Son Duy Dao
Class Enhancement Losses with Pseudo Labels for Zero-shot Semantic Segmentation
Jan 18, 2023



Abstract:Recent mask proposal models have significantly improved the performance of zero-shot semantic segmentation. However, the use of a `background' embedding during training in these methods is problematic as the resulting model tends to over-learn and assign all unseen classes as the background class instead of their correct labels. Furthermore, they ignore the semantic relationship of text embeddings, which arguably can be highly informative for zero-shot prediction as seen classes may have close relationship with unseen classes. To this end, this paper proposes novel class enhancement losses to bypass the use of the background embbedding during training, and simultaneously exploit the semantic relationship between text embeddings and mask proposals by ranking the similarity scores. To further capture the relationship between seen and unseen classes, we propose an effective pseudo label generation pipeline using pretrained vision-language model. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets show that our method achieves overall the best performance for zero-shot semantic segmentation. Our method is flexible, and can also be applied to the challenging open-vocabulary semantic segmentation problem.
A Note On The Popularity of Stochastic Optimization Algorithms in Different Fields: A Quantitative Analysis from 2007 to 2017
Jul 03, 2019
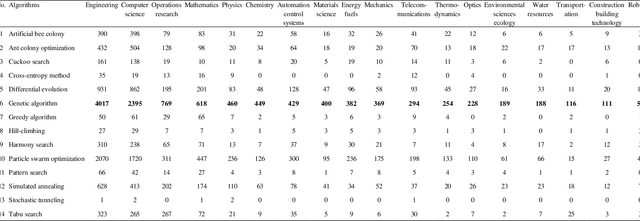
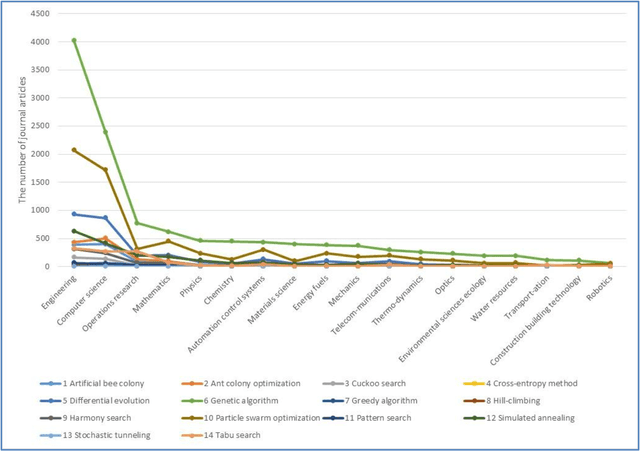
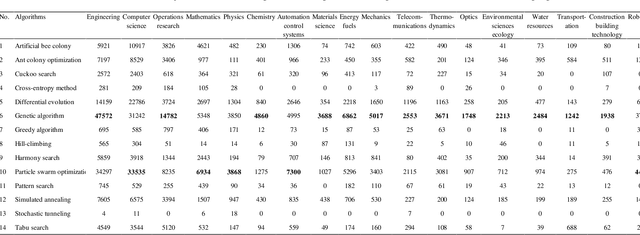
Abstract:Stochastic optimization algorithms are often used to solve complex large-scale optimization problems in various fields. To date, there have been a number of stochastic optimization algorithms such as Genetic Algorithm, Cuckoo Search, Tabu Search, Simulated Annealing, Particle Swarm Optimization, Ant Colony Optimization, etc. Each algorithm has some advantages and disadvantages. Currently, there is no study that can help researchers to choose the most popular optimization algorithm to deal with the problems in different research fields. In this note, a quantitative analysis of the popularity of 14 stochastic optimization algorithms in 18 different research fields in the last ten years from 2007 to 2017 is provided. This quantitative analysis can help researchers/practitioners select the best optimization algorithm to solve complex large-scale optimization problems in the fields of Engineering, Computer science, Operations research, Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Automation control systems, Materials science, Energy fuels, Mechanics, Telecommunications, Thermodynamics, Optics, Environmental sciences ecology, Water resources, Transportation, Construction building technology, and Robotics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge