Suman Dowlagar
CMNEROne at SemEval-2022 Task 11: Code-Mixed Named Entity Recognition by leveraging multilingual data
Jun 15, 2022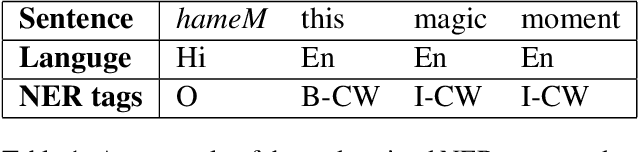
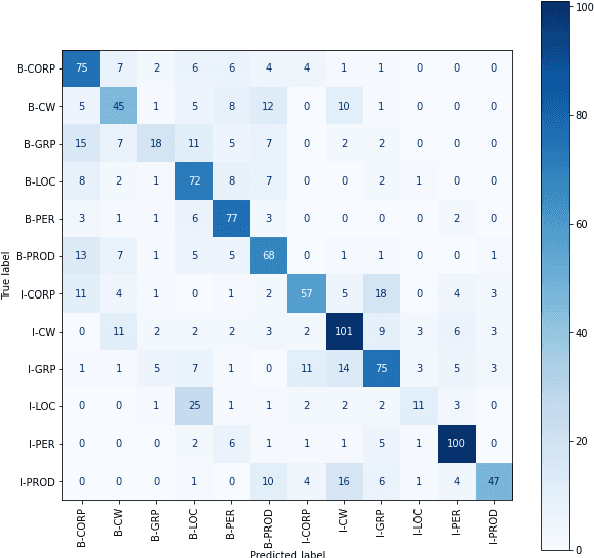
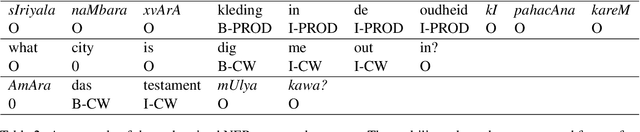
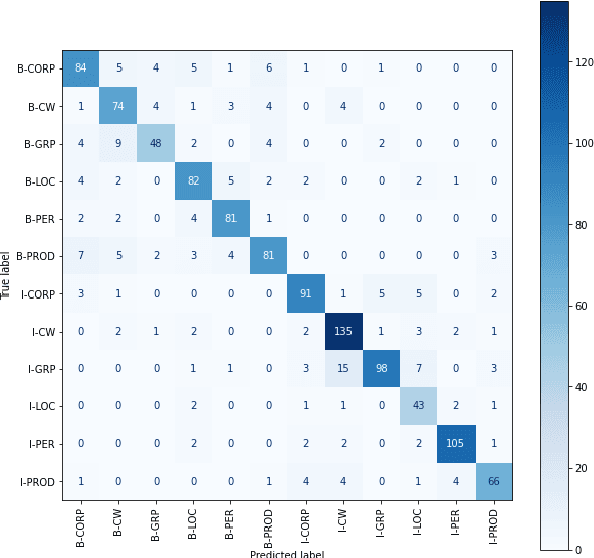
Abstract:Identifying named entities is, in general, a practical and challenging task in the field of Natural Language Processing. Named Entity Recognition on the code-mixed text is further challenging due to the linguistic complexity resulting from the nature of the mixing. This paper addresses the submission of team CMNEROne to the SEMEVAL 2022 shared task 11 MultiCoNER. The Code-mixed NER task aimed to identify named entities on the code-mixed dataset. Our work consists of Named Entity Recognition (NER) on the code-mixed dataset by leveraging the multilingual data. We achieved a weighted average F1 score of 0.7044, i.e., 6% greater than the baseline.
Unsupervised Technical Domain Terms Extraction using Term Extractor
Jan 22, 2021
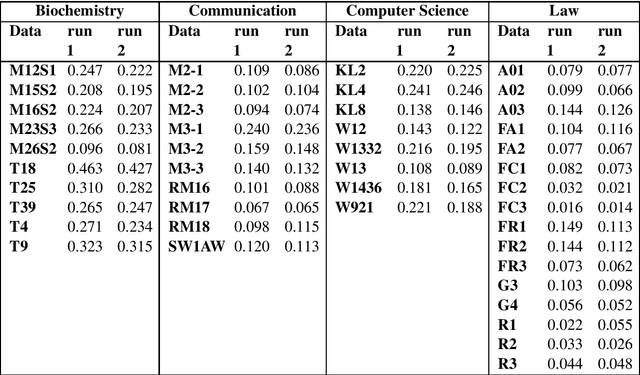

Abstract:Terminology extraction, also known as term extraction, is a subtask of information extraction. The goal of terminology extraction is to extract relevant words or phrases from a given corpus automatically. This paper focuses on the unsupervised automated domain term extraction method that considers chunking, preprocessing, and ranking domain-specific terms using relevance and cohesion functions for ICON 2020 shared task 2: TermTraction.
Multilingual Pre-Trained Transformers and Convolutional NN Classification Models for Technical Domain Identification
Jan 22, 2021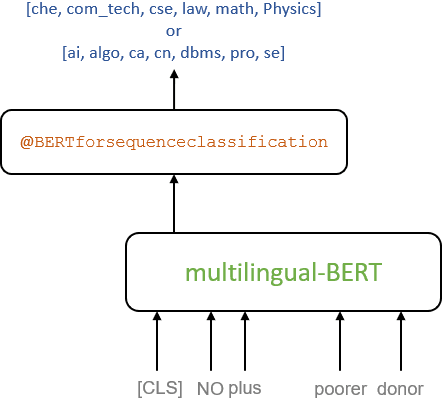
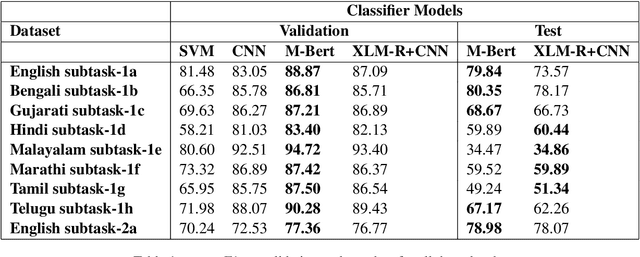
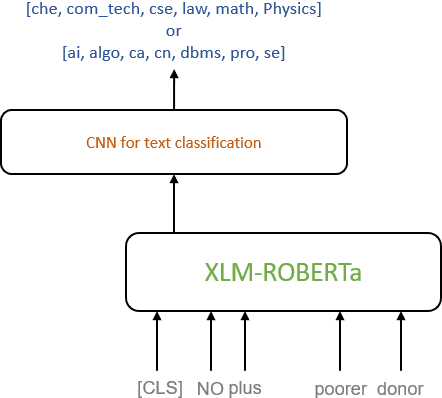
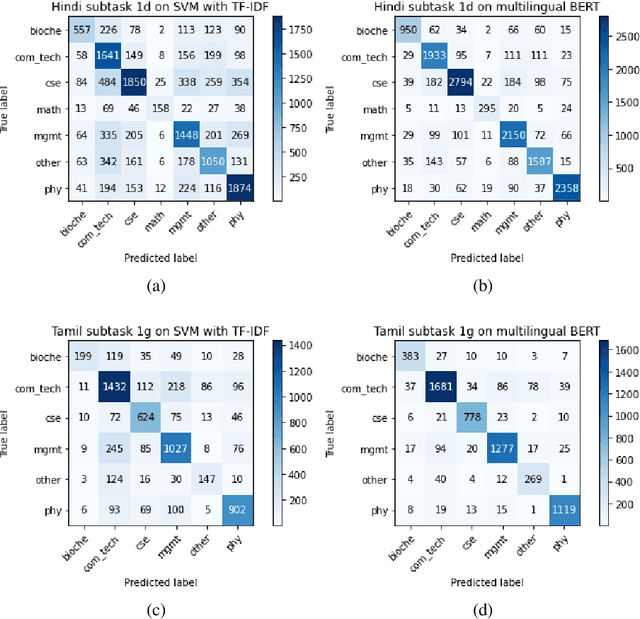
Abstract:In this paper, we present a transfer learning system to perform technical domain identification on multilingual text data. We have submitted two runs, one uses the transformer model BERT, and the other uses XLM-ROBERTa with the CNN model for text classification. These models allowed us to identify the domain of the given sentences for the ICON 2020 shared Task, TechDOfication: Technical Domain Identification. Our system ranked the best for the subtasks 1d, 1g for the given TechDOfication dataset.
Does a Hybrid Neural Network based Feature Selection Model Improve Text Classification?
Jan 22, 2021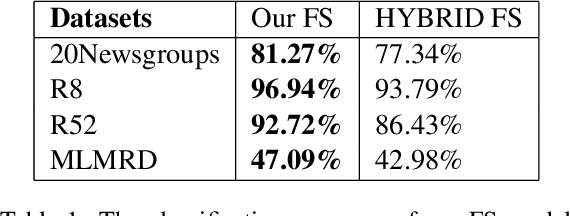
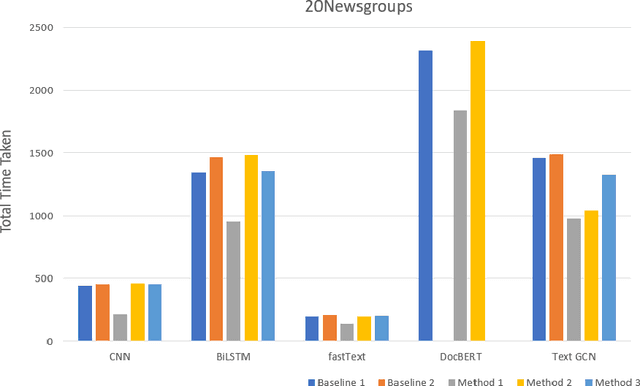
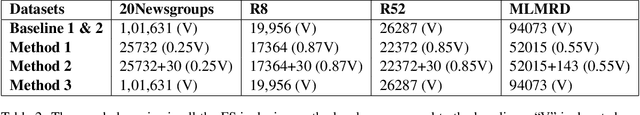
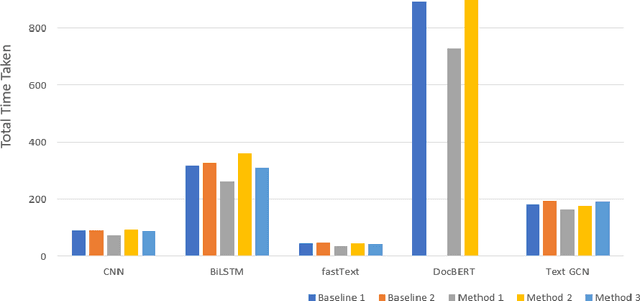
Abstract:Text classification is a fundamental problem in the field of natural language processing. Text classification mainly focuses on giving more importance to all the relevant features that help classify the textual data. Apart from these, the text can have redundant or highly correlated features. These features increase the complexity of the classification algorithm. Thus, many dimensionality reduction methods were proposed with the traditional machine learning classifiers. The use of dimensionality reduction methods with machine learning classifiers has achieved good results. In this paper, we propose a hybrid feature selection method for obtaining relevant features by combining various filter-based feature selection methods and fastText classifier. We then present three ways of implementing a feature selection and neural network pipeline. We observed a reduction in training time when feature selection methods are used along with neural networks. We also observed a slight increase in accuracy on some datasets.
HASOCOne@FIRE-HASOC2020: Using BERT and Multilingual BERT models for Hate Speech Detection
Jan 22, 2021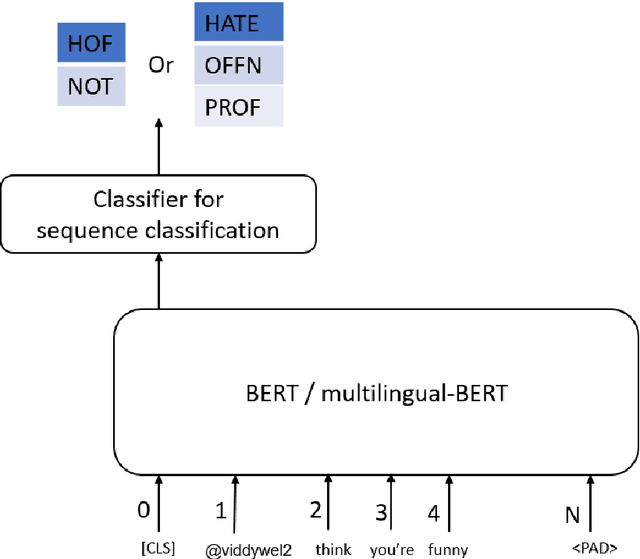
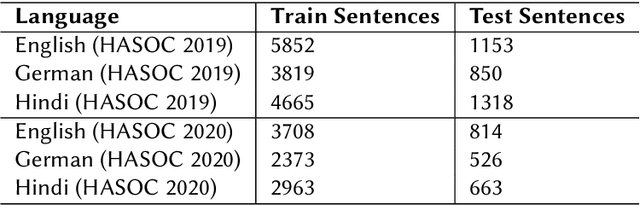
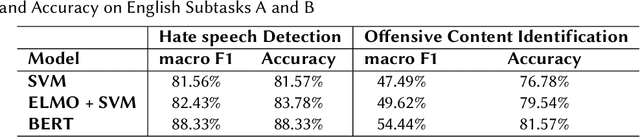
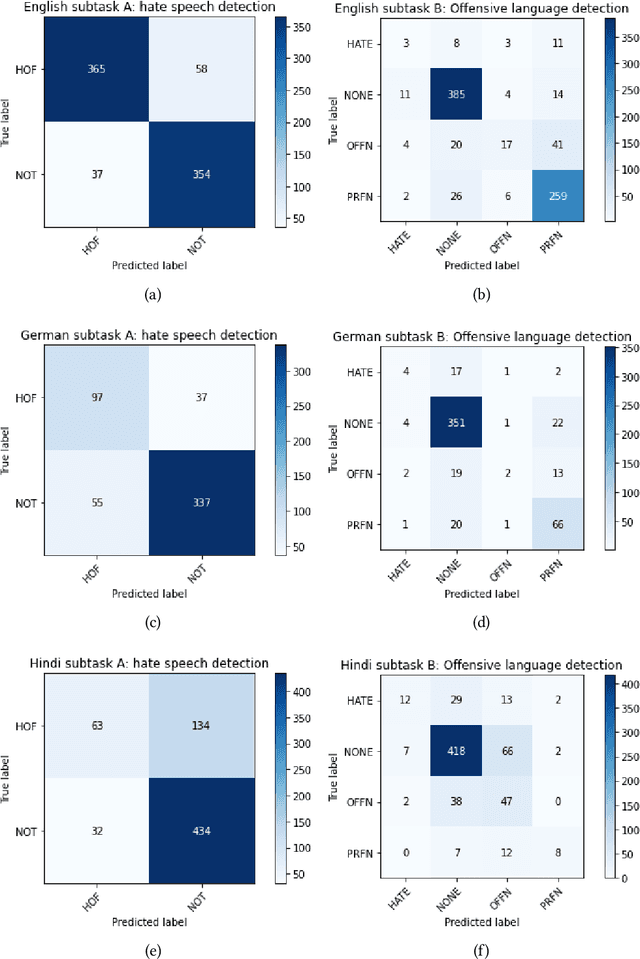
Abstract:Hateful and Toxic content has become a significant concern in today's world due to an exponential rise in social media. The increase in hate speech and harmful content motivated researchers to dedicate substantial efforts to the challenging direction of hateful content identification. In this task, we propose an approach to automatically classify hate speech and offensive content. We have used the datasets obtained from FIRE 2019 and 2020 shared tasks. We perform experiments by taking advantage of transfer learning models. We observed that the pre-trained BERT model and the multilingual-BERT model gave the best results. The code is made publically available at https://github.com/suman101112/hasoc-fire-2020.
CMSAOne@Dravidian-CodeMix-FIRE2020: A Meta Embedding and Transformer model for Code-Mixed Sentiment Analysis on Social Media Text
Jan 22, 2021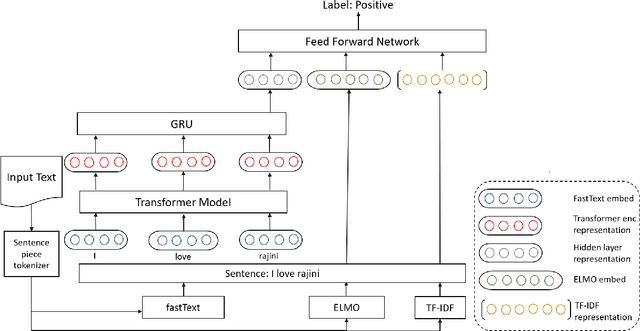


Abstract:Code-mixing(CM) is a frequently observed phenomenon that uses multiple languages in an utterance or sentence. CM is mostly practiced on various social media platforms and in informal conversations. Sentiment analysis (SA) is a fundamental step in NLP and is well studied in the monolingual text. Code-mixing adds a challenge to sentiment analysis due to its non-standard representations. This paper proposes a meta embedding with a transformer method for sentiment analysis on the Dravidian code-mixed dataset. In our method, we used meta embeddings to capture rich text representations. We used the proposed method for the Task: "Sentiment Analysis for Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text", and it achieved an F1 score of $0.58$ and $0.66$ for the given Dravidian code mixed data sets. The code is provided in the Github https://github.com/suman101112/fire-2020-Dravidian-CodeMix.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge