Seyed Mojtaba Tabatabaie
APS: A Large-Scale Multi-Modal Indoor Camera Positioning System
Feb 08, 2021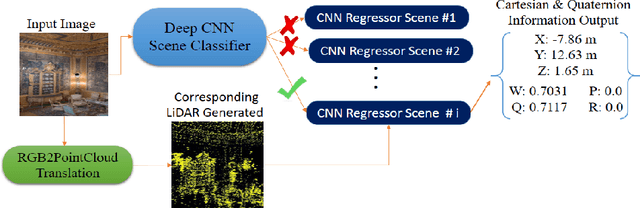
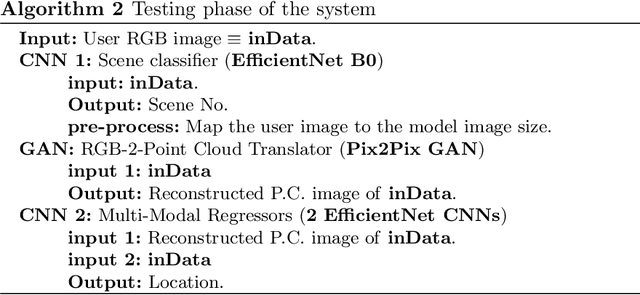
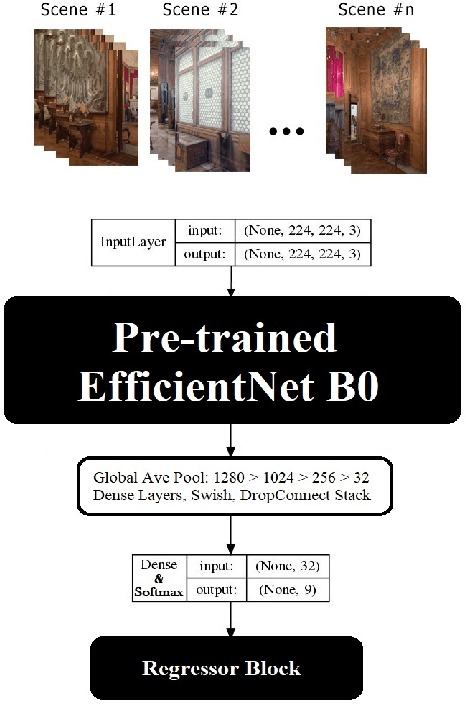
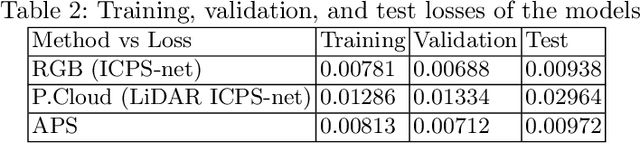
Abstract:Navigation inside a closed area with no GPS-signal accessibility is a highly challenging task. In order to tackle this problem, recently the imaging-based methods have grabbed the attention of many researchers. These methods either extract the features (e.g. using SIFT, or SOSNet) and map the descriptive ones to the camera position and rotation information, or deploy an end-to-end system that directly estimates this information out of RGB images, similar to PoseNet. While the former methods suffer from heavy computational burden during the test process, the latter suffers from lack of accuracy and robustness against environmental changes and object movements. However, end-to-end systems are quite fast during the test and inference and are pretty qualified for real-world applications, even though their training phase could be longer than the former ones. In this paper, a novel multi-modal end-to-end system for large-scale indoor positioning has been proposed, namely APS (Alpha Positioning System), which integrates a Pix2Pix GAN network to reconstruct the point cloud pair of the input query image, with a deep CNN network in order to robustly estimate the position and rotation information of the camera. For this integration, the existing datasets have the shortcoming of paired RGB/point cloud images for indoor environments. Therefore, we created a new dataset to handle this situation. By implementing the proposed APS system, we could achieve a highly accurate camera positioning with a precision level of less than a centimeter.
Attention-Based Face AntiSpoofing of RGB Images, using a Minimal End-2-End Neural Network
Dec 18, 2019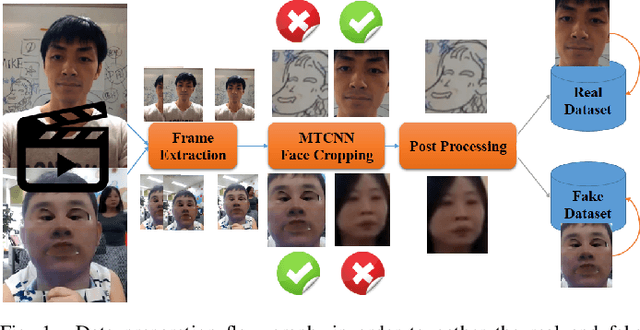
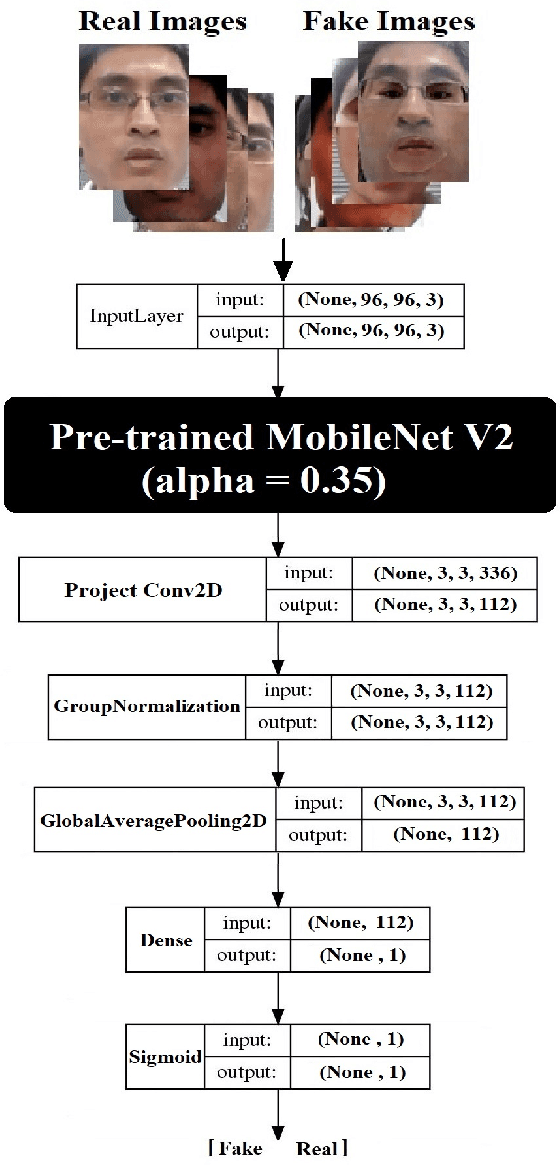
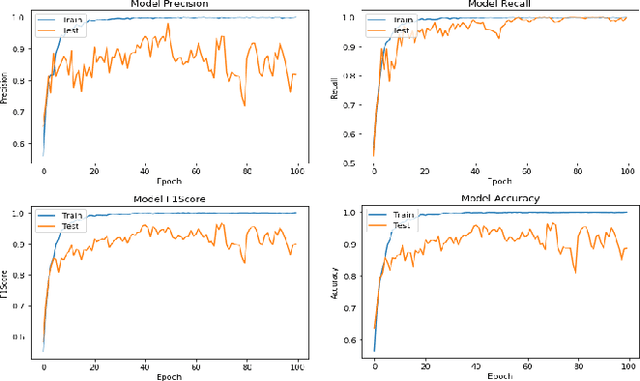

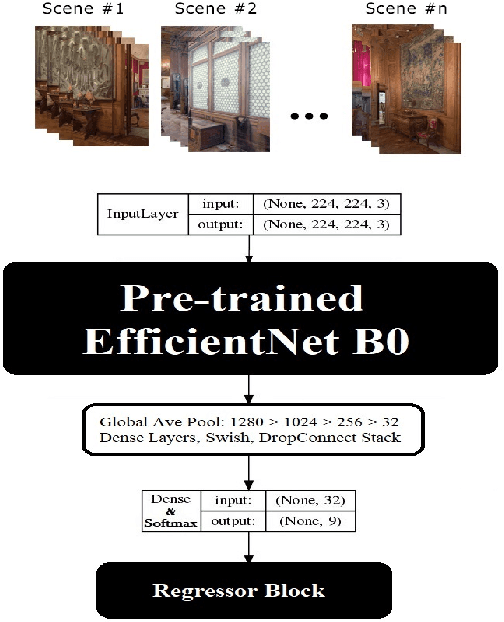
Abstract:Face anti-spoofing aims at identifying the real face, as well as the fake one, and gains a high attention in security-sensitive applications, liveness detection, fingerprinting, and so on. In this paper, we address the anti-spoofing problem by proposing two end-to-end systems of convolutional neural networks. One model is developed based on the EfficientNet B0 network which has been modified in the final dense layers. The second one, is a very light model of the MobileNet V2, which has been contracted, modified and retrained efficiently on the data being created based on the Rose-Youtu dataset, for this purpose. The experiments show that, both of the proposed architectures achieve remarkable results on detecting the real and fake images of the face input data. The experiments clearly show that the heavy-weight model could be efficiently employed in server-side implementations, whereas the low-weight model could be easily implemented on the hand-held devices and both perform perfectly well using merely RGB input images.
LiDAR ICPS-net: Indoor Camera Positioning based-on Generative Adversarial Network for RGB to Point-Cloud Translation
Nov 14, 2019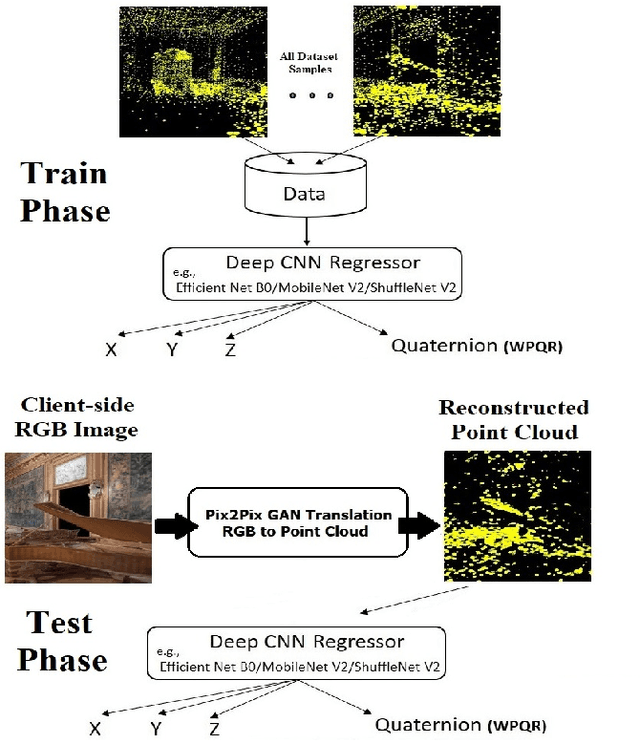
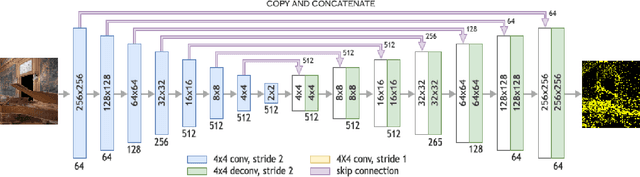

Abstract:Indoor positioning aims at navigation inside areas with no GPS-data availability and could be employed in many applications such as augmented reality, autonomous driving specially inside closed areas and tunnels. In this paper, a deep neural network-based architecture has been proposed to address this problem. In this regard, a tandem set of convolutional neural networks, as well as a Pix2Pix GAN network have been leveraged to perform as the scene classifier, scene RGB image to point cloud converter, and position regressor, respectively. The proposed architecture outperforms the previous works, including our recent work, in the sense that it makes data generation task easier and more robust against scene small variations, whilst the accuracy of the positioning is remarkably well, for both Cartesian position and quaternion information of the camera.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge