Sourajit Das
SC3D: Dynamic and Differentiable Causal Discovery for Temporal and Instantaneous Graphs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Discovering causal structures from multivariate time series is a key problem because interactions span across multiple lags and possibly involve instantaneous dependencies. Additionally, the search space of the dynamic graphs is combinatorial in nature. In this study, we propose \textit{Stable Causal Dynamic Differentiable Discovery (SC3D)}, a two-stage differentiable framework that jointly learns lag-specific adjacency matrices and, if present, an instantaneous directed acyclic graph (DAG). In Stage 1, SC3D performs edge preselection through node-wise prediction to obtain masks for lagged and instantaneous edges, whereas Stage 2 refines these masks by optimizing a likelihood with sparsity along with enforcing acyclicity on the instantaneous block. Numerical results across synthetic and benchmark dynamical systems demonstrate that SC3D achieves improved stability and more accurate recovery of both lagged and instantaneous causal structures compared to existing temporal baselines.
Opportunistic Routing in Wireless Communications via Learnable State-Augmented Policies
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of packet-based information routing in large-scale wireless communication networks. The problem is framed as a constrained statistical learning task, where each network node operates using only local information. Opportunistic routing exploits the broadcast nature of wireless communication to dynamically select optimal forwarding nodes, enabling the information to reach the destination through multiple relay nodes simultaneously. To solve this, we propose a State-Augmentation (SA) based distributed optimization approach aimed at maximizing the total information handled by the source nodes in the network. The problem formulation leverages Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), which perform graph convolutions based on the topological connections between network nodes. Using an unsupervised learning paradigm, we extract routing policies from the GNN architecture, enabling optimal decisions for source nodes across various flows. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior performance when training a GNN-parameterized model, particularly when compared to baseline algorithms. Additionally, applying the method to real-world network topologies and wireless ad-hoc network test beds validates its effectiveness, highlighting the robustness and transferability of GNNs.
Learning State-Augmented Policies for Information Routing in Communication Networks
Sep 30, 2023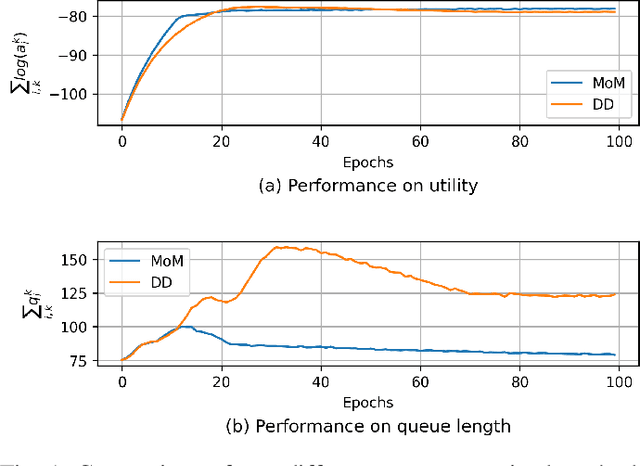
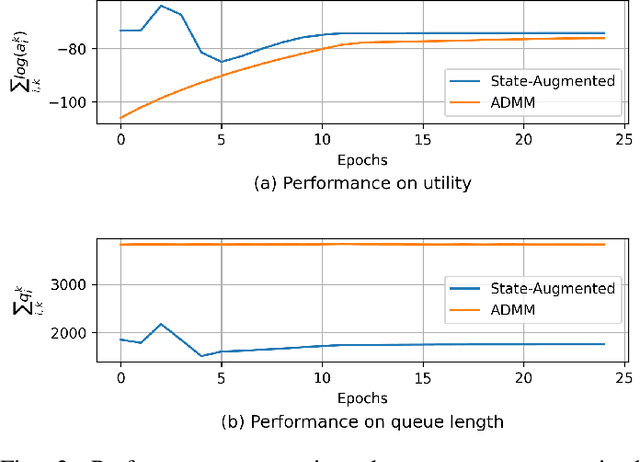
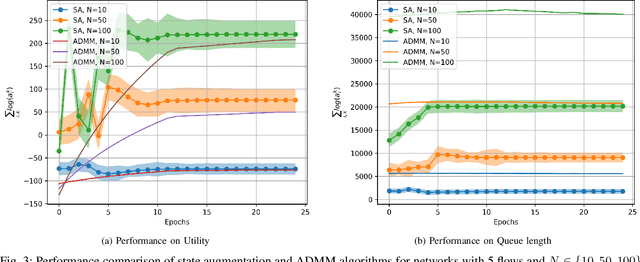
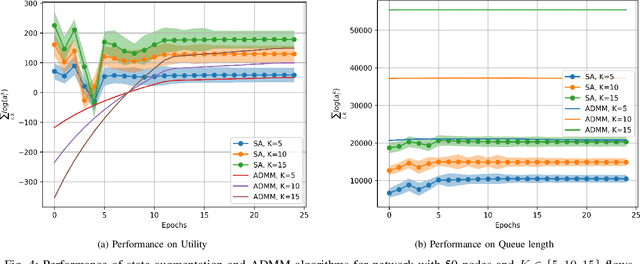
Abstract:This paper examines the problem of information routing in a large-scale communication network, which can be formulated as a constrained statistical learning problem having access to only local information. We delineate a novel State Augmentation (SA) strategy to maximize the aggregate information at source nodes using graph neural network (GNN) architectures, by deploying graph convolutions over the topological links of the communication network. The proposed technique leverages only the local information available at each node and efficiently routes desired information to the destination nodes. We leverage an unsupervised learning procedure to convert the output of the GNN architecture to optimal information routing strategies. In the experiments, we perform the evaluation on real-time network topologies to validate our algorithms. Numerical simulations depict the improved performance of the proposed method in training a GNN parameterization as compared to baseline algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge