Shruti Phadke
The Gray Area: Characterizing Moderator Disagreement on Reddit
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Volunteer moderators play a crucial role in sustaining online dialogue, but they often disagree about what should or should not be allowed. In this paper, we study the complexity of content moderation with a focus on disagreements between moderators, which we term the ``gray area'' of moderation. Leveraging 5 years and 4.3 million moderation log entries from 24 subreddits of different topics and sizes, we characterize how gray area, or disputed cases, differ from undisputed cases. We show that one-in-seven moderation cases are disputed among moderators, often addressing transgressions where users' intent is not directly legible, such as in trolling and brigading, as well as tensions around community governance. This is concerning, as almost half of all gray area cases involved automated moderation decisions. Through information-theoretic evaluations, we demonstrate that gray area cases are inherently harder to adjudicate than undisputed cases and show that state-of-the-art language models struggle to adjudicate them. We highlight the key role of expert human moderators in overseeing the moderation process and provide insights about the challenges of current moderation processes and tools.
MultiSiam: A Multiple Input Siamese Network For Social Media Text Classification And Duplicate Text Detection
Jan 06, 2024Abstract:Social media accounts post increasingly similar content, creating a chaotic experience across platforms, which makes accessing desired information difficult. These posts can be organized by categorizing and grouping duplicates across social handles and accounts. There can be more than one duplicate of a post, however, a conventional Siamese neural network only considers a pair of inputs for duplicate text detection. In this paper, we first propose a multiple-input Siamese network, MultiSiam. This condensed network is then used to propose another model, SMCD (Social Media Classification and Duplication Model) to perform both duplicate text grouping and categorization. The MultiSiam network, just like the Siamese, can be used in multiple applications by changing the sub-network appropriately.
Pathways through Conspiracy: The Evolution of Conspiracy Radicalization through Engagement in Online Conspiracy Discussions
Apr 22, 2022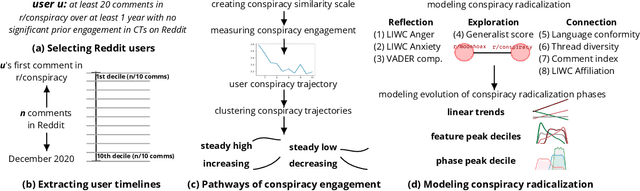

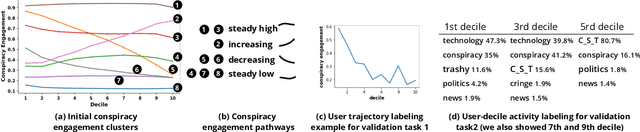
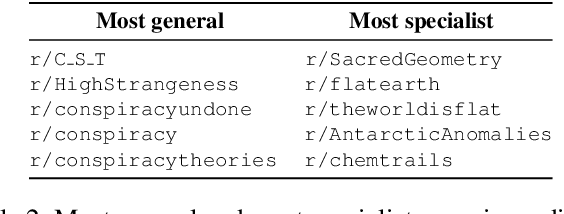
Abstract:The disruptive offline mobilization of participants in online conspiracy theory (CT) discussions has highlighted the importance of understanding how online users may form radicalized conspiracy beliefs. While prior work researched the factors leading up to joining online CT discussions and provided theories of how conspiracy beliefs form, we have little understanding of how conspiracy radicalization evolves after users join CT discussion communities. In this paper, we provide the empirical modeling of various radicalization phases in online CT discussion participants. To unpack how conspiracy engagement is related to radicalization, we first characterize the users' journey through CT discussions via conspiracy engagement pathways. Specifically, by studying 36K Reddit users through their 169M contributions, we uncover four distinct pathways of conspiracy engagement: steady high, increasing, decreasing, and steady low. We further model three successive stages of radicalization guided by prior theoretical works. Specific sub-populations of users, namely those on steady high and increasing conspiracy engagement pathways, progress successively through various radicalization stages. In contrast, users on the decreasing engagement pathway show distinct behavior: they limit their CT discussions to specialized topics, participate in diverse discussion groups, and show reduced conformity with conspiracy subreddits. By examining users who disengage from online CT discussions, this paper provides promising insights about conspiracy recovery process.
Characterizing Social Imaginaries and Self-Disclosures of Dissonance in Online Conspiracy Discussion Communities
Jul 21, 2021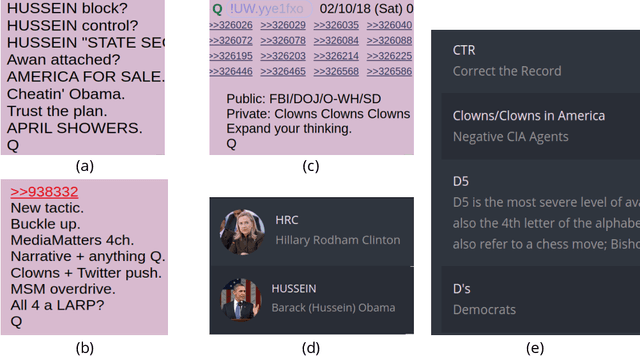

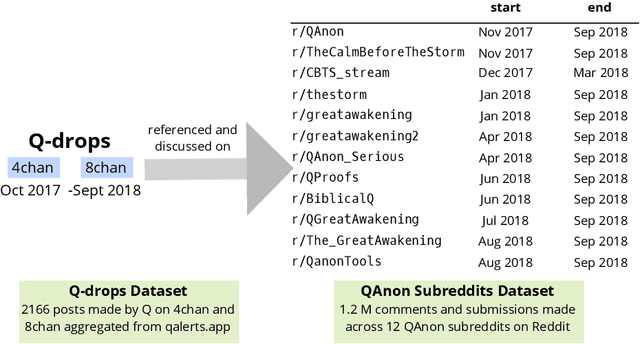
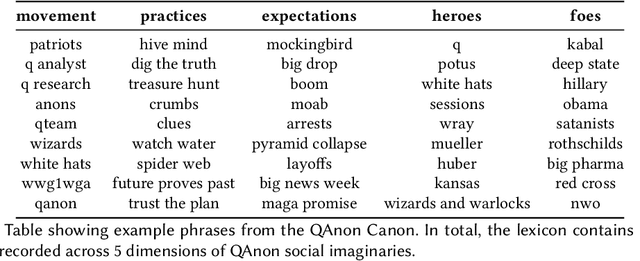
Abstract:Online discussion platforms offer a forum to strengthen and propagate belief in misinformed conspiracy theories. Yet, they also offer avenues for conspiracy theorists to express their doubts and experiences of cognitive dissonance. Such expressions of dissonance may shed light on who abandons misguided beliefs and under which circumstances. This paper characterizes self-disclosures of dissonance about QAnon, a conspiracy theory initiated by a mysterious leader Q and popularized by their followers, anons in conspiracy theory subreddits. To understand what dissonance and disbelief mean within conspiracy communities, we first characterize their social imaginaries, a broad understanding of how people collectively imagine their social existence. Focusing on 2K posts from two image boards, 4chan and 8chan, and 1.2 M comments and posts from 12 subreddits dedicated to QAnon, we adopt a mixed methods approach to uncover the symbolic language representing the movement, expectations, practices, heroes and foes of the QAnon community. We use these social imaginaries to create a computational framework for distinguishing belief and dissonance from general discussion about QAnon. Further, analyzing user engagement with QAnon conspiracy subreddits, we find that self-disclosures of dissonance correlate with a significant decrease in user contributions and ultimately with their departure from the community. We contribute a computational framework for identifying dissonance self-disclosures and measuring the changes in user engagement surrounding dissonance. Our work can provide insights into designing dissonance-based interventions that can potentially dissuade conspiracists from online conspiracy discussion communities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge