Subhashis Das
CSSDM Ontology to Enable Continuity of Care Data Interoperability
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of digital technologies and recent global pandemic scenarios have led to a growing focus on how these technologies can enhance healthcare service delivery and workflow to address crises. Action plans that consolidate existing digital transformation programs are being reviewed to establish core infrastructure and foundations for sustainable healthcare solutions. Reforming health and social care to personalize home care, for example, can help avoid treatment in overcrowded acute hospital settings and improve the experiences and outcomes for both healthcare professionals and service users. In this information-intensive domain, addressing the interoperability challenge through standards-based roadmaps is crucial for enabling effective connections between health and social care services. This approach facilitates safe and trustworthy data workflows between different healthcare system providers. In this paper, we present a methodology for extracting, transforming, and loading data through a semi-automated process using a Common Semantic Standardized Data Model (CSSDM) to create personalized healthcare knowledge graph (KG). The CSSDM is grounded in the formal ontology of ISO 13940 ContSys and incorporates FHIR-based specifications to support structural attributes for generating KGs. We propose that the CSSDM facilitates data harmonization and linking, offering an alternative approach to interoperability. This approach promotes a novel form of collaboration between companies developing health information systems and cloud-enabled health services. Consequently, it provides multiple stakeholders with access to high-quality data and information sharing.
CSSDH: An Ontology for Social Determinants of Health to Operational Continuity of Care Data Interoperability
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:The rise of digital platforms has led to an increasing reliance on technology-driven, home-based healthcare solutions, enabling individuals to monitor their health and share information with healthcare professionals as needed. However, creating an efficient care plan management system requires more than just analyzing hospital summaries and Electronic Health Records (EHRs). Factors such as individual user needs and social determinants of health, including living conditions and the flow of healthcare information between different settings, must also be considered. Challenges in this complex healthcare network involve schema diversity (in EHRs, personal health records, etc.) and terminology diversity (e.g., ICD, SNOMED-CT) across ancillary healthcare operations. Establishing interoperability among various systems and applications is crucial, with the European Interoperability Framework (EIF) emphasizing the need for patient-centric access and control of healthcare data. In this paper, we propose an integrated ontological model, the Common Semantic Data Model for Social Determinants of Health (CSSDH), by combining ISO/DIS 13940:2024 ContSys with WHO Social Determinants of Health. CSSDH aims to achieve interoperability within the Continuity of Care Network.
From Knowledge Organization to Knowledge Representation and Back
Jan 22, 2024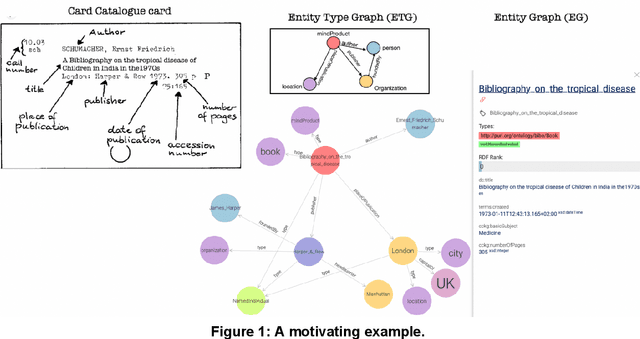
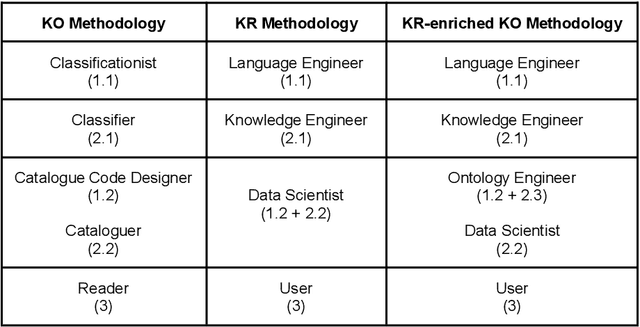
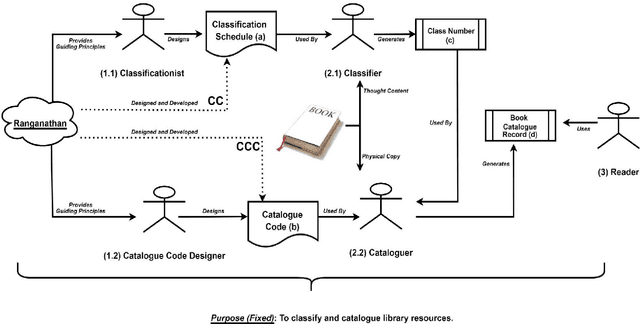
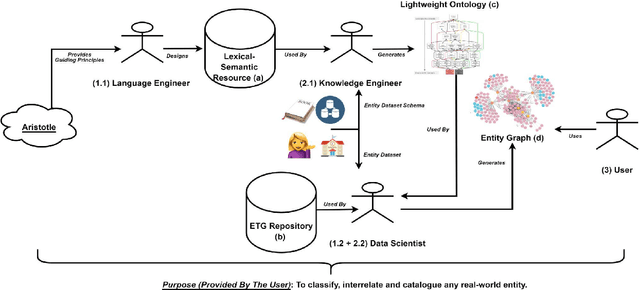
Abstract:Knowledge Organization (KO) and Knowledge Representation (KR) have been the two mainstream methodologies of knowledge modelling in the Information Science community and the Artificial Intelligence community, respectively. The facet-analytical tradition of KO has developed an exhaustive set of guiding canons for ensuring quality in organising and managing knowledge but has remained limited in terms of technology-driven activities to expand its scope and services beyond the bibliographic universe of knowledge. KR, on the other hand, boasts of a robust ecosystem of technologies and technology-driven service design which can be tailored to model any entity or scale to any service in the entire universe of knowledge. This paper elucidates both the facet-analytical KO and KR methodologies in detail and provides a functional mapping between them. Out of the mapping, the paper proposes an integrated KR-enriched KO methodology with all the standard components of a KO methodology plus the advanced technologies provided by the KR approach. The practical benefits of the methodological integration has been exemplified through the flagship application of the Digital University at the University of Trento, Italy.
Reorganizing Educational Institutional Domain using Faceted Ontological Principles
Jun 17, 2023



Abstract:The purpose of this work is to find out how different library classification systems and linguistic ontologies arrange a particular domain of interest and what are the limitations for information retrieval. We use knowledge representation techniques and languages for construction of a domain specific ontology. This ontology would help not only in problem solving, but it would demonstrate the ease with which complex queries can be handled using principles of domain ontology, thereby facilitating better information retrieval.
* 26 pages, 12 figures, KNOWLEDGE ORGANIZATION Journal Paper
Disentangling Domain Ontologies
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we introduce and illustrate the novel phenomenon of Conceptual Entanglement which emerges due to the representational manifoldness immanent while incrementally modelling domain ontologies step-by-step across the following five levels: perception, labelling, semantic alignment, hierarchical modelling and intensional definition. In turn, we propose Conceptual Disentanglement, a multi-level conceptual modelling strategy which enforces and explicates, via guiding principles, semantic bijections with respect to each level of conceptual entanglement (across all the above five levels) paving the way for engineering conceptually disentangled domain ontologies. We also briefly argue why state-of-the-art ontology development methodologies and approaches are insufficient with respect to our characterization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge