Shahzad Ali
Towards Efficient and Accurate CT Segmentation via Edge-Preserving Probabilistic Downsampling
Apr 05, 2024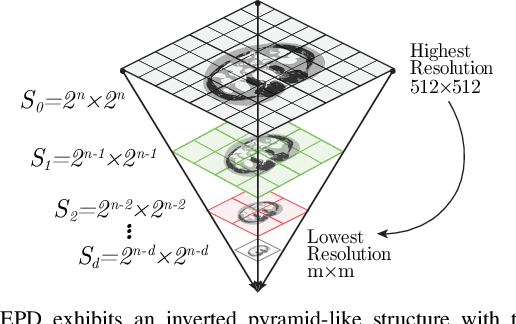

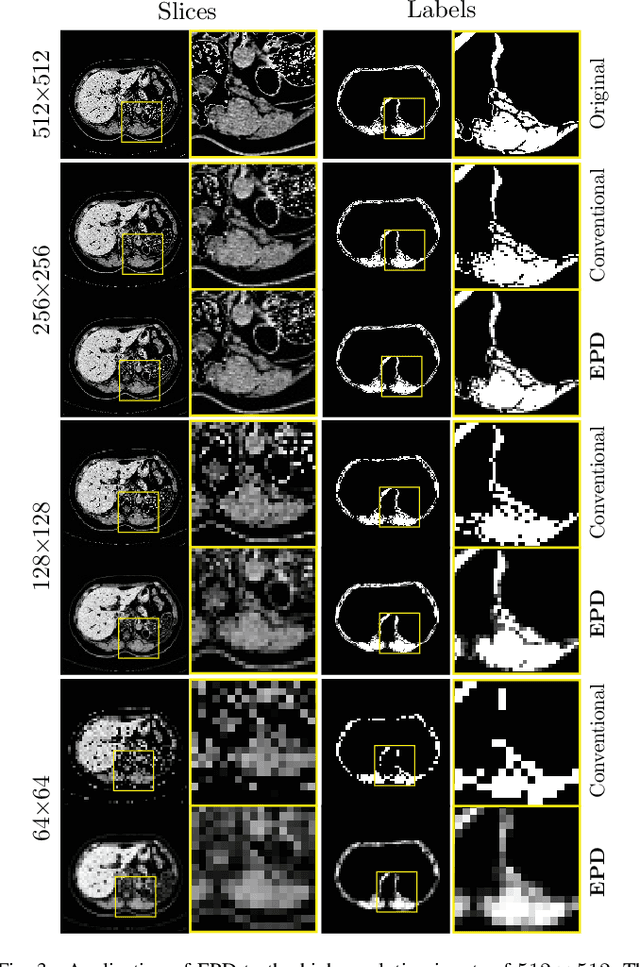
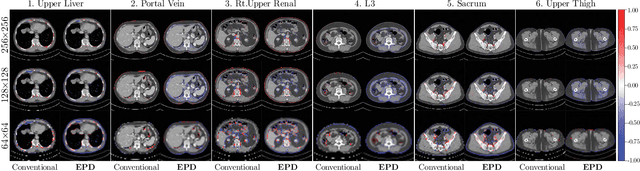
Abstract:Downsampling images and labels, often necessitated by limited resources or to expedite network training, leads to the loss of small objects and thin boundaries. This undermines the segmentation network's capacity to interpret images accurately and predict detailed labels, resulting in diminished performance compared to processing at original resolutions. This situation exemplifies the trade-off between efficiency and accuracy, with higher downsampling factors further impairing segmentation outcomes. Preserving information during downsampling is especially critical for medical image segmentation tasks. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a novel method named Edge-preserving Probabilistic Downsampling (EPD). It utilizes class uncertainty within a local window to produce soft labels, with the window size dictating the downsampling factor. This enables a network to produce quality predictions at low resolutions. Beyond preserving edge details more effectively than conventional nearest-neighbor downsampling, employing a similar algorithm for images, it surpasses bilinear interpolation in image downsampling, enhancing overall performance. Our method significantly improved Intersection over Union (IoU) to 2.85%, 8.65%, and 11.89% when downsampling data to 1/2, 1/4, and 1/8, respectively, compared to conventional interpolation methods.
Lightweight Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Foot Ulcer Segmentation
Jul 06, 2022Abstract:Continuous monitoring of foot ulcer healing is needed to ensure the efficacy of a given treatment and to avoid any possibility of deterioration. Foot ulcer segmentation is an essential step in wound diagnosis. We developed a model that is similar in spirit to the well-established encoder-decoder and residual convolution neural networks. Our model includes a residual connection along with a channel and spatial attention integrated within each convolution block. A simple patch-based approach for model training, test time augmentations, and majority voting on the obtained predictions resulted in superior performance. Our model did not leverage any readily available backbone architecture, pre-training on a similar external dataset, or any of the transfer learning techniques. The total number of network parameters being around 5 million made it a significantly lightweight model as compared with the available state-of-the-art models used for the foot ulcer segmentation task. Our experiments presented results at the patch-level and image-level. Applied on publicly available Foot Ulcer Segmentation (FUSeg) Challenge dataset from MICCAI 2021, our model achieved state-of-the-art image-level performance of 88.22% in terms of Dice similarity score and ranked second in the official challenge leaderboard. We also showed an extremely simple solution that could be compared against the more advanced architectures.
* Published version of this article is available at https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-06381-7_17
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge