Shreyash Gupta
IIT Bombay Racing Driverless: Autonomous Driving Stack for Formula Student AI
Aug 12, 2024Abstract:This work presents the design and development of IIT Bombay Racing's Formula Student style autonomous racecar algorithm capable of running at the racing events of Formula Student-AI, held in the UK. The car employs a cutting-edge sensor suite of the compute unit NVIDIA Jetson Orin AGX, 2 ZED2i stereo cameras, 1 Velodyne Puck VLP16 LiDAR and SBG Systems Ellipse N GNSS/INS IMU. It features deep learning algorithms and control systems to navigate complex tracks and execute maneuvers without any human intervention. The design process involved extensive simulations and testing to optimize the vehicle's performance and ensure its safety. The algorithms have been tested on a small scale, in-house manufactured 4-wheeled robot and on simulation software. The results obtained for testing various algorithms in perception, simultaneous localization and mapping, path planning and controls have been detailed.
RL-based Variable Horizon Model Predictive Control of Multi-Robot Systems using Versatile On-Demand Collision Avoidance
Aug 14, 2023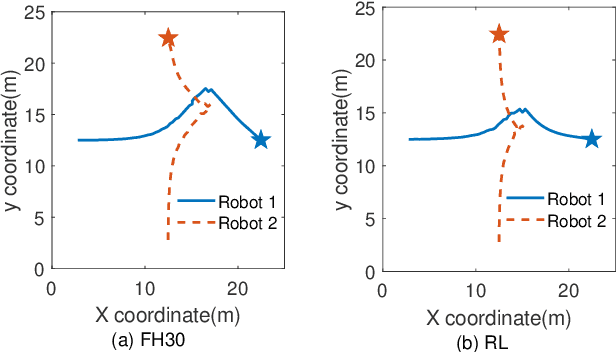
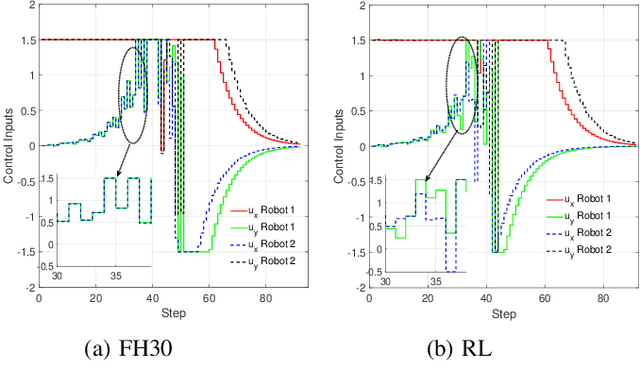
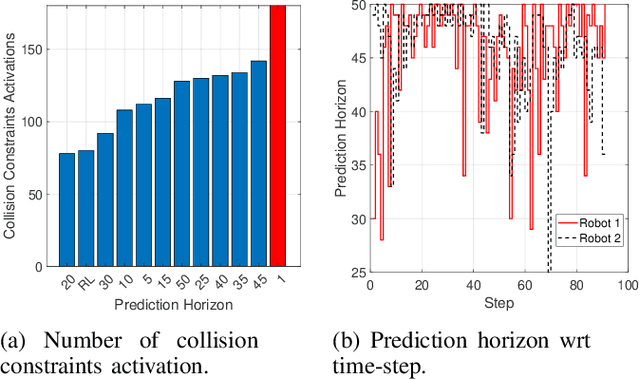
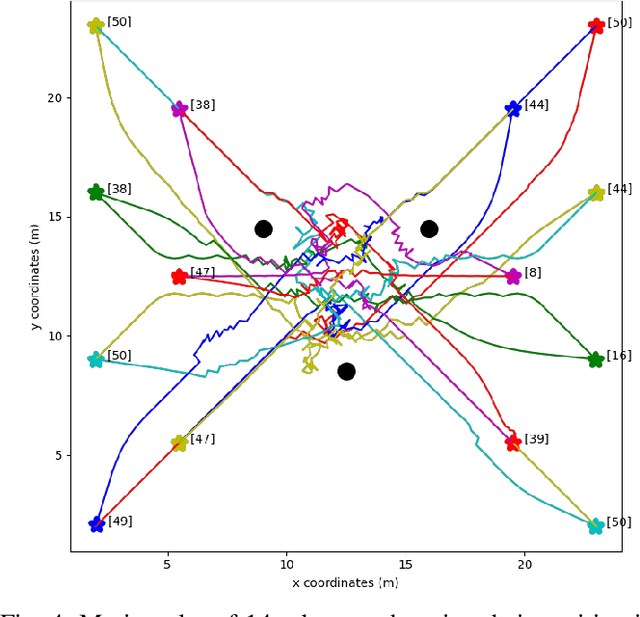
Abstract:Multi-robot systems have become very popular in recent years because of their wide spectrum of applications, ranging from surveillance to cooperative payload transportation. Model Predictive Control (MPC) is a promising controller for multi-robot control because of its preview capability and ability to handle constraints easily. The performance of the MPC widely depends on many parameters, among which the prediction horizon is the major contributor. Increasing the prediction horizon beyond a limit drastically increases the computation cost. Tuning the value of the prediction horizon can be very time-consuming, and the tuning process must be repeated for every task. Moreover, instead of using a fixed horizon for an entire task, a better balance between performance and computation cost can be established if different prediction horizons can be employed for every robot at each time step. Further, for such variable prediction horizon MPC for multiple robots, on-demand collision avoidance is the key requirement. We propose Versatile On-demand Collision Avoidance (VODCA) strategy to comply with the variable horizon model predictive control. We also present a framework for learning the prediction horizon for the multi-robot system as a function of the states of the robots using the Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) RL algorithm. The results are illustrated and validated numerically for different multi-robot tasks.
Intelligent Acoustic Module for Autonomous Vehicles using Fast Gated Recurrent approach
Dec 06, 2021
Abstract:This paper elucidates a model for acoustic single and multi-tone classification in resource constrained edge devices. The proposed model is of State-of-the-art Fast Accurate Stable Tiny Gated Recurrent Neural Network. This model has resulted in improved performance metrics and lower size compared to previous hypothesized methods by using lesser parameters with higher efficiency and employment of a noise reduction algorithm. The model is implemented as an acoustic AI module, focused for the application of sound identification, localization, and deployment on AI systems like that of an autonomous car. Further, the inclusion of localization techniques carries the potential of adding a new dimension to the multi-tone classifiers present in autonomous vehicles, as its demand increases in urban cities and developing countries in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge