Rahil Mahdian Toroghi
Music Harmony Generation, through Deep Learning and Using a Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm
Feb 16, 2021



Abstract:Automatic music generation has become an epicenter research topic for many scientists in artificial intelligence, who are also interested in the music industry. Being a balanced combination of math and art, music in collaboration with A.I. can simplify the generation process for new musical pieces, and ease the interpretation of it to a tangible level. On the other hand, the artistic nature of music and its mingling with the senses and feelings of the composer makes the artificial generation and mathematical modeling of it infeasible. In fact, there are no clear evaluation measures that can combine the objective music grammar and structure with the subjective audience satisfaction goal. Also, original music contains different elements that it is inevitable to put together. Therefore, in this paper, a method based on a genetic multi-objective evolutionary optimization algorithm for the generation of polyphonic music (melody with rhythm and harmony or appropriate chords) is introduced in which three specific goals determine the qualifications of the music generated. One of the goals is the rules and regulations of music, which, along with the other two goals, including the scores of music experts and ordinary listeners, fits the cycle of evolution to get the most optimal response. The scoring of experts and listeners separately is modeled using a Bi-LSTM neural network and has been incorporated in the fitness function of the algorithm. The results show that the proposed method is able to generate difficult and pleasant pieces with desired styles and lengths, along with harmonic sounds that follow the grammar while attracting the listener, at the same time.
APS: A Large-Scale Multi-Modal Indoor Camera Positioning System
Feb 08, 2021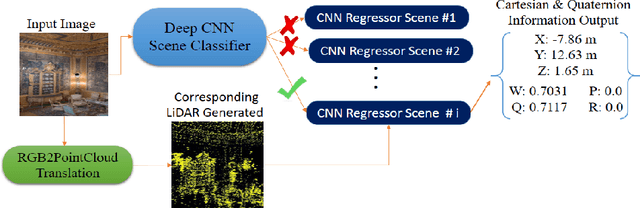
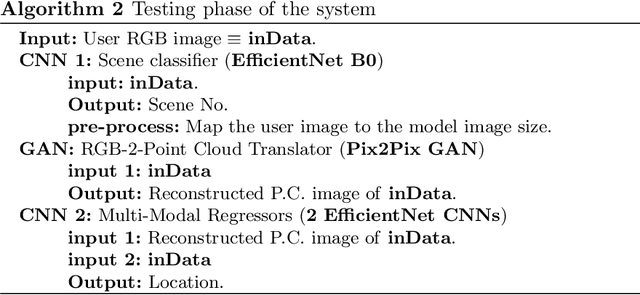
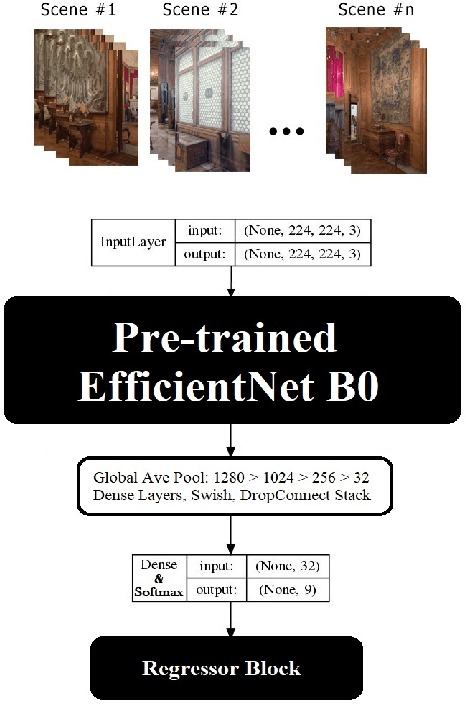
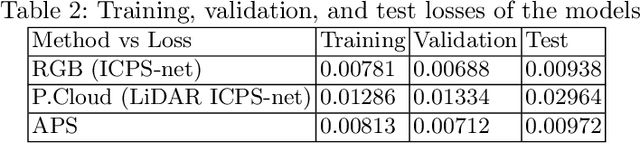
Abstract:Navigation inside a closed area with no GPS-signal accessibility is a highly challenging task. In order to tackle this problem, recently the imaging-based methods have grabbed the attention of many researchers. These methods either extract the features (e.g. using SIFT, or SOSNet) and map the descriptive ones to the camera position and rotation information, or deploy an end-to-end system that directly estimates this information out of RGB images, similar to PoseNet. While the former methods suffer from heavy computational burden during the test process, the latter suffers from lack of accuracy and robustness against environmental changes and object movements. However, end-to-end systems are quite fast during the test and inference and are pretty qualified for real-world applications, even though their training phase could be longer than the former ones. In this paper, a novel multi-modal end-to-end system for large-scale indoor positioning has been proposed, namely APS (Alpha Positioning System), which integrates a Pix2Pix GAN network to reconstruct the point cloud pair of the input query image, with a deep CNN network in order to robustly estimate the position and rotation information of the camera. For this integration, the existing datasets have the shortcoming of paired RGB/point cloud images for indoor environments. Therefore, we created a new dataset to handle this situation. By implementing the proposed APS system, we could achieve a highly accurate camera positioning with a precision level of less than a centimeter.
GGA-MG: Generative Genetic Algorithm for Music Generation
Apr 07, 2020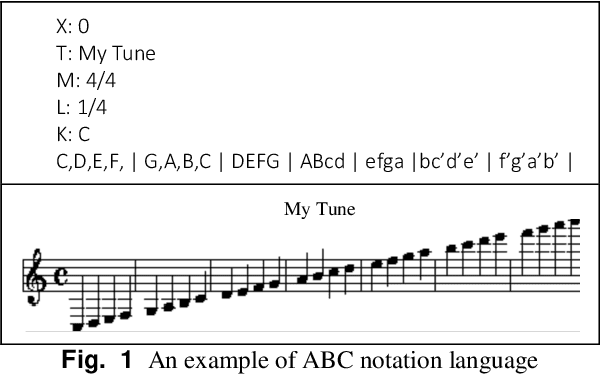
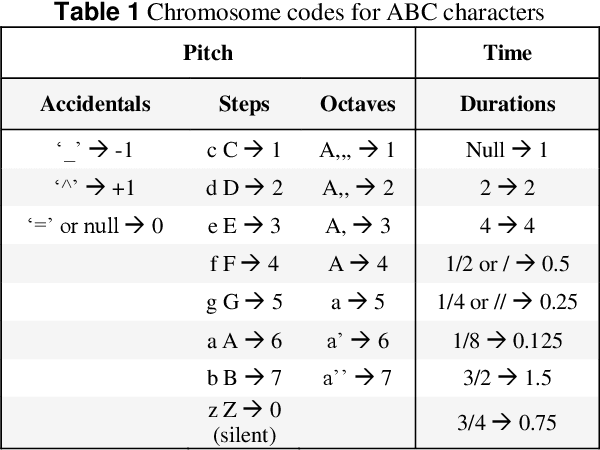
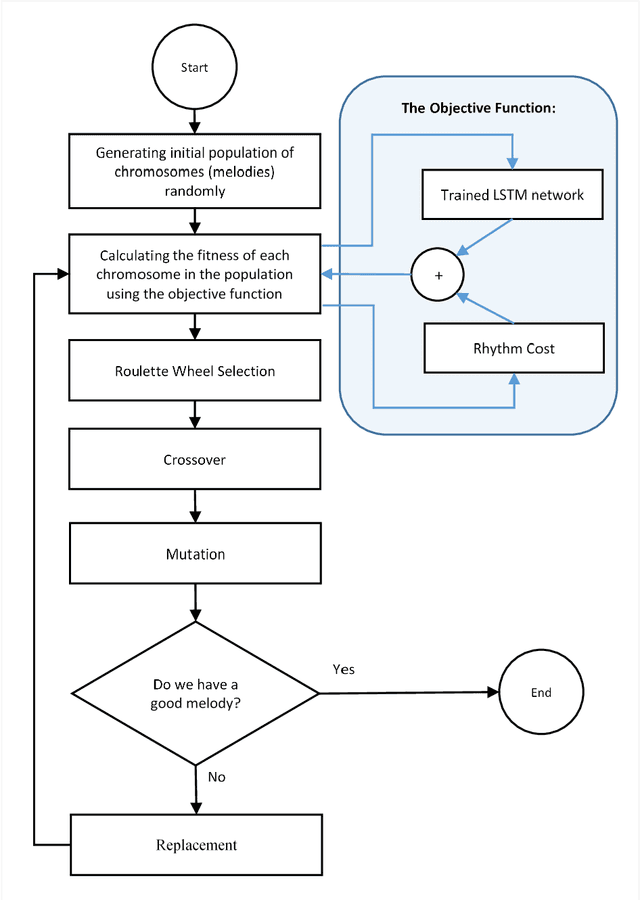
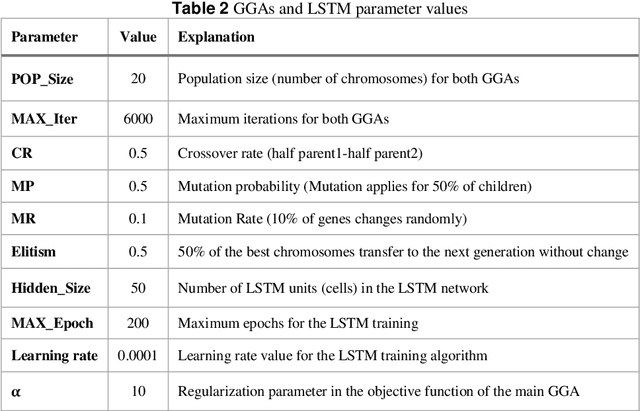
Abstract:Music Generation (MG) is an interesting research topic that links the art of music and Artificial Intelligence (AI). The goal is to train an artificial composer to generate infinite, fresh, and pleasurable musical pieces. Music has different parts such as melody, harmony, and rhythm. In this paper, we propose a Generative Genetic Algorithm (GGA) to produce a melody automatically. The main GGA uses a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) recurrent neural network as the objective function, which should be trained by a spectrum of bad-to-good melodies. These melodies have to be provided by another GGA with a different objective function. Good melodies have been provided by CAMPINs collection. We have considered the rhythm in this work, too. The experimental results clearly show that the proposed GGA method is able to generate eligible melodies with natural transitions and without rhythm error.
Attention-Based Face AntiSpoofing of RGB Images, using a Minimal End-2-End Neural Network
Dec 18, 2019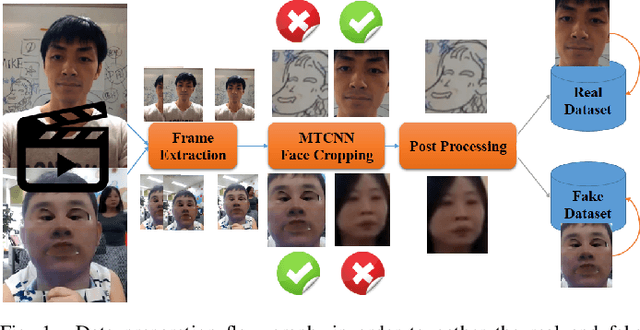
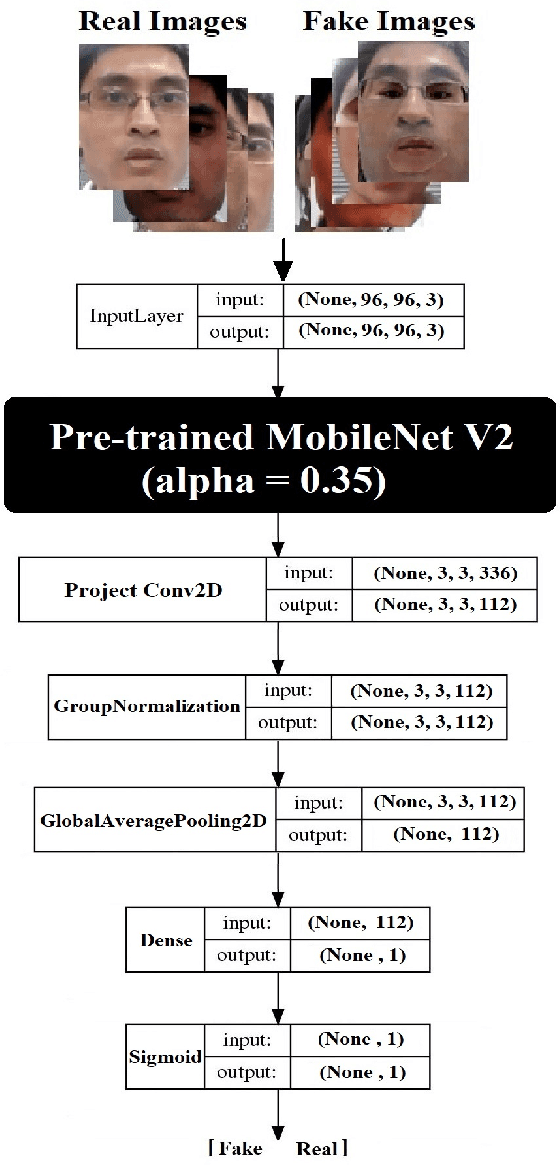
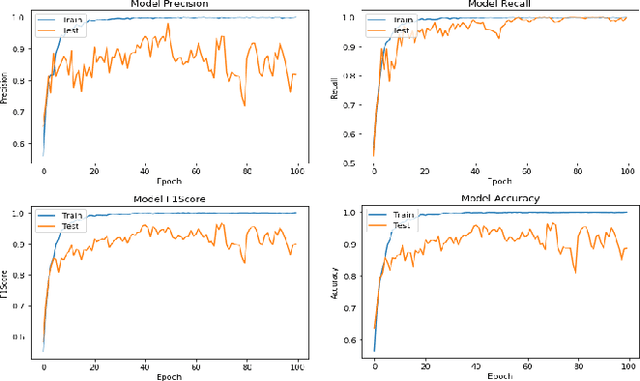

Abstract:Face anti-spoofing aims at identifying the real face, as well as the fake one, and gains a high attention in security-sensitive applications, liveness detection, fingerprinting, and so on. In this paper, we address the anti-spoofing problem by proposing two end-to-end systems of convolutional neural networks. One model is developed based on the EfficientNet B0 network which has been modified in the final dense layers. The second one, is a very light model of the MobileNet V2, which has been contracted, modified and retrained efficiently on the data being created based on the Rose-Youtu dataset, for this purpose. The experiments show that, both of the proposed architectures achieve remarkable results on detecting the real and fake images of the face input data. The experiments clearly show that the heavy-weight model could be efficiently employed in server-side implementations, whereas the low-weight model could be easily implemented on the hand-held devices and both perform perfectly well using merely RGB input images.
Capsule-Based Persian/Arabic Robust Handwritten Digit Recognition Using EM Routing
Dec 18, 2019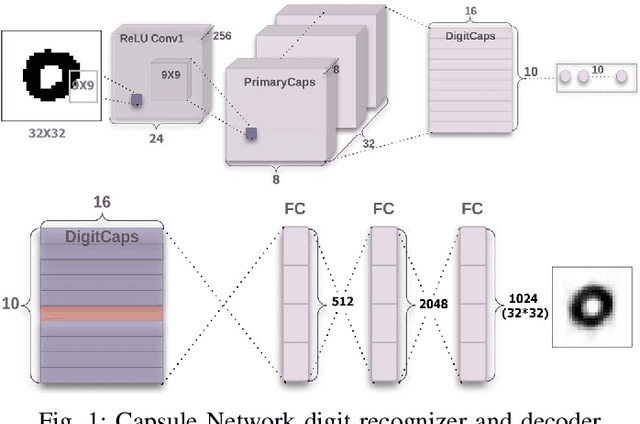
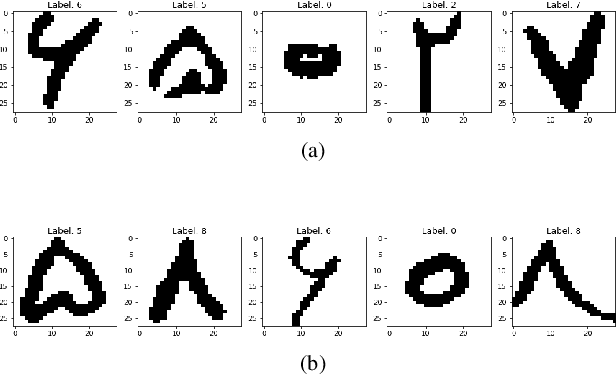
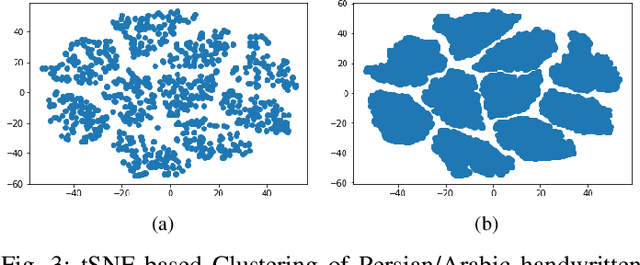

Abstract:In this paper, the problem of handwritten digit recognition has been addressed. However, the underlying language is Persian/Arabic, and the system with which this task is a capsule network (CapsNet) has recently emerged as a more advanced architecture than its ancestor, namely CNN (Convolutional Neural Network). The training of the architecture is performed using the Hoda dataset, which has been provided for Persian/Arabic handwritten digits. The output of the system clearly outperforms the results achieved by its ancestors, as well as other previously presented recognition algorithms.
LiDAR ICPS-net: Indoor Camera Positioning based-on Generative Adversarial Network for RGB to Point-Cloud Translation
Nov 14, 2019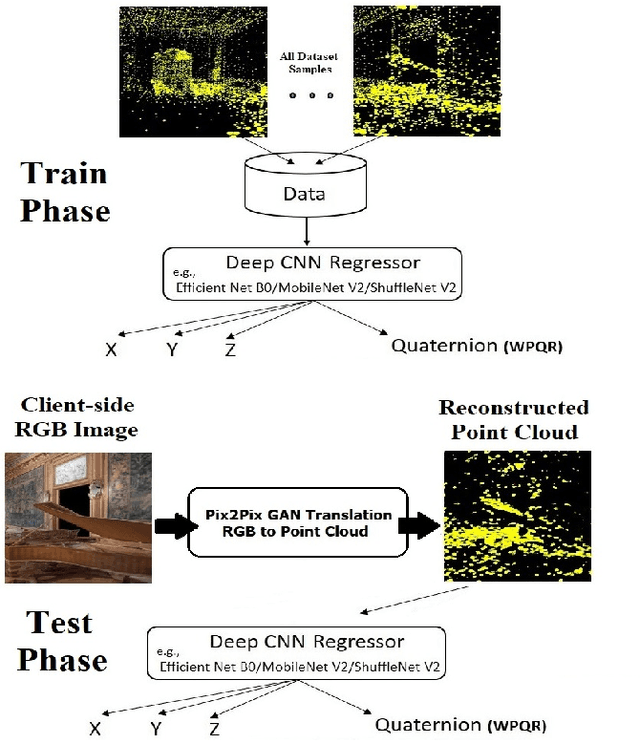
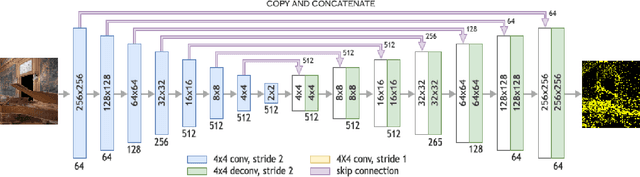
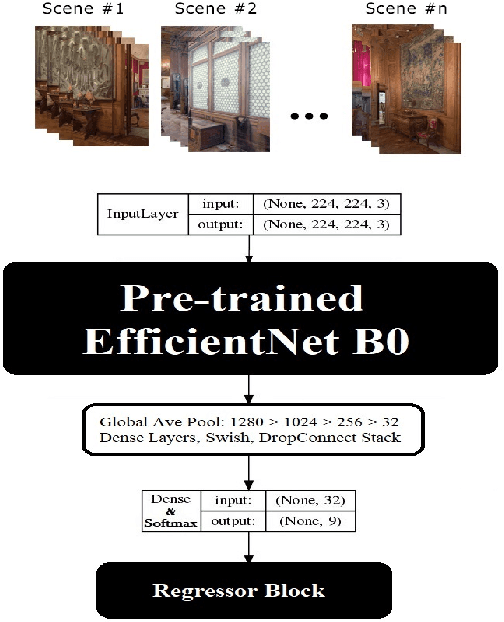

Abstract:Indoor positioning aims at navigation inside areas with no GPS-data availability and could be employed in many applications such as augmented reality, autonomous driving specially inside closed areas and tunnels. In this paper, a deep neural network-based architecture has been proposed to address this problem. In this regard, a tandem set of convolutional neural networks, as well as a Pix2Pix GAN network have been leveraged to perform as the scene classifier, scene RGB image to point cloud converter, and position regressor, respectively. The proposed architecture outperforms the previous works, including our recent work, in the sense that it makes data generation task easier and more robust against scene small variations, whilst the accuracy of the positioning is remarkably well, for both Cartesian position and quaternion information of the camera.
ICPS-net: An End-to-End RGB-based Indoor Camera Positioning System using deep convolutional neural networks
Oct 14, 2019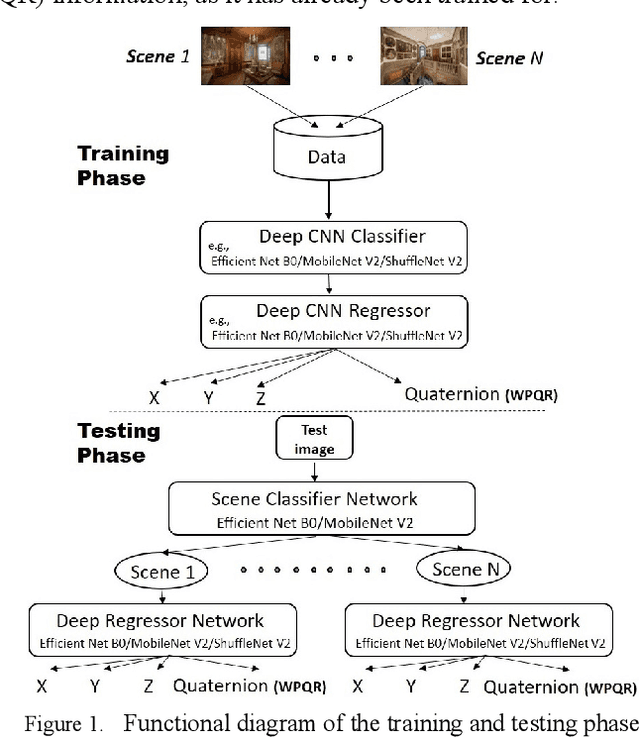
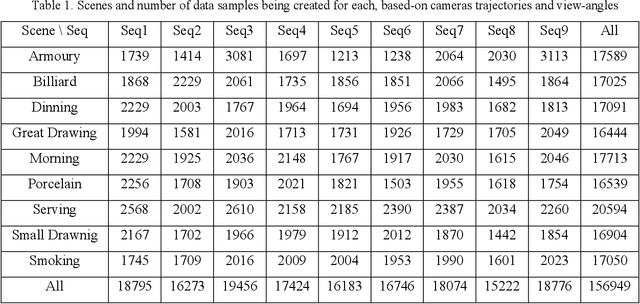
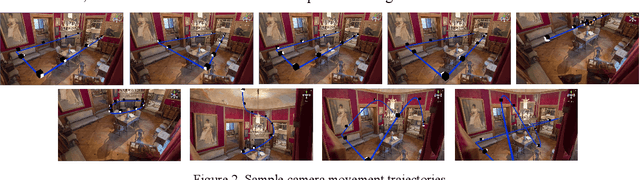

Abstract:Indoor positioning and navigation inside an area with no GPS-data availability is a challenging problem. There are applications such as augmented reality, autonomous driving, navigation of drones inside tunnels, in which indoor positioning gets crucial. In this paper, a tandem architecture of deep network-based systems, for the first time to our knowledge, is developed to address this problem. This structure is trained on the scene images being obtained through scanning of the desired area segments using photogrammetry. A CNN structure based on EfficientNet is trained as a classifier of the scenes, followed by a MobileNet CNN structure which is trained to perform as a regressor. The proposed system achieves amazingly fine precisions for both Cartesian position and Quaternion information of the camera.
Melody Generation using an Interactive Evolutionary Algorithm
Jul 07, 2019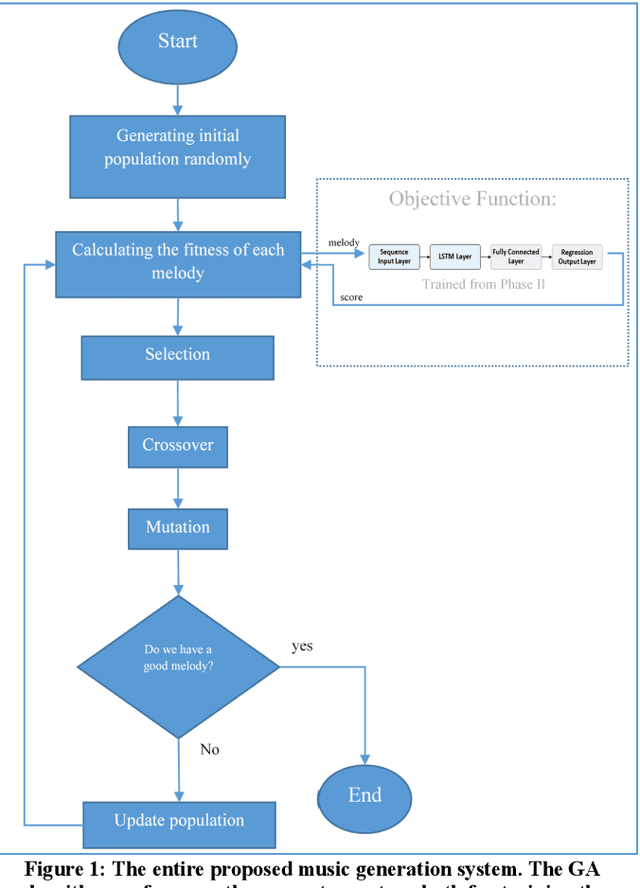
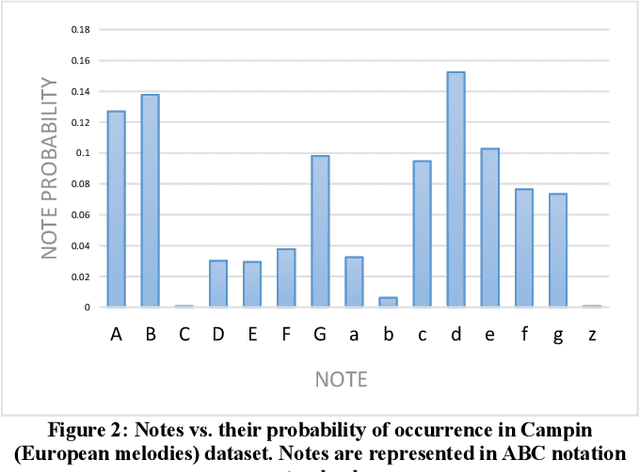
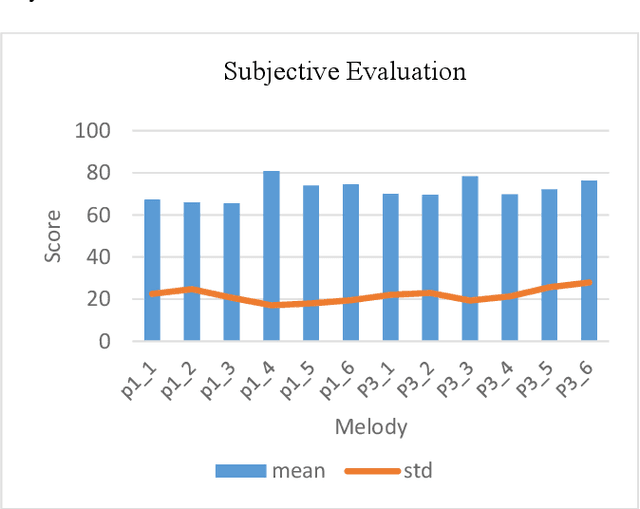
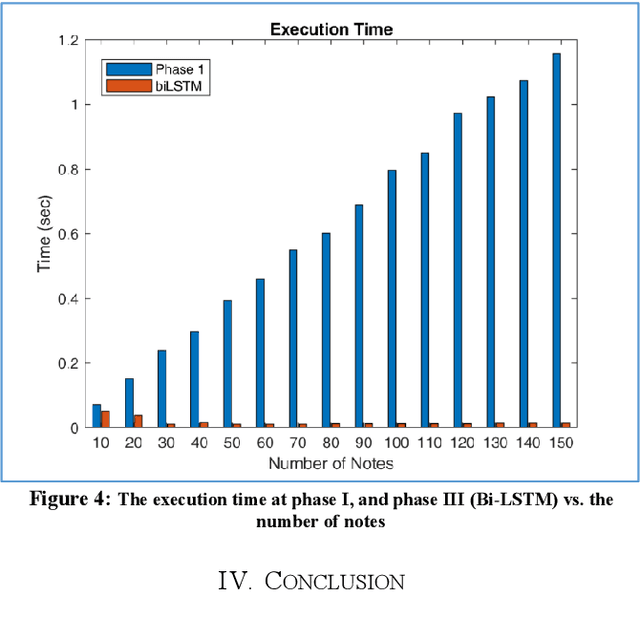
Abstract:Music generation with the aid of computers has been recently grabbed the attention of many scientists in the area of artificial intelligence. Deep learning techniques have evolved sequence production methods for this purpose. Yet, a challenging problem is how to evaluate generated music by a machine. In this paper, a methodology has been developed based upon an interactive evolutionary optimization method, with which the scoring of the generated melodies is primarily performed by human expertise, during the training. This music quality scoring is modeled using a Bi-LSTM recurrent neural network. Moreover, the innovative generated melody through a Genetic algorithm will then be evaluated using this Bi-LSTM network. The results of this mechanism clearly show that the proposed method is able to create pleasurable melodies with desired styles and pieces. This method is also quite fast, compared to the state-of-the-art data-oriented evolutionary systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge