Suvidha Mhatre
Enhancing AI Transparency: XRL-Based Resource Management and RAN Slicing for 6G ORAN Architecture
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:This research introduces an advanced Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) framework designed to elucidate the decision-making processes of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) agents in ORAN architectures. By offering network-oriented explanations, the proposed scheme addresses the critical challenge of understanding and optimizing the control actions of DRL agents for resource management and allocation. Traditional methods, both model-agnostic and model-specific approaches, fail to address the unique challenges presented by XAI in the dynamic and complex environment of RAN slicing. This paper transcends these limitations by incorporating intent-based action steering, allowing for precise embedding and configuration across various operational timescales. This is particularly evident in its integration with xAPP and rAPP sitting at near-real-time and non-real-time RIC, respectively, enhancing the system's adaptability and performance. Our findings demonstrate the framework's significant impact on improving Key Performance Indicator (KPI)-based rewards, facilitated by the ability to make informed multimodal decisions involving multiple control parameters by a DRL agent. Thus, our work marks a significant step forward in the practical application and effectiveness of XAI in optimizing ORAN resource management strategies.
AIaaS for ORAN-based 6G Networks: Multi-time scale slice resource management with DRL
Nov 20, 2023


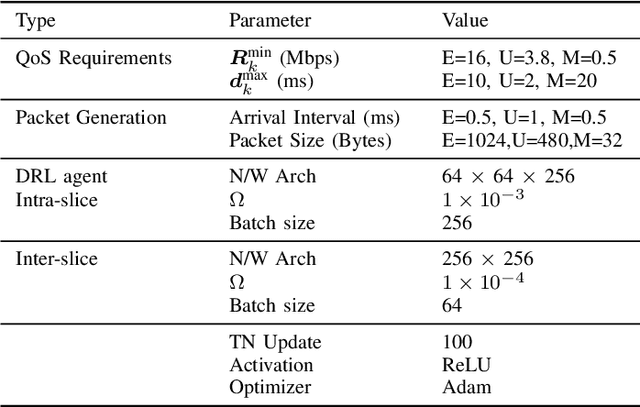
Abstract:This paper addresses how to handle slice resources for 6G networks at different time scales in an architecture based on an open radio access network (ORAN). The proposed solution includes artificial intelligence (AI) at the edge of the network and applies two control-level loops to obtain optimal performance compared to other techniques. The ORAN facilitates programmable network architectures to support such multi-time scale management using AI approaches. The proposed algorithms analyze the maximum utilization of resources from slice performance to take decisions at the inter-slice level. Inter-slice intelligent agents work at a non-real-time level to reconfigure resources within various slices. Further than meeting the slice requirements, the intra-slice objective must also include the minimization of maximum resource utilization. This enables smart utilization of the resources within each slice without affecting slice performance. Here, each xApp that is an intra-slice agent aims at meeting the optimal QoS of the users, but at the same time, some inter-slice objectives should be included to coordinate intra- and inter-slice agents. This is done without penalizing the main intra-slice objective. All intelligent agents use deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms to meet their objectives. We have presented results for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low latency (URLLC), and massive machine type communication (mMTC) slice categories.
Intelligent QoS aware slice resource allocation with user association parameterization for beyond 5G ORAN based architecture using DRL
Nov 02, 2023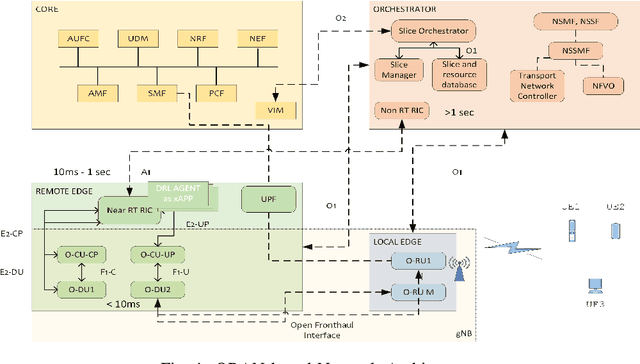

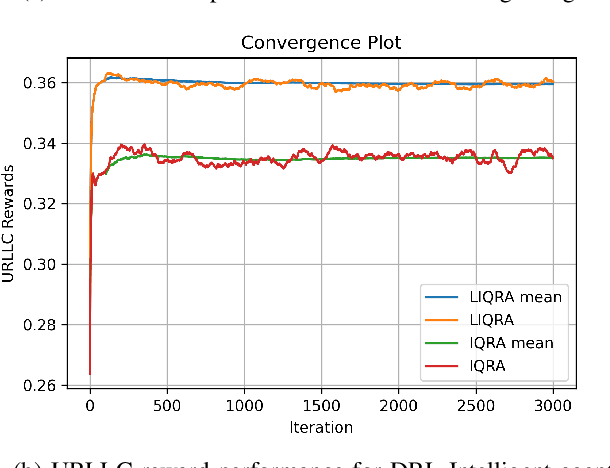

Abstract:The diverse requirements of beyond 5G services increase design complexity and demand dynamic adjustments to the network parameters. This can be achieved with slicing and programmable network architectures such as the open radio access network (ORAN). It facilitates the tuning of the network components exactly to the demands of future-envisioned applications as well as intelligence at the edge of the network. Artificial intelligence (AI) has recently drawn a lot of interest for its potential to solve challenging issues in wireless communication. Due to the non-deterministic, random, and complex behavior of models and parameters involved in the process, radio resource management is one of the topics that needs to be addressed with such techniques. The study presented in this paper proposes quality of service (QoS)-aware intra-slice resource allocation that provides superior performance compared to baseline and state of the art strategies. The slice-dedicated intelligent agents learn how to handle resources at near-RT RIC level time granularities while optimizing various key performance indicators (KPIs) and meeting QoS requirements for each end user. In order to improve KPIs and system performance with various reward functions, the study discusses Markov's decision process (MDP) and deep reinforcement learning (DRL) techniques, notably the deep Q network (DQN). The simulation evaluates the efficacy of the algorithm under dynamic conditions and various network characteristics. Results and analysis demonstrate the improvement in the performance of the network for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and ultra-reliable low latency (URLLC) slice categories.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge