Shankar P. Bhattacharyya
PIDNet: A Real-time Semantic Segmentation Network Inspired from PID Controller
Jun 04, 2022
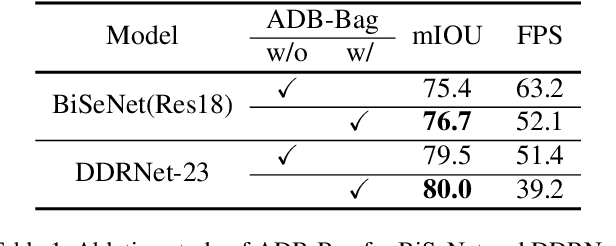

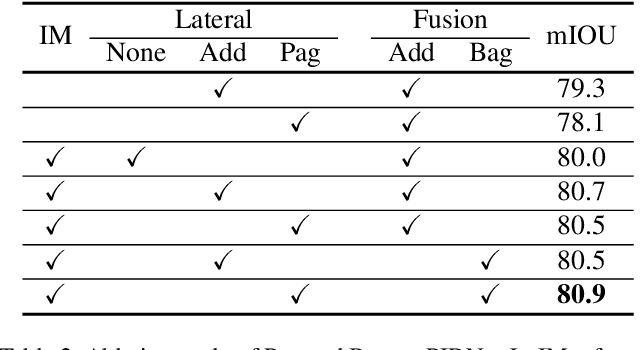
Abstract:Two-branch network architecture has shown its efficiency and effectiveness for real-time semantic segmentation tasks. However, direct fusion of low-level details and high-level semantics will lead to a phenomenon that the detailed features are easily overwhelmed by surrounding contextual information, namely overshoot in this paper, which limits the improvement of the accuracy of existed two-branch models. In this paper, we bridge a connection between Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller and reveal that the two-branch network is nothing but a Proportional-Integral (PI) controller, which inherently suffers from the similar overshoot issue. To alleviate this issue, we propose a novel three-branch network architecture: PIDNet, which possesses three branches to parse the detailed, context and boundary information (derivative of semantics), respectively, and employs boundary attention to guide the fusion of detailed and context branches in final stage. The family of PIDNets achieve the best trade-off between inference speed and accuracy and their test accuracy surpasses all the existed models with similar inference speed on Cityscapes, CamVid and COCO-Stuff datasets. Especially, PIDNet-S achieves 78.6% mIOU with inference speed of 93.2 FPS on Cityscapes test set and 81.6% mIOU with speed of 153.7 FPS on CamVid test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge