Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Shriya Suryavanshi
Comparison of Privacy-Preserving Distributed Deep Learning Methods in Healthcare
Dec 23, 2020Authors:Manish Gawali, Arvind C S, Shriya Suryavanshi, Harshit Madaan, Ashrika Gaikwad, Bhanu Prakash KN, Viraj Kulkarni, Aniruddha Pant
Figures and Tables: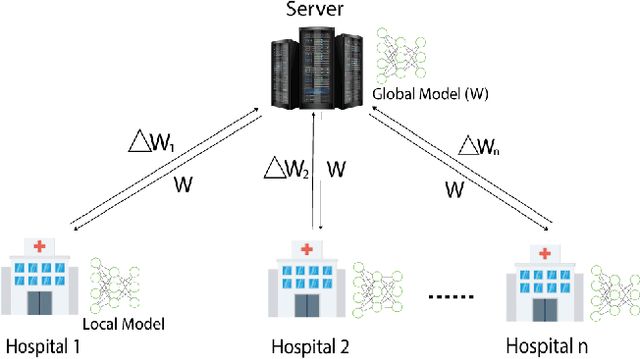
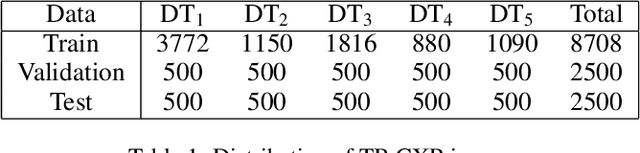
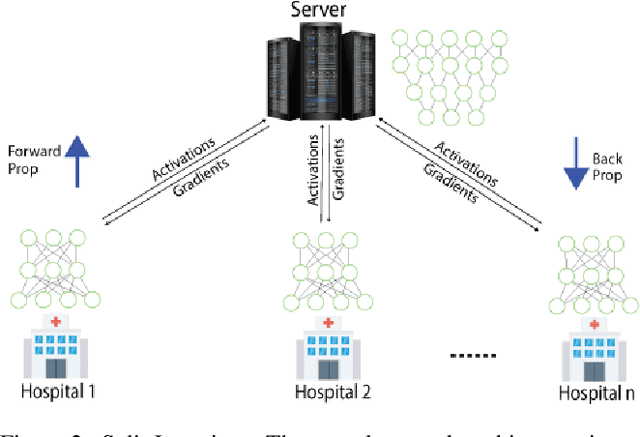
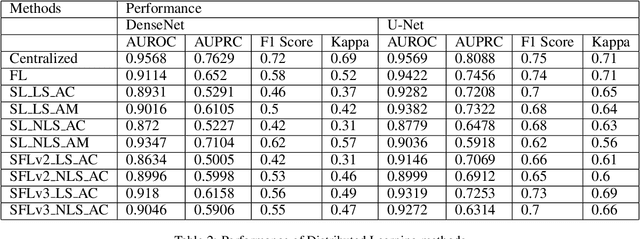




Abstract:In this paper, we compare three privacy-preserving distributed learning techniques: federated learning, split learning, and SplitFed. We use these techniques to develop binary classification models for detecting tuberculosis from chest X-rays and compare them in terms of classification performance, communication and computational costs, and training time. We propose a novel distributed learning architecture called SplitFedv3, which performs better than split learning and SplitFedv2 in our experiments. We also propose alternate mini-batch training, a new training technique for split learning, that performs better than alternate client training, where clients take turns to train a model.
* 10 pages, 12 figures
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge