Shuangju Zhou
Physical Adversarial Attack on Monocular Depth Estimation via Shape-Varying Patches
Jul 24, 2024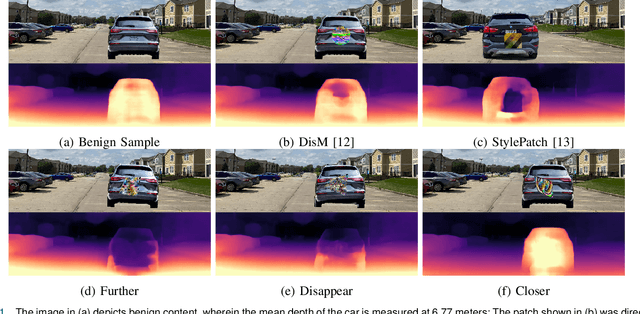
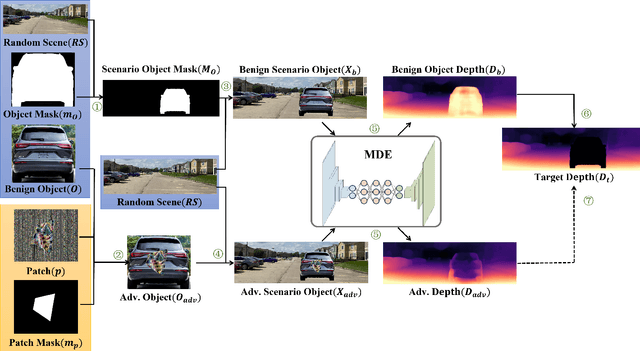
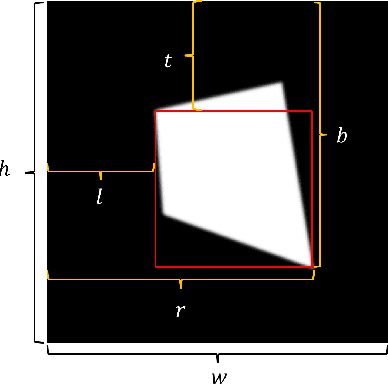
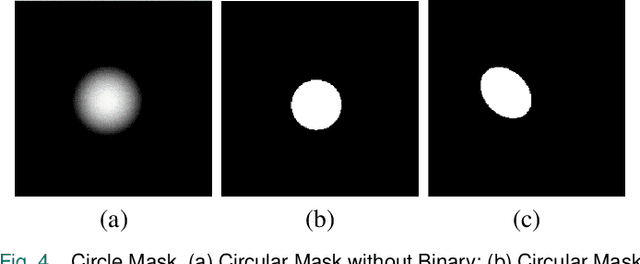
Abstract:Adversarial attacks against monocular depth estimation (MDE) systems pose significant challenges, particularly in safety-critical applications such as autonomous driving. Existing patch-based adversarial attacks for MDE are confined to the vicinity of the patch, making it difficult to affect the entire target. To address this limitation, we propose a physics-based adversarial attack on monocular depth estimation, employing a framework called Attack with Shape-Varying Patches (ASP), aiming to optimize patch content, shape, and position to maximize effectiveness. We introduce various mask shapes, including quadrilateral, rectangular, and circular masks, to enhance the flexibility and efficiency of the attack. Furthermore, we propose a new loss function to extend the influence of the patch beyond the overlapping regions. Experimental results demonstrate that our attack method generates an average depth error of 18 meters on the target car with a patch area of 1/9, affecting over 98\% of the target area.
Flexible Physical Camouflage Generation Based on a Differential Approach
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:This study introduces a novel approach to neural rendering, specifically tailored for adversarial camouflage, within an extensive 3D rendering framework. Our method, named FPA, goes beyond traditional techniques by faithfully simulating lighting conditions and material variations, ensuring a nuanced and realistic representation of textures on a 3D target. To achieve this, we employ a generative approach that learns adversarial patterns from a diffusion model. This involves incorporating a specially designed adversarial loss and covert constraint loss to guarantee the adversarial and covert nature of the camouflage in the physical world. Furthermore, we showcase the effectiveness of the proposed camouflage in sticker mode, demonstrating its ability to cover the target without compromising adversarial information. Through empirical and physical experiments, FPA exhibits strong performance in terms of attack success rate and transferability. Additionally, the designed sticker-mode camouflage, coupled with a concealment constraint, adapts to the environment, yielding diverse styles of texture. Our findings highlight the versatility and efficacy of the FPA approach in adversarial camouflage applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge