Stéphanie Roussel
Learning to Solve Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problems with Duration Uncertainty using Graph Neural Networks
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:The Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP) is a classical scheduling problem that has received significant attention due to of its numerous applications in industry. However, in practice, task durations are subject to uncertainty that must be considered in order to propose resilient scheduling. In this paper, we address the RCPSP variant with uncertain tasks duration (modeled using known probabilities) and aim to minimize the overall expected project duration. Our objective is to produce a baseline schedule that can be reused multiple times in an industrial setting regardless of the actual duration scenario. We leverage Graph Neural Networks in conjunction with Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to develop an effective policy for task scheduling. This policy operates similarly to a priority dispatch rule and is paired with a Serial Schedule Generation Scheme to produce a schedule. Our empirical evaluation on standard benchmarks demonstrates the approach's superiority in terms of performance and its ability to generalize. The developed framework, Wheatley, is made publicly available online to facilitate further research and reproducibility.
Earth Observation Satellite Scheduling with Graph Neural Networks
Aug 27, 2024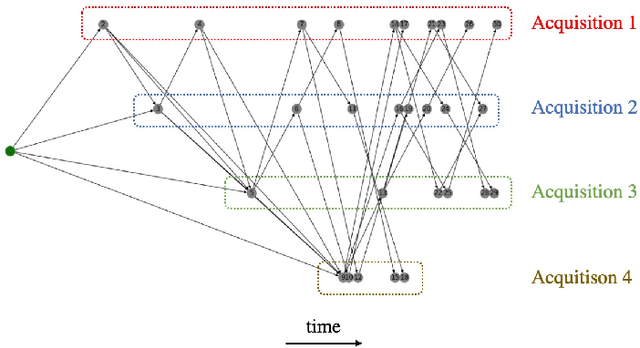
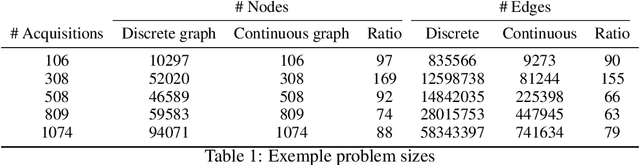
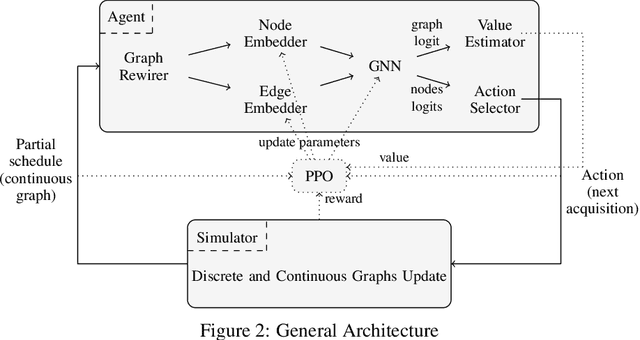
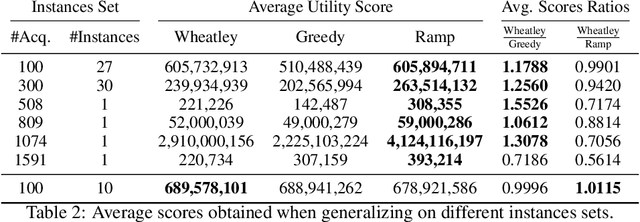
Abstract:The Earth Observation Satellite Planning (EOSP) is a difficult optimization problem with considerable practical interest. A set of requested observations must be scheduled on an agile Earth observation satellite while respecting constraints on their visibility window, as well as maneuver constraints that impose varying delays between successive observations. In addition, the problem is largely oversubscribed: there are much more candidate observations than what can possibly be achieved. Therefore, one must select the set of observations that will be performed while maximizing their weighted cumulative benefit, and propose a feasible schedule for these observations. As previous work mostly focused on heuristic and iterative search algorithms, this paper presents a new technique for selecting and scheduling observations based on Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). GNNs are used to extract relevant information from the graphs representing instances of the EOSP, and DRL drives the search for optimal schedules. Our simulations show that it is able to learn on small problem instances and generalize to larger real-world instances, with very competitive performance compared to traditional approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge