Shantala Manchenahally
Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Inventory Management
Apr 18, 2023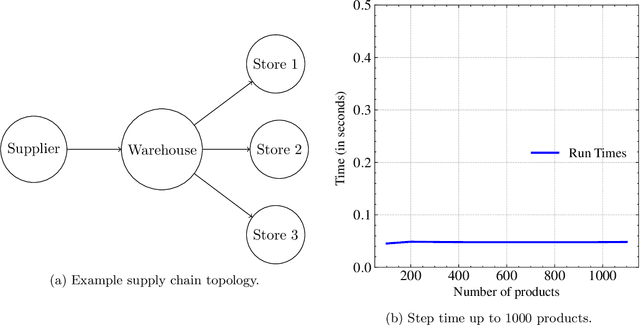
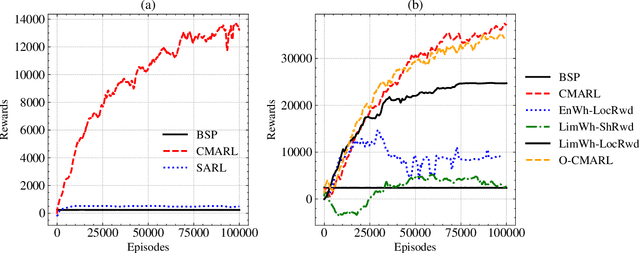
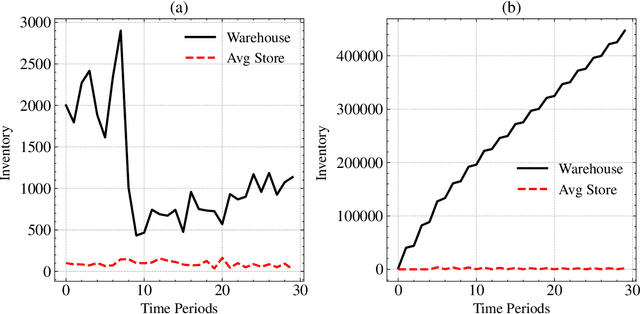
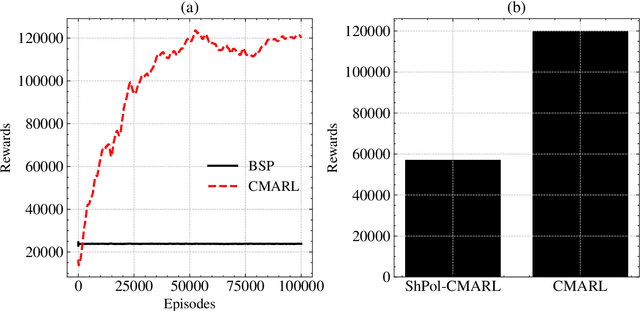
Abstract:With Reinforcement Learning (RL) for inventory management (IM) being a nascent field of research, approaches tend to be limited to simple, linear environments with implementations that are minor modifications of off-the-shelf RL algorithms. Scaling these simplistic environments to a real-world supply chain comes with a few challenges such as: minimizing the computational requirements of the environment, specifying agent configurations that are representative of dynamics at real world stores and warehouses, and specifying a reward framework that encourages desirable behavior across the whole supply chain. In this work, we present a system with a custom GPU-parallelized environment that consists of one warehouse and multiple stores, a novel architecture for agent-environment dynamics incorporating enhanced state and action spaces, and a shared reward specification that seeks to optimize for a large retailer's supply chain needs. Each vertex in the supply chain graph is an independent agent that, based on its own inventory, able to place replenishment orders to the vertex upstream. The warehouse agent, aside from placing orders from the supplier, has the special property of also being able to constrain replenishment to stores downstream, which results in it learning an additional allocation sub-policy. We achieve a system that outperforms standard inventory control policies such as a base-stock policy and other RL-based specifications for 1 product, and lay out a future direction of work for multiple products.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge