Sergis Nicolaou
Dialog speech sentiment classification for imbalanced datasets
Sep 15, 2021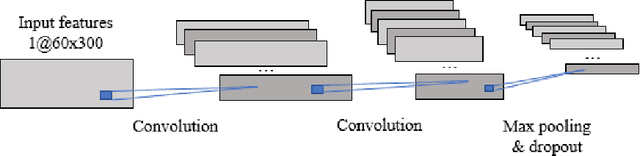
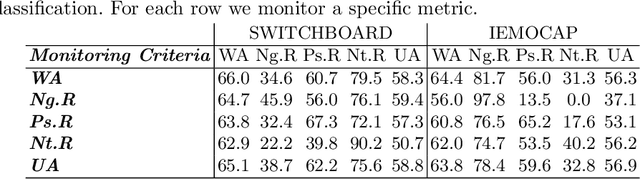
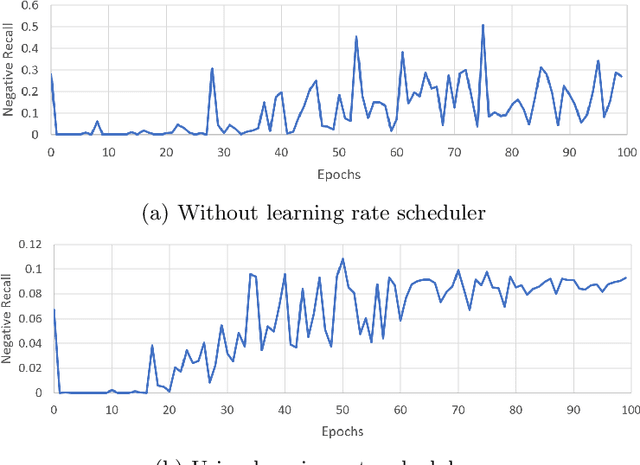
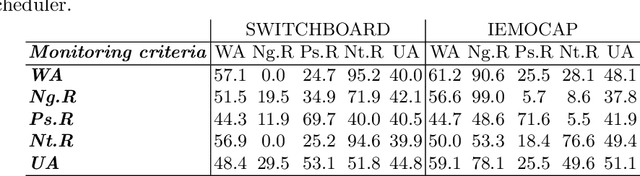
Abstract:Speech is the most common way humans express their feelings, and sentiment analysis is the use of tools such as natural language processing and computational algorithms to identify the polarity of these feelings. Even though this field has seen tremendous advancements in the last two decades, the task of effectively detecting under represented sentiments in different kinds of datasets is still a challenging task. In this paper, we use single and bi-modal analysis of short dialog utterances and gain insights on the main factors that aid in sentiment detection, particularly in the underrepresented classes, in datasets with and without inherent sentiment component. Furthermore, we propose an architecture which uses a learning rate scheduler and different monitoring criteria and provides state-of-the-art results for the SWITCHBOARD imbalanced sentiment dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge