Stanisław Łaniewski
Enhancing literature review with LLM and NLP methods. Algorithmic trading case
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:This study utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze and organize knowledge in the field of algorithmic trading. By filtering a dataset of 136 million research papers, we identified 14,342 relevant articles published between 1956 and Q1 2020. We compare traditional practices-such as keyword-based algorithms and embedding techniques-with state-of-the-art topic modeling methods that employ dimensionality reduction and clustering. This comparison allows us to assess the popularity and evolution of different approaches and themes within algorithmic trading. We demonstrate the usefulness of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in the automatic extraction of knowledge, highlighting the new possibilities created by the latest iterations of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. The rationale for focusing on this topic stems from our analysis, which reveals that research articles on algorithmic trading are increasing at a faster rate than the overall number of publications. While stocks and main indices comprise more than half of all assets considered, certain asset classes, such as cryptocurrencies, exhibit a much stronger growth trend. Machine learning models have become the most popular methods in recent years. The study demonstrates the efficacy of LLMs in refining datasets and addressing intricate questions about the analyzed articles, such as comparing the efficiency of different models. Our research shows that by decomposing tasks into smaller components and incorporating reasoning steps, we can effectively tackle complex questions supported by case analyses. This approach contributes to a deeper understanding of algorithmic trading methodologies and underscores the potential of advanced NLP techniques in literature reviews.
MAIR: Framework for mining relationships between research articles, strategies, and regulations in the field of explainable artificial intelligence
Jul 29, 2021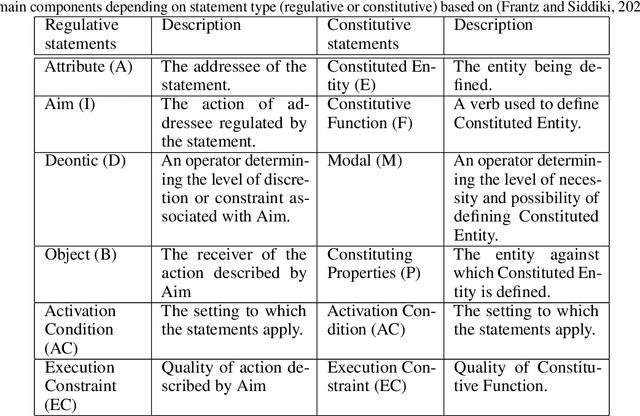
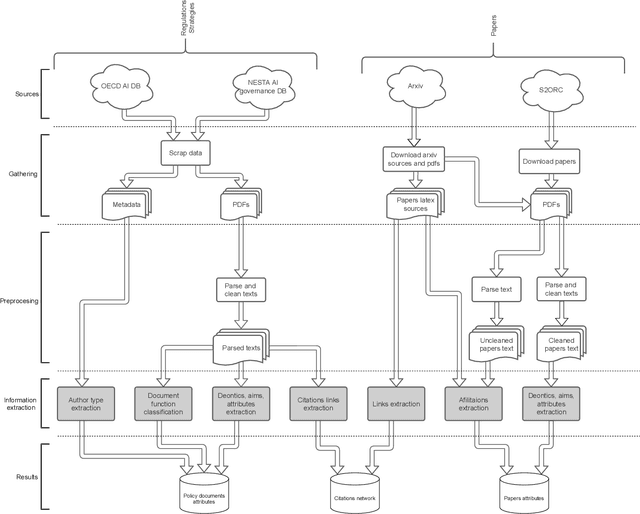
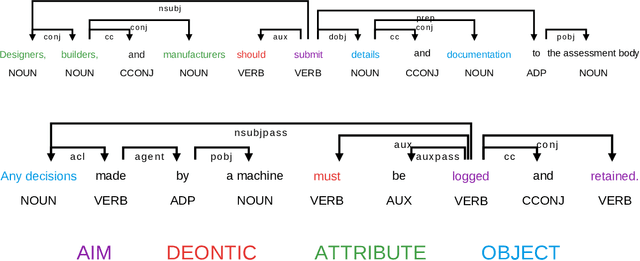
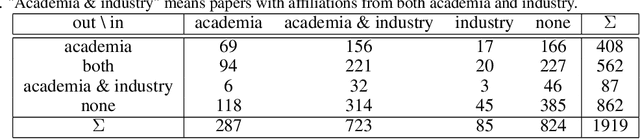
Abstract:The growing number of AI applications, also for high-stake decisions, increases the interest in Explainable and Interpretable Machine Learning (XI-ML). This trend can be seen both in the increasing number of regulations and strategies for developing trustworthy AI and the growing number of scientific papers dedicated to this topic. To ensure the sustainable development of AI, it is essential to understand the dynamics of the impact of regulation on research papers as well as the impact of scientific discourse on AI-related policies. This paper introduces a novel framework for joint analysis of AI-related policy documents and eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) research papers. The collected documents are enriched with metadata and interconnections, using various NLP methods combined with a methodology inspired by Institutional Grammar. Based on the information extracted from collected documents, we showcase a series of analyses that help understand interactions, similarities, and differences between documents at different stages of institutionalization. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to use automatic language analysis tools to understand the dynamics between XI-ML methods and regulations. We believe that such a system contributes to better cooperation between XAI researchers and AI policymakers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge