Tadeo Corradi
The Cross-Depiction Problem: Computer Vision Algorithms for Recognising Objects in Artwork and in Photographs
May 01, 2015
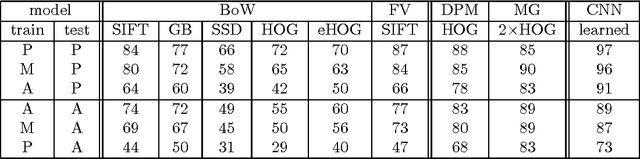


Abstract:The cross-depiction problem is that of recognising visual objects regardless of whether they are photographed, painted, drawn, etc. It is a potentially significant yet under-researched problem. Emulating the remarkable human ability to recognise objects in an astonishingly wide variety of depictive forms is likely to advance both the foundations and the applications of Computer Vision. In this paper we benchmark classification, domain adaptation, and deep learning methods; demonstrating that none perform consistently well in the cross-depiction problem. Given the current interest in deep learning, the fact such methods exhibit the same behaviour as all but one other method: they show a significant fall in performance over inhomogeneous databases compared to their peak performance, which is always over data comprising photographs only. Rather, we find the methods that have strong models of spatial relations between parts tend to be more robust and therefore conclude that such information is important in modelling object classes regardless of appearance details.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge