Sohail Iqbal
CVEH: A Dynamic Framework To Profile Vehicle Movements To Mitigate Hit And Run Cases Using Crowdsourcing
Jun 28, 2021



Abstract:In developed countries like the USA, Germany, and the UK, the security forces used highly sophisticated equipment, fast vehicles, drones, and helicopters to catch offenders' vehicles. Whereas, in developing countries with limited resources such schemes cannot be utilized due to management cost and other constraints. In this paper, we proposed a framework called CVEH that enables developing countries to profile the offender vehicle movements through crowdsourcing technique and act as an early warning system to the law forcing agencies. It also engages citizens to play their role in improving security conditions. The proposed CVEH framework allows Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication to monitor the movement of the offender's vehicle and shared its information with the Command and Control (CC) centre. The CC centre projects the path and engages nearly located law enforcement agencies. CVEH is developed and evaluated on android smartphones. Simulations conducted for this study exhibit the effectiveness of our framework.
Classification of COVID-19 via Homology of CT-SCAN
Feb 21, 2021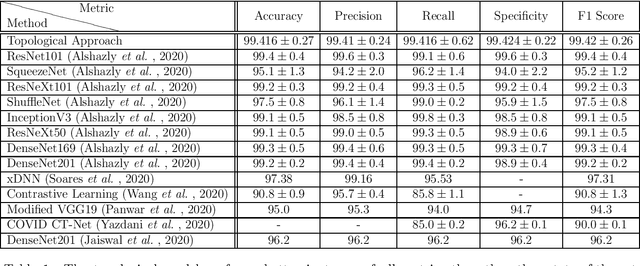
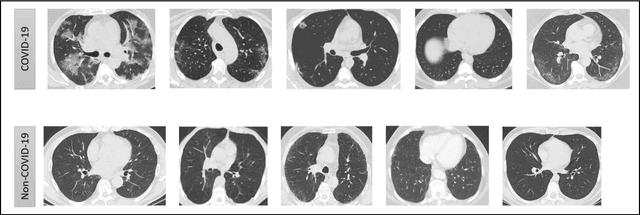
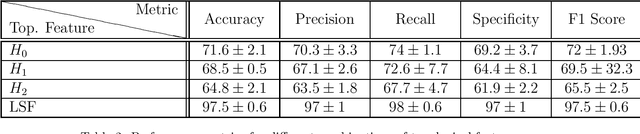
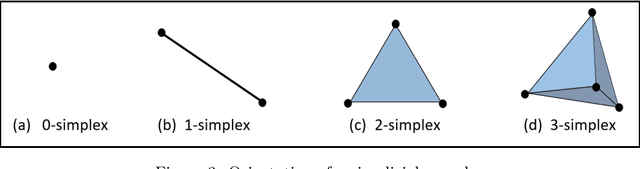
Abstract:In this worldwide spread of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, it is of utmost importance to detect the disease at an early stage especially in the hot spots of this epidemic. There are more than 110 Million infected cases on the globe, sofar. Due to its promptness and effective results computed tomography (CT)-scan image is preferred to the reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Early detection and isolation of the patient is the only possible way of controlling the spread of the disease. Automated analysis of CT-Scans can provide enormous support in this process. In this article, We propose a novel approach to detect SARS-CoV-2 using CT-scan images. Our method is based on a very intuitive and natural idea of analyzing shapes, an attempt to mimic a professional medic. We mainly trace SARS-CoV-2 features by quantifying their topological properties. We primarily use a tool called persistent homology, from Topological Data Analysis (TDA), to compute these topological properties. We train and test our model on the "SARS-CoV-2 CT-scan dataset" \citep{soares2020sars}, an open-source dataset, containing 2,481 CT-scans of normal and COVID-19 patients. Our model yielded an overall benchmark F1 score of $99.42\% $, accuracy $99.416\%$, precision $99.41\%$, and recall $99.42\%$. The TDA techniques have great potential that can be utilized for efficient and prompt detection of COVID-19. The immense potential of TDA may be exploited in clinics for rapid and safe detection of COVID-19 globally, in particular in the low and middle-income countries where RT-PCR labs and/or kits are in a serious crisis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge