Shan Dai
Understanding and Guiding Layer Placement in Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) continue to grow, the cost of full-parameter fine-tuning has made parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) the default strategy for downstream adaptation. Constraints from inference latency in scalable serving and fine-tuning cost in edge or rapid-deployment settings make the choice of which layers to fine-tune unavoidable. Yet current practice typically applies PEFT uniformly across all layers, with limited understanding or leverage of layer selection. This paper develops a unified projected residual view of PEFT on top of a frozen base model. Under a local quadratic approximation, layerwise adaptation is governed by three quantities: (i) the projected residual norm (resnorm), which measures how much correctable bias a layer can capture; (ii) the activation energy, which determines feature conditioning; and (iii) layer coupling, which quantifies how strongly residuals interact across layers. We show that, for squared loss and linear adapters, the resnorm equals a normalized gradient norm, activation energy controls ill-conditioning and noise amplification, and weak coupling yields approximately additive layerwise contributions. Building on these insights, we introduce the Layer Card, a reusable diagnostic that summarizes residual signal strength, compute cost, and performance for each layer of a given model. With an identical model and LoRA configuration, Layer Card-guided placement refines the choice of adapted layers to flexibly prioritize different objectives, such as maximizing performance or reducing fine-tuning cost. Moreover, on Qwen3-8B, we show that selectively adapting a subset of layers can achieve performance close to full-layer LoRA while substantially reducing fine-tuning cost and the number of adapter-augmented layers during inference, offering a more cost-performance-aware alternative to full-layer insertion.
Mamba Hawkes Process
Jul 07, 2024

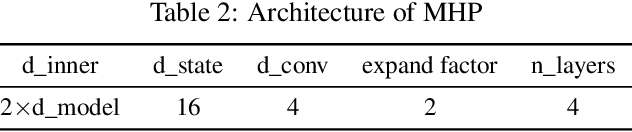

Abstract:Irregular and asynchronous event sequences are prevalent in many domains, such as social media, finance, and healthcare. Traditional temporal point processes (TPPs), like Hawkes processes, often struggle to model mutual inhibition and nonlinearity effectively. While recent neural network models, including RNNs and Transformers, address some of these issues, they still face challenges with long-term dependencies and computational efficiency. In this paper, we introduce the Mamba Hawkes Process (MHP), which leverages the Mamba state space architecture to capture long-range dependencies and dynamic event interactions. Our results show that MHP outperforms existing models across various datasets. Additionally, we propose the Mamba Hawkes Process Extension (MHP-E), which combines Mamba and Transformer models to enhance predictive capabilities. We present the novel application of the Mamba architecture to Hawkes processes, a flexible and extensible model structure, and a theoretical analysis of the synergy between state space models and Hawkes processes. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of both MHP and MHP-E, advancing the field of temporal point process modeling.
RoTHP: Rotary Position Embedding-based Transformer Hawkes Process
May 11, 2024



Abstract:Temporal Point Processes (TPPs), especially Hawkes Process are commonly used for modeling asynchronous event sequences data such as financial transactions and user behaviors in social networks. Due to the strong fitting ability of neural networks, various neural Temporal Point Processes are proposed, among which the Neural Hawkes Processes based on self-attention such as Transformer Hawkes Process (THP) achieve distinct performance improvement. Although the THP has gained increasing studies, it still suffers from the {sequence prediction issue}, i.e., training on history sequences and inferencing about the future, which is a prevalent paradigm in realistic sequence analysis tasks. What's more, conventional THP and its variants simply adopt initial sinusoid embedding in transformers, which shows performance sensitivity to temporal change or noise in sequence data analysis by our empirical study. To deal with the problems, we propose a new Rotary Position Embedding-based THP (RoTHP) architecture in this paper. Notably, we show the translation invariance property and {sequence prediction flexibility} of our RoTHP induced by the {relative time embeddings} when coupled with Hawkes process theoretically. Furthermore, we demonstrate empirically that our RoTHP can be better generalized in sequence data scenarios with timestamp translations and in sequence prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge