Simon Hachmeier
On the Robustness of Cover Version Identification Models: A Study Using Cover Versions from YouTube
Jan 02, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in cover song identification have shown great success. However, models are usually tested on a fixed set of datasets which are relying on the online cover song database SecondHandSongs. It is unclear how well models perform on cover songs on online video platforms, which might exhibit alterations that are not expected. In this paper, we annotate a subset of songs from YouTube sampled by a multi-modal uncertainty sampling approach and evaluate state-of-the-art models. We find that existing models achieve significantly lower ranking performance on our dataset compared to a community dataset. We additionally measure the performance of different types of versions (e.g., instrumental versions) and find several types that are particularly hard to rank. Lastly, we provide a taxonomy of alterations in cover versions on the web.
A Benchmark and Robustness Study of In-Context-Learning with Large Language Models in Music Entity Detection
Dec 16, 2024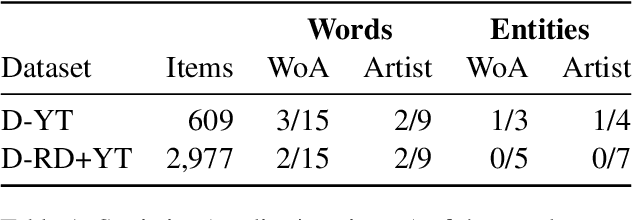

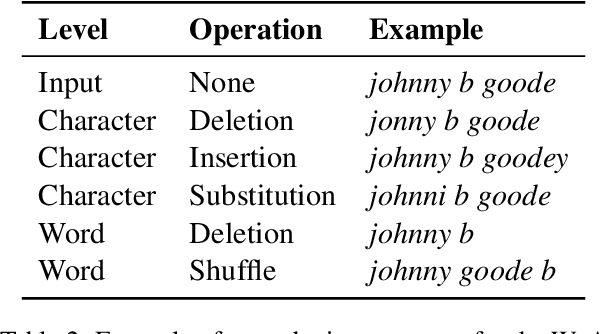
Abstract:Detecting music entities such as song titles or artist names is a useful application to help use cases like processing music search queries or analyzing music consumption on the web. Recent approaches incorporate smaller language models (SLMs) like BERT and achieve high results. However, further research indicates a high influence of entity exposure during pre-training on the performance of the models. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), these outperform SLMs in a variety of downstream tasks. However, researchers are still divided if this is applicable to tasks like entity detection in texts due to issues like hallucination. In this paper, we provide a novel dataset of user-generated metadata and conduct a benchmark and a robustness study using recent LLMs with in-context-learning (ICL). Our results indicate that LLMs in the ICL setting yield higher performance than SLMs. We further uncover the large impact of entity exposure on the best performing LLM in our study.
Leveraging User-Generated Metadata of Online Videos for Cover Song Identification
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:YouTube is a rich source of cover songs. Since the platform itself is organized in terms of videos rather than songs, the retrieval of covers is not trivial. The field of cover song identification addresses this problem and provides approaches that usually rely on audio content. However, including the user-generated video metadata available on YouTube promises improved identification results. In this paper, we propose a multi-modal approach for cover song identification on online video platforms. We combine the entity resolution models with audio-based approaches using a ranking model. Our findings implicate that leveraging user-generated metadata can stabilize cover song identification performance on YouTube.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge