Taegyun Kim
A Sharp Universality Dichotomy for the Free Energy of Spherical Spin Glasses
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:We study the free energy for pure and mixed spherical $p$-spin models with i.i.d.\ disorder. In the mixed case, each $p$-interaction layer is assumed either to have regularly varying tails with exponent $α_p$ or to satisfy a finite $2p$-th moment condition. For the pure spherical $p$-spin model with regularly varying disorder of tail index $α$, we introduce a tail-adapted normalization that interpolates between the classical Gaussian scaling and the extreme-value scale, and we prove a sharp universality dichotomy for the quenched free energy. In the subcritical regime $α<2p$, the thermodynamics is driven by finitely many extremal couplings and the free energy converges to a non-degenerate random limit described by the NIM (non-intersecting monomial) model, depending only on extreme-order statistics. At the critical exponent $α=2p$, we obtain a random one-dimensional TAP-type variational formula capturing the coexistence of an extremal spike and a universal Gaussian bulk on spherical slices. In the supercritical regime $α>2p$ (more generally, under a finite $2p$-th moment assumption), the free energy is universal and agrees with the deterministic Crisanti--Sommers/Parisi value of the corresponding Gaussian model, as established in [Sawhney-Sellke'24]. We then extend the subcritical and critical results to mixed spherical models in which each $p$-layer is either heavy-tailed with $α_p\le 2p$ or has finite $2p$-th moment. In particular, we derive a TAP-type variational representation for the mixed model, yielding a unified universality classification of the quenched free energy across tail exponents and mixtures.
BaitWatcher: A lightweight web interface for the detection of incongruent news headlines
Mar 23, 2020

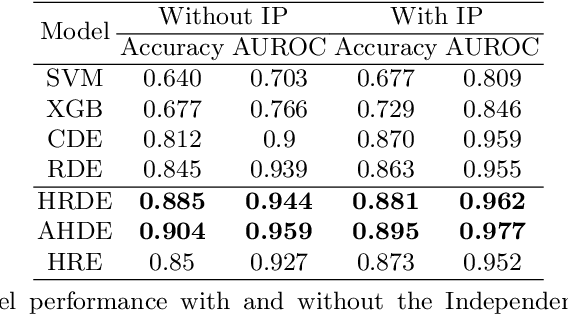
Abstract:In digital environments where substantial amounts of information are shared online, news headlines play essential roles in the selection and diffusion of news articles. Some news articles attract audience attention by showing exaggerated or misleading headlines. This study addresses the \textit{headline incongruity} problem, in which a news headline makes claims that are either unrelated or opposite to the contents of the corresponding article. We present \textit{BaitWatcher}, which is a lightweight web interface that guides readers in estimating the likelihood of incongruence in news articles before clicking on the headlines. BaitWatcher utilizes a hierarchical recurrent encoder that efficiently learns complex textual representations of a news headline and its associated body text. For training the model, we construct a million scale dataset of news articles, which we also release for broader research use. Based on the results of a focus group interview, we discuss the importance of developing an interpretable AI agent for the design of a better interface for mitigating the effects of online misinformation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge