T. Li
Highly Compressed Tokenizer Can Generate Without Training
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Commonly used image tokenizers produce a 2D grid of spatially arranged tokens. In contrast, so-called 1D image tokenizers represent images as highly compressed one-dimensional sequences of as few as 32 discrete tokens. We find that the high degree of compression achieved by a 1D tokenizer with vector quantization enables image editing and generative capabilities through heuristic manipulation of tokens, demonstrating that even very crude manipulations -- such as copying and replacing tokens between latent representations of images -- enable fine-grained image editing by transferring appearance and semantic attributes. Motivated by the expressivity of the 1D tokenizer's latent space, we construct an image generation pipeline leveraging gradient-based test-time optimization of tokens with plug-and-play loss functions such as reconstruction or CLIP similarity. Our approach is demonstrated for inpainting and text-guided image editing use cases, and can generate diverse and realistic samples without requiring training of any generative model.
Fast digital refocusing and depth of field extended Fourier ptychography microscopy
May 06, 2021

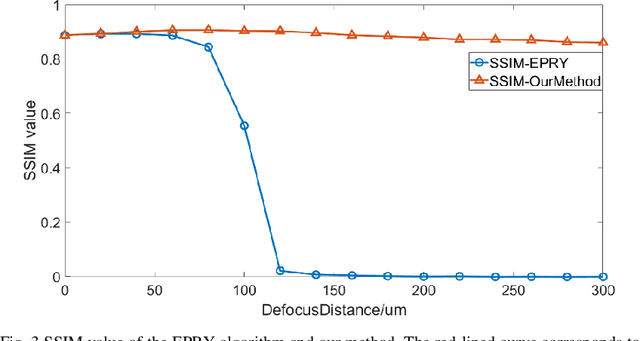
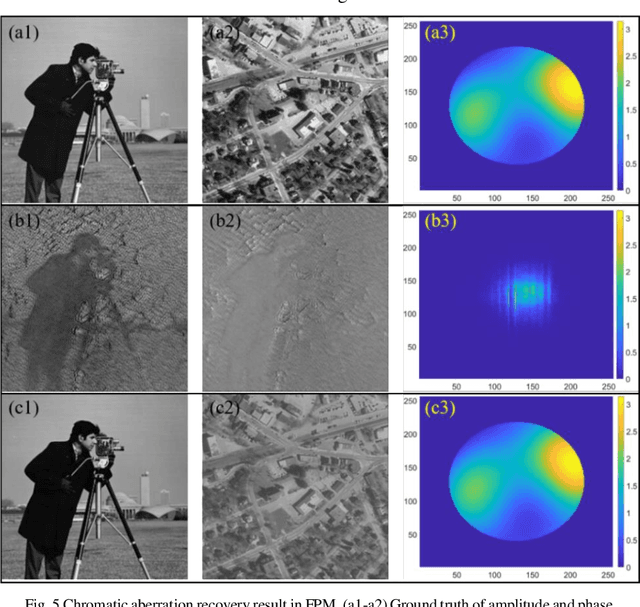
Abstract:Fourier ptychography microscopy (FPM), sharing its roots with synthetic aperture technique and phase retrieval method, is a recently developed computational microscopic super-resolution technique. By turning on the light-emitting diode (LED) elements sequentially and acquiring the corresponding images that contain different spatial frequencies, FPM can achieve a wide field-of-view (FOV), high-spatial-resolution imaging, and phase recovery simultaneously. Conventional FPM assumes that the sample is sufficiently thin and strictly in focus. Nevertheless, even for a relatively thin sample, the non-planar distribution characteristics and the non-ideal position/posture of the sample will cause all or part of FOV to be defocused. In this paper, we proposed a fast digital refocusing and depth-of-field (DOF) extended FPM strategy by taking the advantages of image lateral shift caused by sample defocusing and varied-angle illuminations. The lateral shift amount is proportional to the defocus distance and the tangent of the illumination angle. Instead of searching the optimal defocus distance in optimization strategy, which is time-consuming, the defocus distance of each subregion of the sample can be precisely and quickly obtained by calculating the relative lateral shift amounts corresponding to different oblique illuminations. And then, the digital refocusing strategy rooting in the Fresnel propagator is integrated into the FPM framework to achieve the high-resolution and phase information reconstruction for each part of the sample, which means the DOF the FPM is effectively extended. The feasibility of the proposed method in fast digital refocusing and FOV extending is verified in the actual experiments with the USAF chart and biological samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge