Shreeshail Hingane
SAFIN: Arbitrary Style Transfer With Self-Attentive Factorized Instance Normalization
May 20, 2021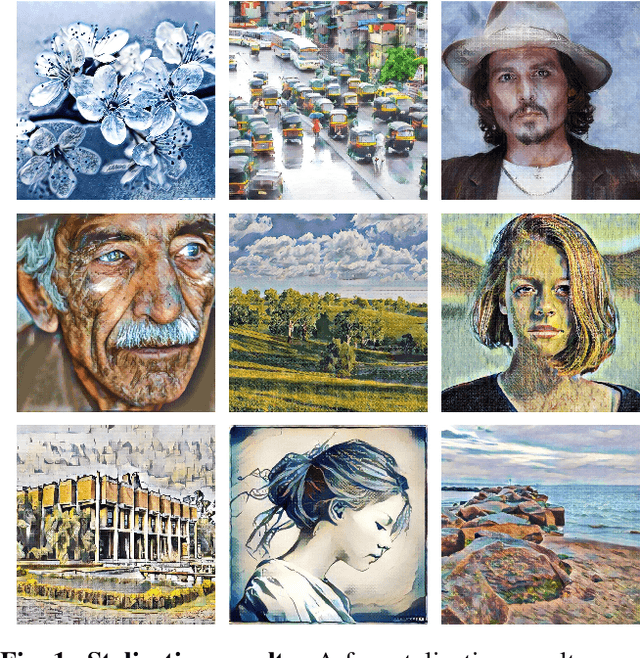
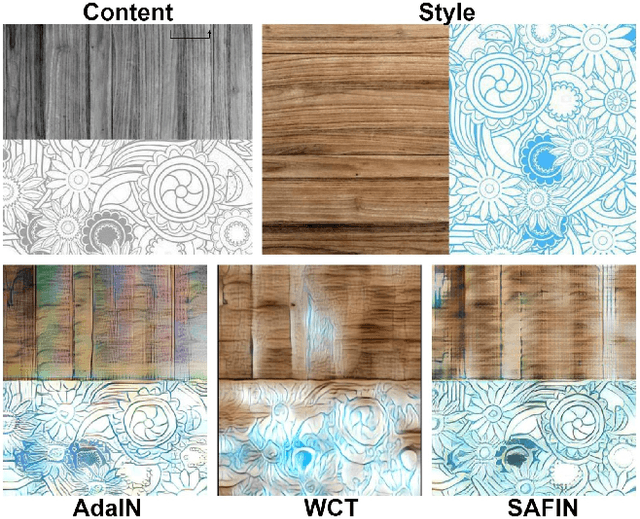
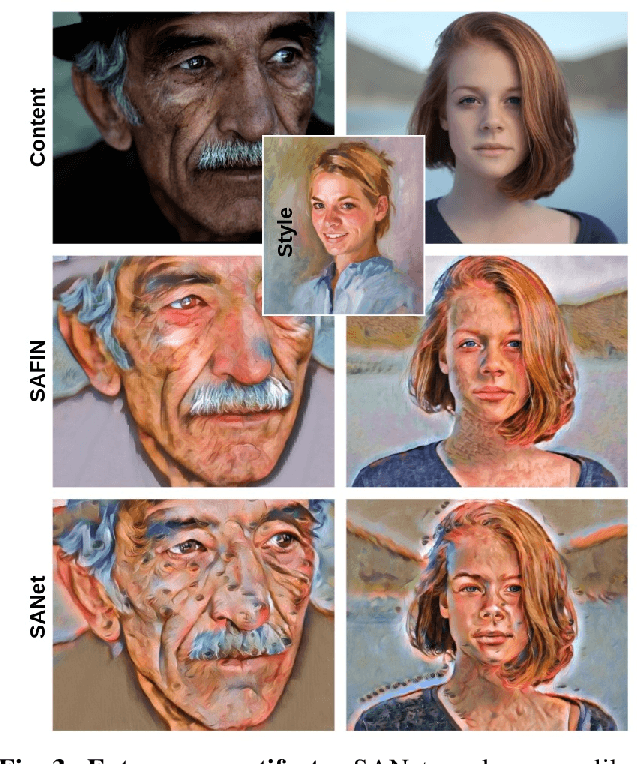
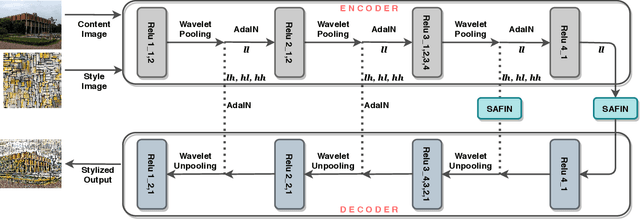
Abstract:Artistic style transfer aims to transfer the style characteristics of one image onto another image while retaining its content. Existing approaches commonly leverage various normalization techniques, although these face limitations in adequately transferring diverse textures to different spatial locations. Self-Attention-based approaches have tackled this issue with partial success but suffer from unwanted artifacts. Motivated by these observations, this paper aims to combine the best of both worlds: self-attention and normalization. That yields a new plug-and-play module that we name Self-Attentive Factorized Instance Normalization (SAFIN). SAFIN is essentially a spatially adaptive normalization module whose parameters are inferred through attention on the content and style image. We demonstrate that plugging SAFIN into the base network of another state-of-the-art method results in enhanced stylization. We also develop a novel base network composed of Wavelet Transform for multi-scale style transfer, which when combined with SAFIN, produces visually appealing results with lesser unwanted textures.
An End-to-End Network for Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction
Mar 03, 2021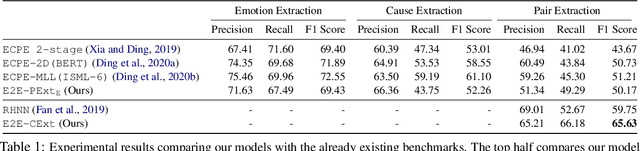
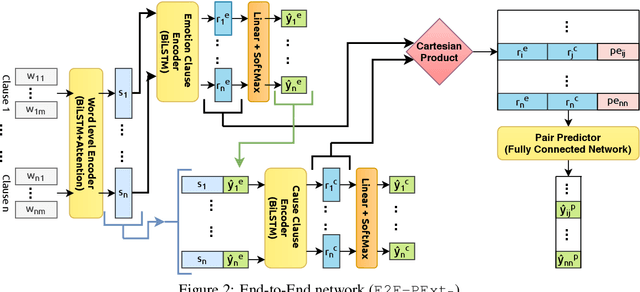

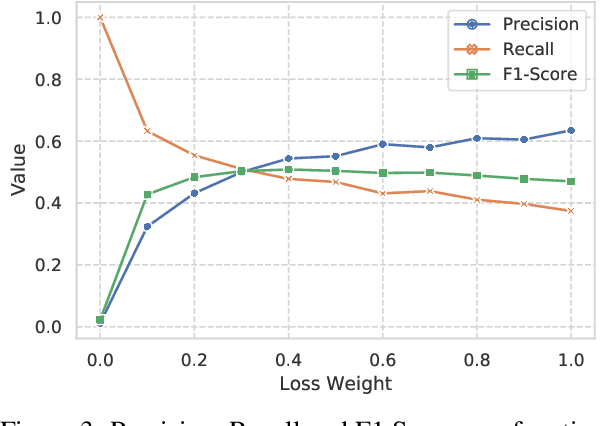
Abstract:The task of Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction (ECPE) aims to extract all potential clause-pairs of emotions and their corresponding causes in a document. Unlike the more well-studied task of Emotion Cause Extraction (ECE), ECPE does not require the emotion clauses to be provided as annotations. Previous works on ECPE have either followed a multi-stage approach where emotion extraction, cause extraction, and pairing are done independently or use complex architectures to resolve its limitations. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end model for the ECPE task. Due to the unavailability of an English language ECPE corpus, we adapt the NTCIR-13 ECE corpus and establish a baseline for the ECPE task on this dataset. On this dataset, the proposed method produces significant performance improvements (~6.5 increase in F1 score) over the multi-stage approach and achieves comparable performance to the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge