Intelligent QoS aware slice resource allocation with user association parameterization for beyond 5G ORAN based architecture using DRL
Paper and Code
Nov 02, 2023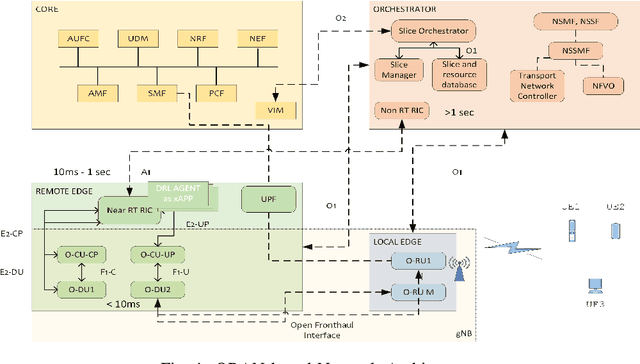

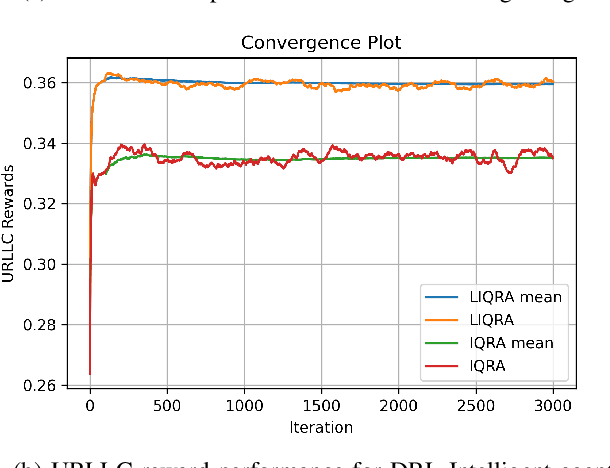

The diverse requirements of beyond 5G services increase design complexity and demand dynamic adjustments to the network parameters. This can be achieved with slicing and programmable network architectures such as the open radio access network (ORAN). It facilitates the tuning of the network components exactly to the demands of future-envisioned applications as well as intelligence at the edge of the network. Artificial intelligence (AI) has recently drawn a lot of interest for its potential to solve challenging issues in wireless communication. Due to the non-deterministic, random, and complex behavior of models and parameters involved in the process, radio resource management is one of the topics that needs to be addressed with such techniques. The study presented in this paper proposes quality of service (QoS)-aware intra-slice resource allocation that provides superior performance compared to baseline and state of the art strategies. The slice-dedicated intelligent agents learn how to handle resources at near-RT RIC level time granularities while optimizing various key performance indicators (KPIs) and meeting QoS requirements for each end user. In order to improve KPIs and system performance with various reward functions, the study discusses Markov's decision process (MDP) and deep reinforcement learning (DRL) techniques, notably the deep Q network (DQN). The simulation evaluates the efficacy of the algorithm under dynamic conditions and various network characteristics. Results and analysis demonstrate the improvement in the performance of the network for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and ultra-reliable low latency (URLLC) slice categories.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge