This even allows us to post-process existing fairness methods to further improve the trade-off between accuracy and fairness. Moreover, our model has low computational cost. We provide rigorous theoretical analysis on the convergence of our optimization algorithm and the trade-off between accuracy and fairness of our method. Our method theoretically enables a better upper bound in near optimality than existing method under same condition. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods and obtains the result that is closest to the theoretical accuracy-fairness trade-off boundary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge