Stephane Landeau
IR image databases generation under target intrinsic thermal variability constraints
Nov 12, 2024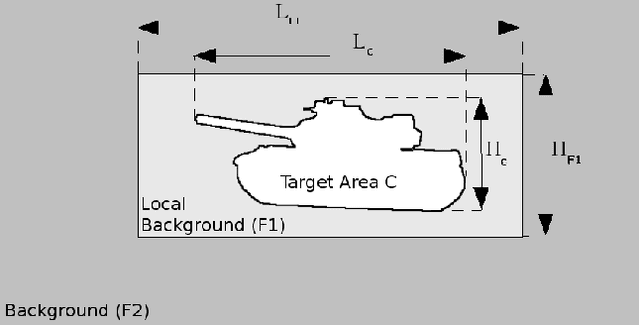
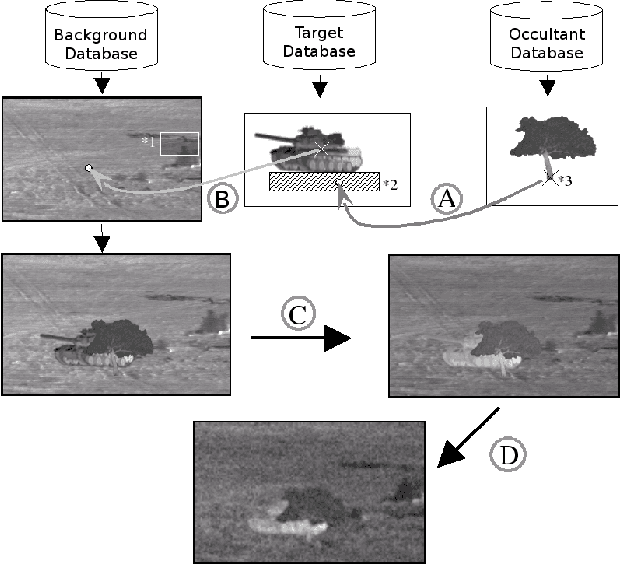

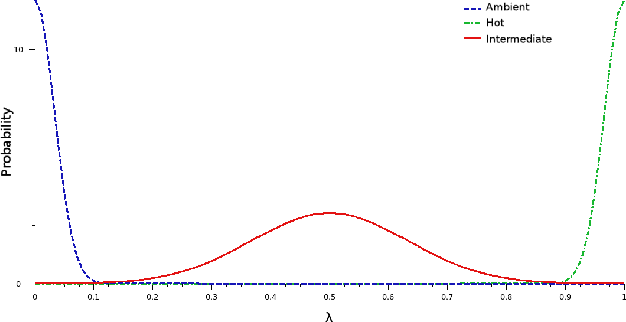
Abstract:This paper deals with the problem of infrared image database generation for ATR assessment purposes. Huge databases are required to have quantitative and objective performance evaluations. We propose a method which superimpose targets and occultants on background under image quality metrics constraints to generate realistic images. We also propose a method to generate target signatures with intrinsic thermal variability based on 3D models plated with real infrared textures.
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2411.06695
Génération de bases de données images IR sous contraintes avec variabilité thermique intrinsèque des cibles
Nov 12, 2024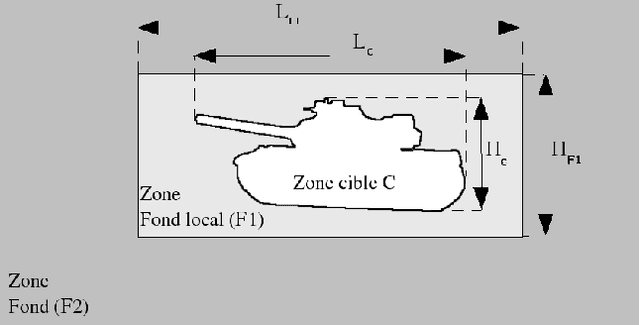
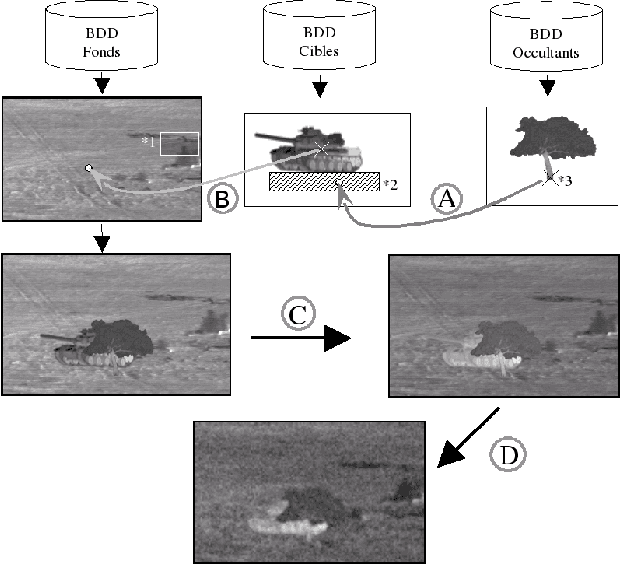

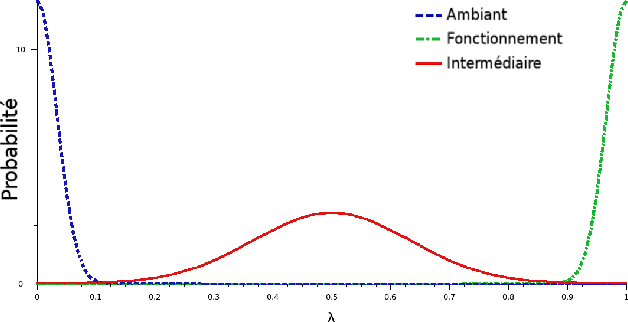
Abstract:In this communication, we propose a method which permits to simulate images of targets in infrared imagery by superimposition of vehicle signatures in background, eventually with occultants. We develop a principle which authorizes us to generate different thermal configurations of target signatures. This method enables us to easily generate huge datasets for ATR algorithms performance evaluation.
Efficient single image non-uniformity correction algorithm
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a new way to correct the non-uniformity (NU) in uncooled infrared-type images. The main defect of these uncooled images is the lack of a column (resp. line) time-dependent cross-calibration, resulting in a strong column (resp. line) and time dependent noise. This problem can be considered as a 1D flicker of the columns inside each frame. Thus, classic movie deflickering algorithms can be adapted, to equalize the columns (resp. the lines). The proposed method therefore applies to the series formed by the columns of an infrared image a movie deflickering algorithm. The obtained single image method works on static images, and therefore requires no registration, no camera motion compensation, and no closed aperture sensor equalization. Thus, the method has only one camera dependent parameter, and is landscape independent. This simple method will be compared to a state of the art total variation single image correction on raw real and simulated images. The method is real time, requiring only two operations per pixel. It involves no test-pattern calibration and produces no "ghost artifacts".
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2411.03615
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge