Shota Takahashi
Blind Deconvolution with Non-smooth Regularization via Bregman Proximal DCAs
May 13, 2022
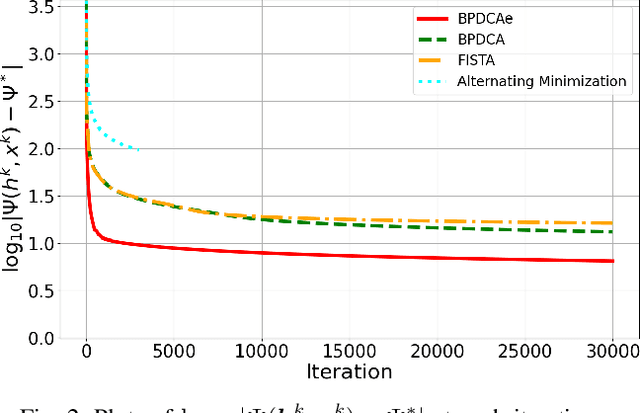
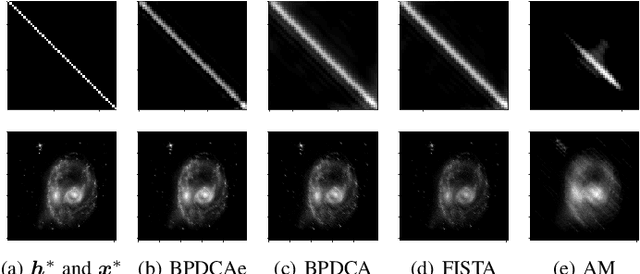

Abstract:Blind deconvolution is a technique to recover an original signal without knowing a convolving filter. It is naturally formulated as a minimization of a quartic objective function under some assumption. Because its differentiable part does not have a Lipschitz continuous gradient, existing first-order methods are not theoretically supported. In this letter, we employ the Bregman-based proximal methods, whose convergence is theoretically guaranteed under the $L$-smad property. We first reformulate the objective function as a difference of convex (DC) functions and apply the Bregman proximal DC algorithm (BPDCA). This DC decomposition satisfies the $L$-smad property. The method is extended to the BPDCA with extrapolation (BPDCAe) for faster convergence. When our regularizer has a sufficiently simple structure, each iteration is solved in a closed-form expression, and thus our algorithms solve large-scale problems efficiently. We also provide the stability analysis of the equilibriums and demonstrate the proposed methods through numerical experiments on image deblurring. The results show that BPDCAe successfully recovered the original image and outperformed other existing algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge