Shohreh Shaghaghian
Yue
Predicting the Success of Domain Adaptation in Text Similarity
Jun 23, 2021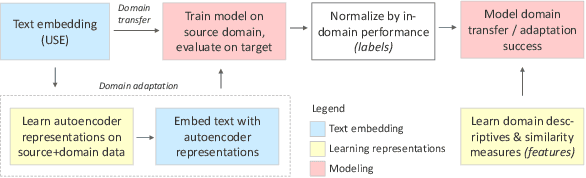
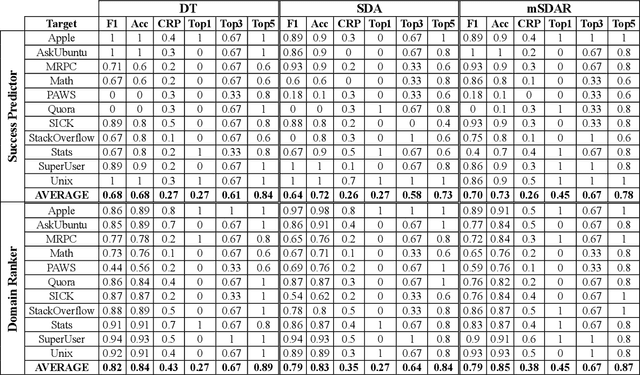

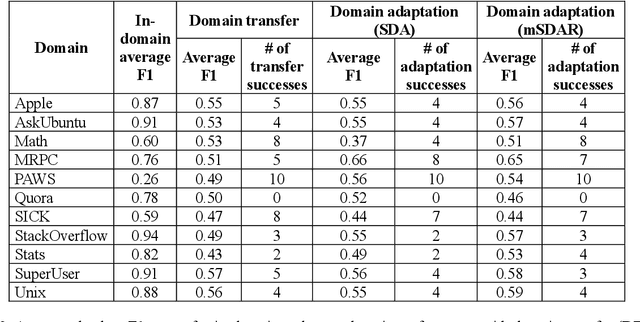
Abstract:Transfer learning methods, and in particular domain adaptation, help exploit labeled data in one domain to improve the performance of a certain task in another domain. However, it is still not clear what factors affect the success of domain adaptation. This paper models adaptation success and selection of the most suitable source domains among several candidates in text similarity. We use descriptive domain information and cross-domain similarity metrics as predictive features. While mostly positive, the results also point to some domains where adaptation success was difficult to predict.
Customizing Contextualized Language Models forLegal Document Reviews
Feb 10, 2021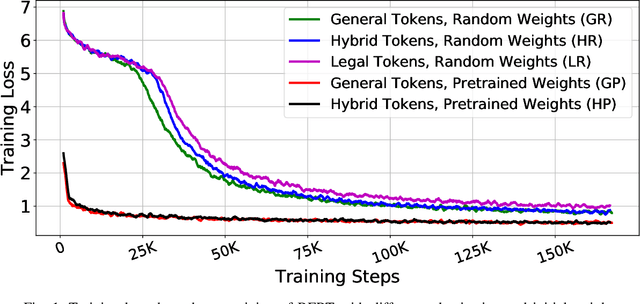
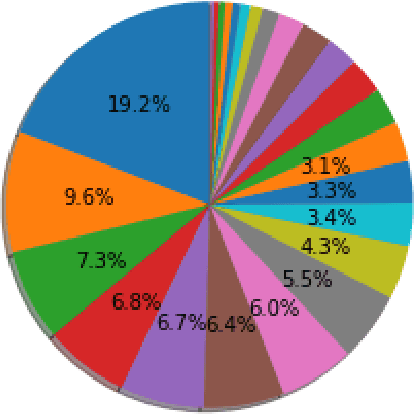

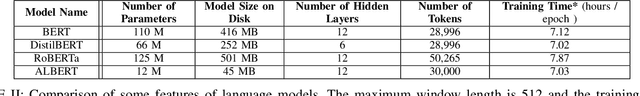
Abstract:Inspired by the inductive transfer learning on computer vision, many efforts have been made to train contextualized language models that boost the performance of natural language processing tasks. These models are mostly trained on large general-domain corpora such as news, books, or Wikipedia.Although these pre-trained generic language models well perceive the semantic and syntactic essence of a language structure, exploiting them in a real-world domain-specific scenario still needs some practical considerations to be taken into account such as token distribution shifts, inference time, memory, and their simultaneous proficiency in multiple tasks. In this paper, we focus on the legal domain and present how different language model strained on general-domain corpora can be best customized for multiple legal document reviewing tasks. We compare their efficiencies with respect to task performances and present practical considerations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge