Swastik Brahma
Reliable Multi-view 3D Reconstruction for `Just-in-time' Edge Environments
Aug 21, 2025Abstract:Multi-view 3D reconstruction applications are revolutionizing critical use cases that require rapid situational-awareness, such as emergency response, tactical scenarios, and public safety. In many cases, their near-real-time latency requirements and ad-hoc needs for compute resources necessitate adoption of `Just-in-time' edge environments where the system is set up on the fly to support the applications during the mission lifetime. However, reliability issues can arise from the inherent dynamism and operational adversities of such edge environments, resulting in spatiotemporally correlated disruptions that impact the camera operations, which can lead to sustained degradation of reconstruction quality. In this paper, we propose a novel portfolio theory inspired edge resource management strategy for reliable multi-view 3D reconstruction against possible system disruptions. Our proposed methodology can guarantee reconstruction quality satisfaction even when the cameras are prone to spatiotemporally correlated disruptions. The portfolio theoretic optimization problem is solved using a genetic algorithm that converges quickly for realistic system settings. Using publicly available and customized 3D datasets, we demonstrate the proposed camera selection strategy's benefits in guaranteeing reliable 3D reconstruction against traditional baseline strategies, under spatiotemporal disruptions.
Poster: Reliable 3D Reconstruction for Ad-hoc Edge Implementations
Nov 16, 2024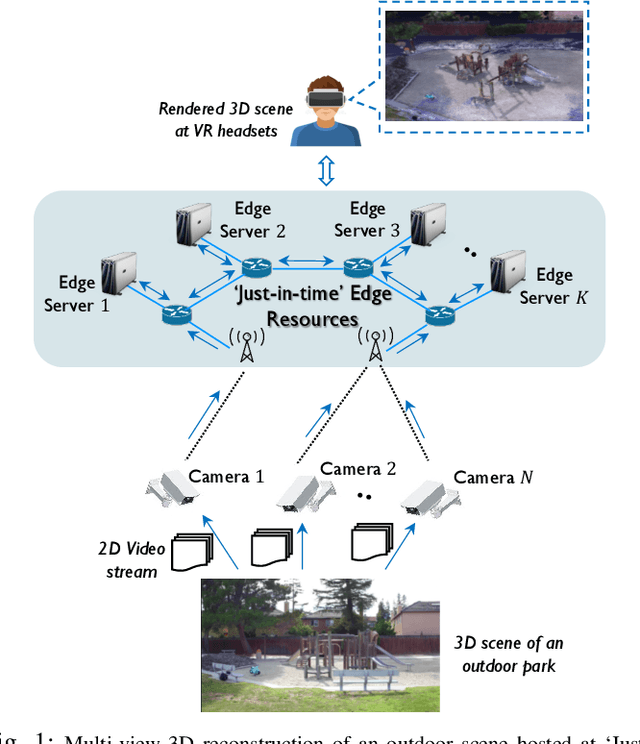
Abstract:Ad-hoc edge deployments to support real-time complex video processing applications such as, multi-view 3D reconstruction often suffer from spatio-temporal system disruptions that greatly impact reconstruction quality. In this poster paper, we present a novel portfolio theory-inspired edge resource management strategy to ensure reliable multi-view 3D reconstruction by accounting for possible system disruptions.
Towards the Design of Prospect-Theory based Human Decision Rules for Hypothesis Testing
Oct 04, 2016



Abstract:Detection rules have traditionally been designed for rational agents that minimize the Bayes risk (average decision cost). With the advent of crowd-sensing systems, there is a need to redesign binary hypothesis testing rules for behavioral agents, whose cognitive behavior is not captured by traditional utility functions such as Bayes risk. In this paper, we adopt prospect theory based models for decision makers. We consider special agent models namely optimists and pessimists in this paper, and derive optimal detection rules under different scenarios. Using an illustrative example, we also show how the decision rule of a human agent deviates from the Bayesian decision rule under various behavioral models, considered in this paper.
Consensus based Detection in the Presence of Data Falsification Attacks
Apr 14, 2015



Abstract:This paper considers the problem of detection in distributed networks in the presence of data falsification (Byzantine) attacks. Detection approaches considered in the paper are based on fully distributed consensus algorithms, where all of the nodes exchange information only with their neighbors in the absence of a fusion center. In such networks, we characterize the negative effect of Byzantines on the steady-state and transient detection performance of the conventional consensus based detection algorithms. To address this issue, we study the problem from the network designer's perspective. More specifically, we first propose a distributed weighted average consensus algorithm that is robust to Byzantine attacks. We show that, under reasonable assumptions, the global test statistic for detection can be computed locally at each node using our proposed consensus algorithm. We exploit the statistical distribution of the nodes' data to devise techniques for mitigating the influence of data falsifying Byzantines on the distributed detection system. Since some parameters of the statistical distribution of the nodes' data might not be known a priori, we propose learning based techniques to enable an adaptive design of the local fusion or update rules.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge