Swapna Thorve
A Generative AI Technique for Synthesizing a Digital Twin for U.S. Residential Solar Adoption and Generation
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:Residential rooftop solar adoption is considered crucial for reducing carbon emissions. The lack of photovoltaic (PV) data at a finer resolution (e.g., household, hourly levels) poses a significant roadblock to informed decision-making. We discuss a novel methodology to generate a highly granular, residential-scale realistic dataset for rooftop solar adoption across the contiguous United States. The data-driven methodology consists of: (i) integrated machine learning models to identify PV adopters, (ii) methods to augment the data using explainable AI techniques to glean insights about key features and their interactions, and (iii) methods to generate household-level hourly solar energy output using an analytical model. The resulting synthetic datasets are validated using real-world data and can serve as a digital twin for modeling downstream tasks. Finally, a policy-based case study utilizing the digital twin for Virginia demonstrated increased rooftop solar adoption with the 30\% Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit, especially in Low-to-Moderate-Income communities.
High-resolution synthetic residential energy use profiles for the United States
Oct 14, 2022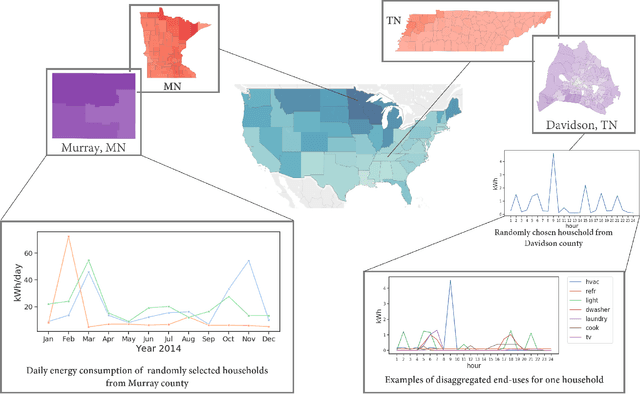


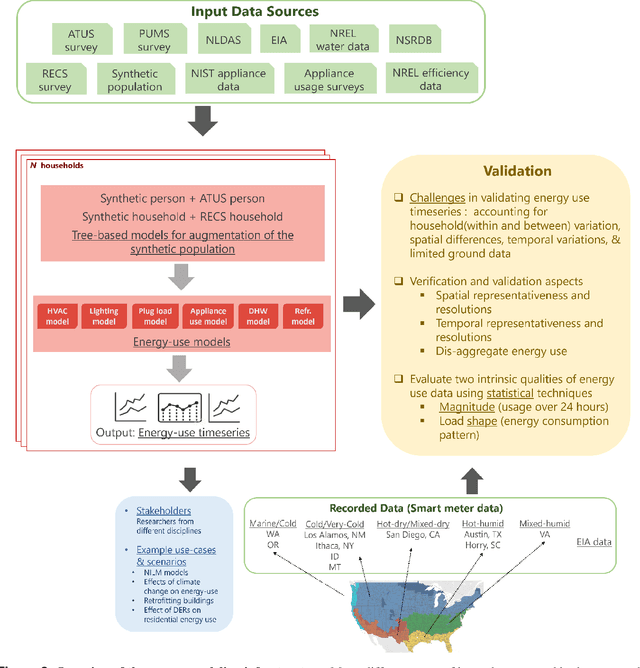
Abstract:Efficient energy consumption is crucial for achieving sustainable energy goals in the era of climate change and grid modernization. Thus, it is vital to understand how energy is consumed at finer resolutions such as household in order to plan demand-response events or analyze the impacts of weather, electricity prices, electric vehicles, solar, and occupancy schedules on energy consumption. However, availability and access to detailed energy-use data, which would enable detailed studies, has been rare. In this paper, we release a unique, large-scale, synthetic, residential energy-use dataset for the residential sector across the contiguous United States covering millions of households. The data comprise of hourly energy use profiles for synthetic households, disaggregated into Thermostatically Controlled Loads (TCL) and appliance use. The underlying framework is constructed using a bottom-up approach. Diverse open-source surveys and first principles models are used for end-use modeling. Extensive validation of the synthetic dataset has been conducted through comparisons with reported energy-use data. We present a detailed, open, high-resolution, residential energy-use dataset for the United States.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge