Sheli Sinha Chaudhuri
Multilevel Threshold Based Gray Scale Image Segmentation using Cuckoo Search
Jul 01, 2013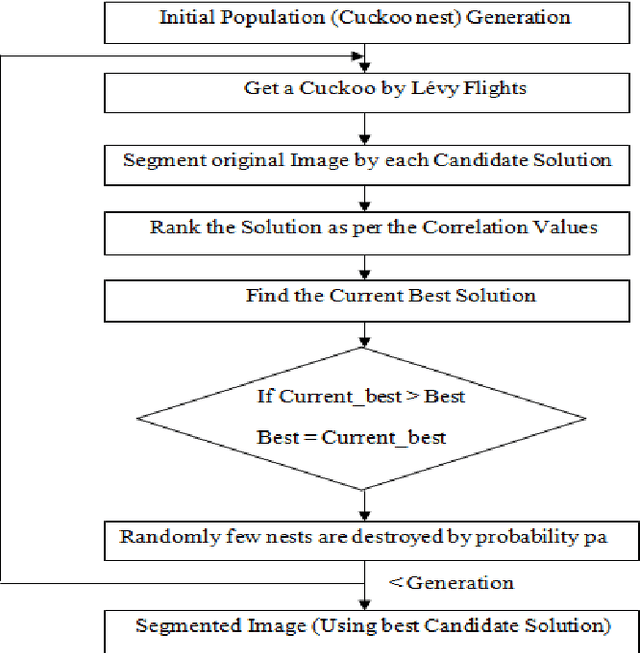
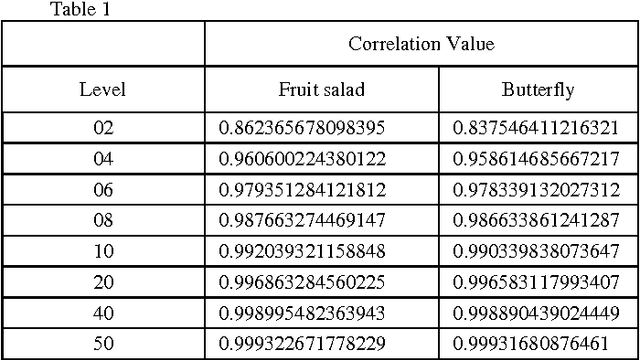
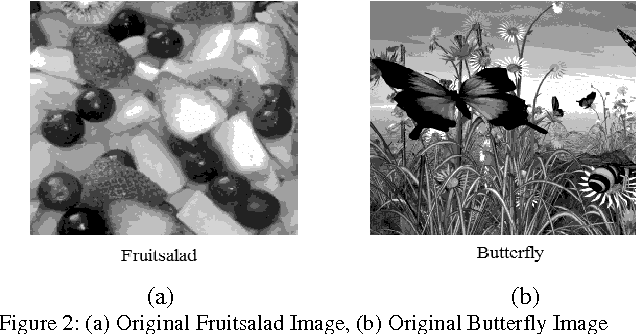

Abstract:Image Segmentation is a technique of partitioning the original image into some distinct classes. Many possible solutions may be available for segmenting an image into a certain number of classes, each one having different quality of segmentation. In our proposed method, multilevel thresholding technique has been used for image segmentation. A new approach of Cuckoo Search (CS) is used for selection of optimal threshold value. In other words, the algorithm is used to achieve the best solution from the initial random threshold values or solutions and to evaluate the quality of a solution correlation function is used. Finally, MSE and PSNR are measured to understand the segmentation quality.
Medical Information Embedding in Compressed Watermarked Intravascular Ultrasound Video
Mar 09, 2013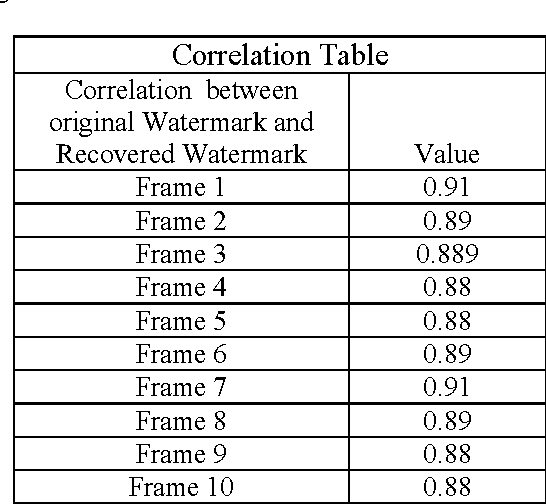
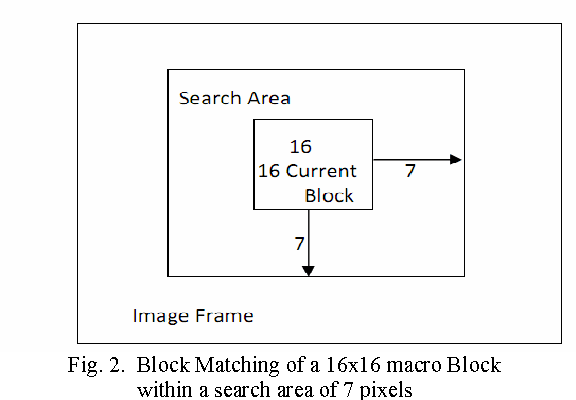
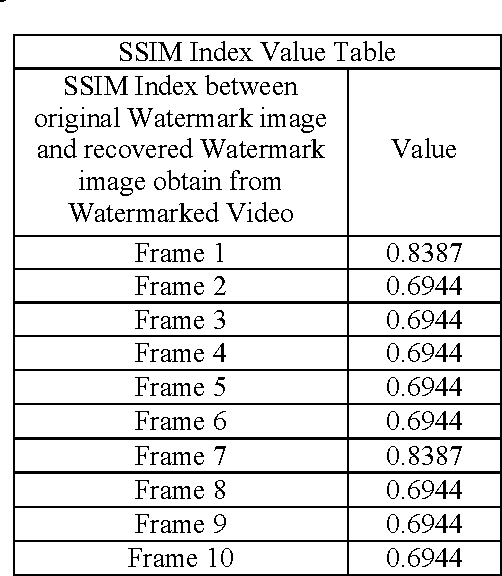
Abstract:In medical field, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is a tomographic imaging modality, which can identify the boundaries of different layers of blood vessels. IVUS can detect myocardial infarction (heart attack) that remains ignored and unattended when only angioplasty is done. During the past decade, it became easier for some individuals or groups to copy and transmits digital information without the permission of the owner. For increasing authentication and security of copyrights, digital watermarking, an information hiding technique, was introduced. Achieving watermarking technique with lesser amount of distortion in biomedical data is a challenging task. Watermark can be embedded into an image or in a video. As video data is a huge amount of information, therefore a large storage area is needed which is not feasible. In this case motion vector based video compression is done to reduce size. In this present paper, an Electronic Patient Record (EPR) is embedded as watermark within an IVUS video and then motion vector is calculated. This proposed method proves robustness as the extracted watermark has good PSNR value and less MSE.
* Pages-7 Fig.-15 Tables-2
Embedding of Blink Frequency in Electrooculography Signal using Difference Expansion based Reversible Watermarking Technique
Mar 09, 2013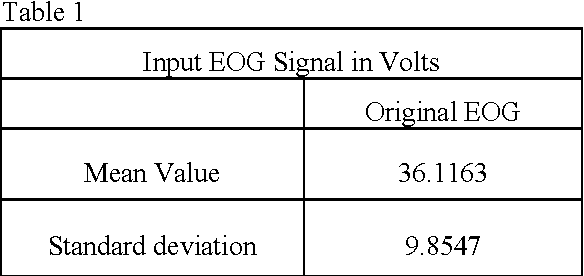

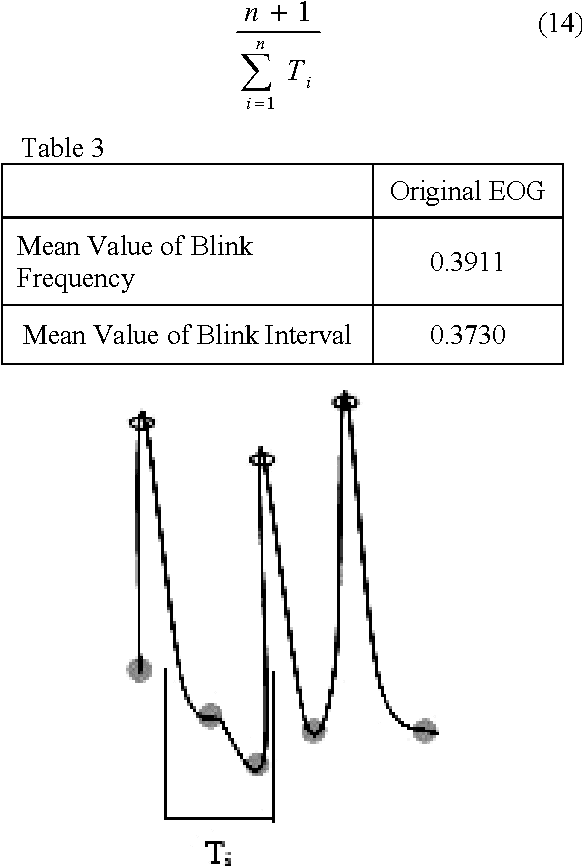
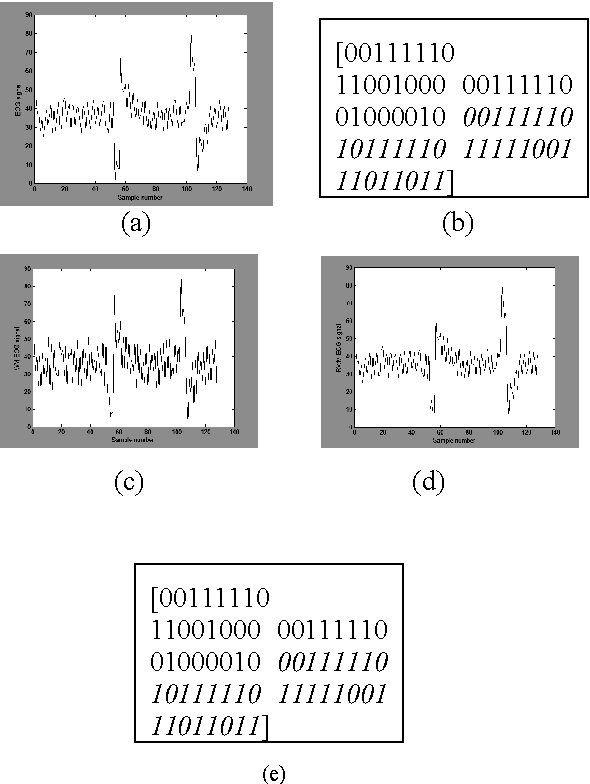
Abstract:In the past few years, like other fields, rapid expansion of digitization and globalization has influenced the medical field as well. For progress of diagnostic results most of the reputed hospitals and diagnostic centres all over the world have started exchanging medical information. In this proposed method, the calculated diagnostic parametric values of the original Electrooculography (EOG) signal are embedded as a watermark by using Difference Expansion (DE) algorithm based reversible watermarking technique. The extracted watermark provides the required parametric values at the recipient end without any post computation of the recovered EOG signal. By computing the parametric values from the recovered signal, the integrity of the extracted watermark can be validated. The time domain features of EOG signal are calculated for the generation of watermark. In the current work, various features are studied and two major features related to blink frequency are used to generate the watermark. The high Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and the Bit Error Rate (BER) claim the robustness of the proposed method.
* 6 Pages, 3 Figures, 4 Tables
Wavelet Based Normal and Abnormal Heart Sound Identification using Spectrogram Analysis
Sep 06, 2012
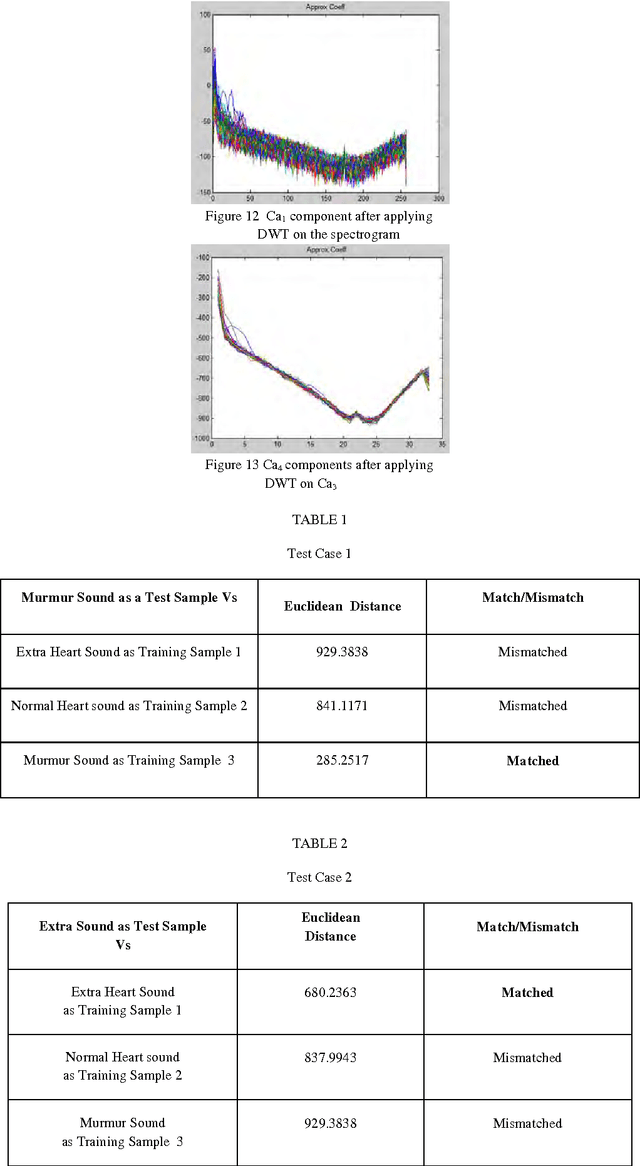
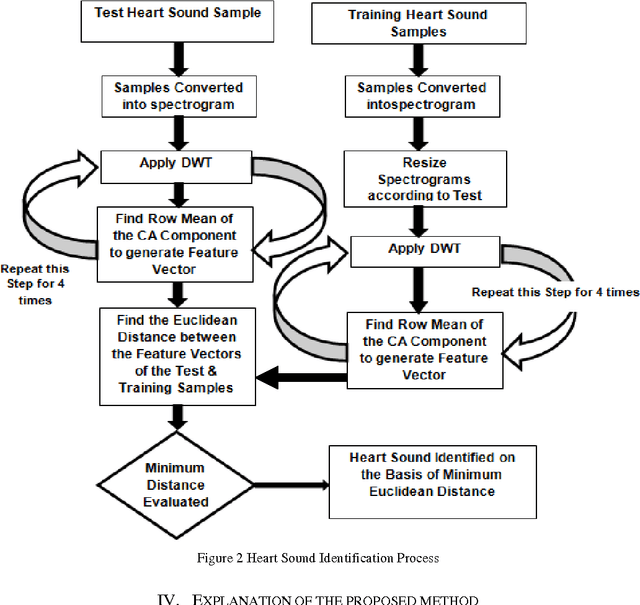
Abstract:The present work proposes a computer-aided normal and abnormal heart sound identification based on Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), it being useful for tele-diagnosis of heart diseases. Due to the presence of Cumulative Frequency components in the spectrogram, DWT is applied on the spectro-gram up to n level to extract the features from the individual approximation components. One dimensional feature vector is obtained by evaluating the Row Mean of the approximation components of these spectrograms. For this present approach, the set of spectrograms has been considered as the database, rather than raw sound samples. Minimum Euclidean distance is computed between feature vector of the test sample and the feature vectors of the stored samples to identify the heart sound. By applying this algorithm, almost 82% of accuracy was achieved.
* 7 pages, 13 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge