Spencer S. Ericksen
Chemical Language Model Linker: blending text and molecules with modular adapters
Oct 26, 2024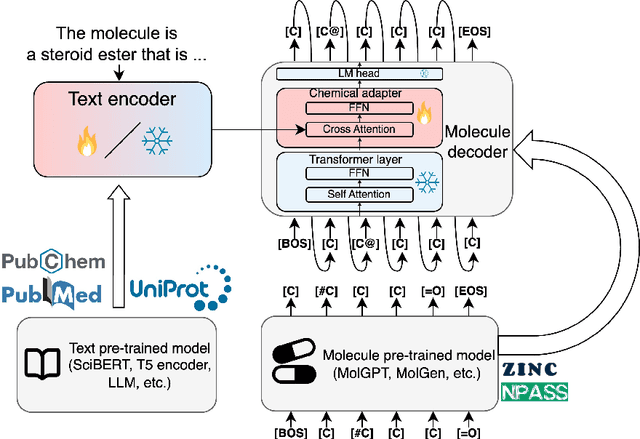
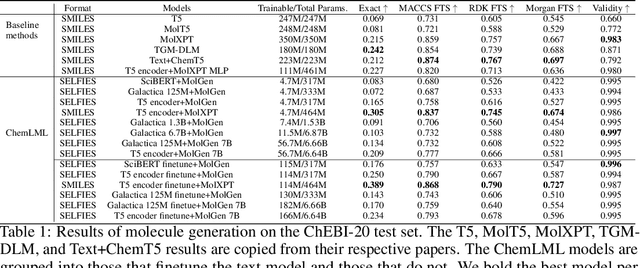
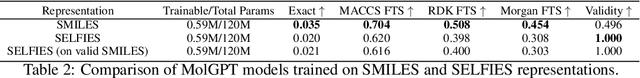
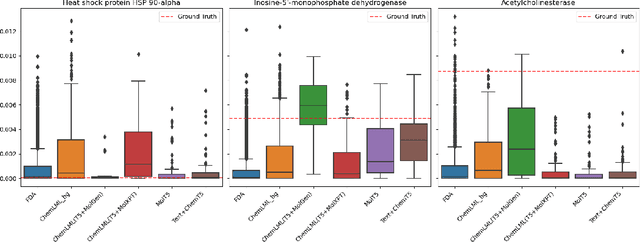
Abstract:The development of large language models and multi-modal models has enabled the appealing idea of generating novel molecules from text descriptions. Generative modeling would shift the paradigm from relying on large-scale chemical screening to find molecules with desired properties to directly generating those molecules. However, multi-modal models combining text and molecules are often trained from scratch, without leveraging existing high-quality pretrained models. That approach consumes more computational resources and prohibits model scaling. In contrast, we propose a lightweight adapter-based strategy named Chemical Language Model Linker (ChemLML). ChemLML blends the two single domain models and obtains conditional molecular generation from text descriptions while still operating in the specialized embedding spaces of the molecular domain. ChemLML can tailor diverse pretrained text models for molecule generation by training relatively few adapter parameters. We find that the choice of molecular representation used within ChemLML, SMILES versus SELFIES, has a strong influence on conditional molecular generation performance. SMILES is often preferable despite not guaranteeing valid molecules. We raise issues in using the large PubChem dataset of molecules and their associated descriptions for evaluating molecule generation and provide a filtered version of the dataset as a generation test set. To demonstrate how ChemLML could be used in practice, we generate candidate protein inhibitors and use docking to assess their quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge