T. Jayaraman
Crop Type Identification for Smallholding Farms: Analyzing Spatial, Temporal and Spectral Resolutions in Satellite Imagery
May 06, 2022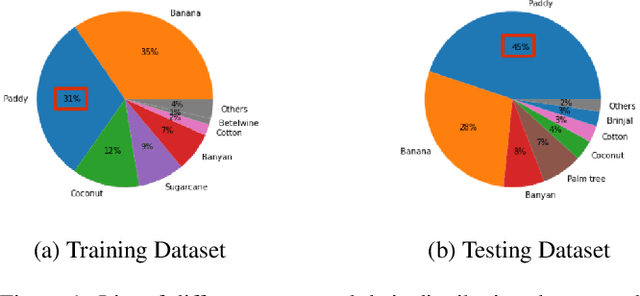
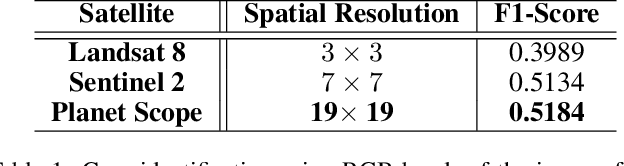
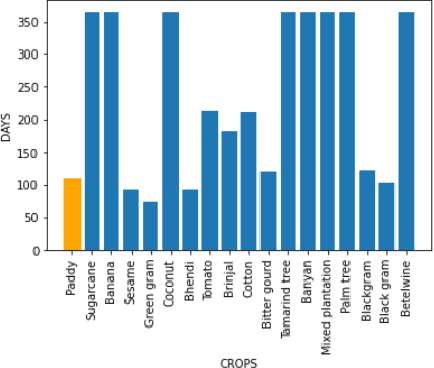
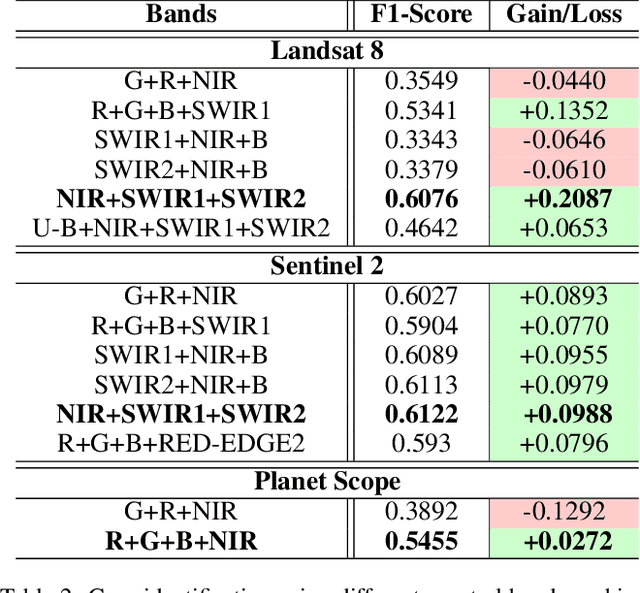
Abstract:The integration of the modern Machine Learning (ML) models into remote sensing and agriculture has expanded the scope of the application of satellite images in the agriculture domain. In this paper, we present how the accuracy of crop type identification improves as we move from medium-spatiotemporal-resolution (MSTR) to high-spatiotemporal-resolution (HSTR) satellite images. We further demonstrate that high spectral resolution in satellite imagery can improve prediction performance for low spatial and temporal resolutions (LSTR) images. The F1-score is increased by 7% when using multispectral data of MSTR images as compared to the best results obtained from HSTR images. Similarly, when crop season based time series of multispectral data is used we observe an increase of 1.2% in the F1-score. The outcome motivates further advancements in the field of synthetic band generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge