Seong Jin Lee
DIVER-1 : Deep Integration of Vast Electrophysiological Recordings at Scale
Dec 22, 2025



Abstract:Electrophysiology signals such as EEG and iEEG are central to neuroscience, brain-computer interfaces, and clinical applications, yet existing foundation models remain limited in scale despite clear evidence that scaling improves performance. We introduce DIVER-1, a family of EEG and iEEG foundation models trained on the largest and most diverse corpus to date-5.3k hours of iEEG and 54k hours of EEG (1.6M channel-hours from over 17.7k subjects)-and scaled up to 1.82B parameters. We present the first systematic scaling law analysis for this domain, showing that they follow data-constrained scaling laws: for a given amount of data and compute, smaller models trained for extended epochs consistently outperform larger models trained briefly. This behavior contrasts with prior electrophysiology foundation models that emphasized model size over training duration. To achieve strong performance, we also design architectural innovations including any-variate attention, sliding temporal conditional positional encoding, and multi-domain reconstruction. DIVER-1 iEEG and EEG models each achieve state-of-the-art performance on their respective benchmarks, establishing a concrete guidelines for efficient scaling and resource allocation in electrophysiology foundation model development.
Low-Rank Contextual Reinforcement Learning from Heterogeneous Human Feedback
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has become a cornerstone for aligning large language models with human preferences. However, the heterogeneity of human feedback, driven by diverse individual contexts and preferences, poses significant challenges for reward learning. To address this, we propose a Low-rank Contextual RLHF (LoCo-RLHF) framework that integrates contextual information to better model heterogeneous feedback while maintaining computational efficiency. Our approach builds on a contextual preference model, leveraging the intrinsic low-rank structure of the interaction between user contexts and query-answer pairs to mitigate the high dimensionality of feature representations. Furthermore, we address the challenge of distributional shifts in feedback through our Pessimism in Reduced Subspace (PRS) policy, inspired by pessimistic offline reinforcement learning techniques. We theoretically demonstrate that our policy achieves a tighter sub-optimality gap compared to existing methods. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of LoCo-RLHF, showcasing its superior performance in personalized RLHF settings and its robustness to distribution shifts.
Low-Rank Online Dynamic Assortment with Dual Contextual Information
Apr 19, 2024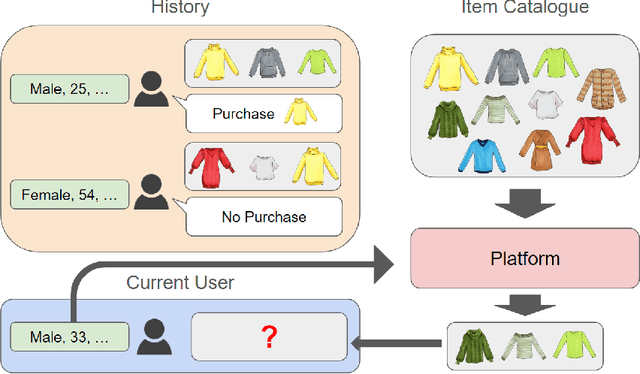
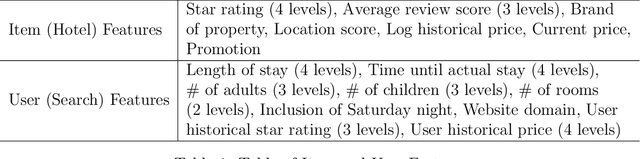
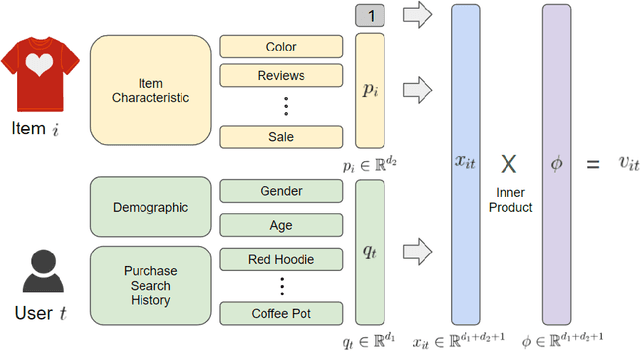
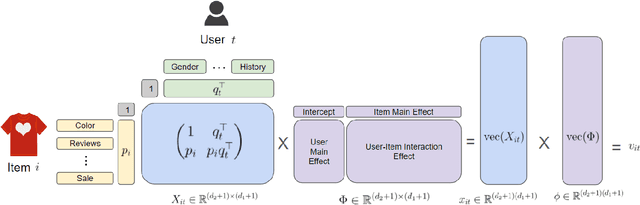
Abstract:As e-commerce expands, delivering real-time personalized recommendations from vast catalogs poses a critical challenge for retail platforms. Maximizing revenue requires careful consideration of both individual customer characteristics and available item features to optimize assortments over time. In this paper, we consider the dynamic assortment problem with dual contexts -- user and item features. In high-dimensional scenarios, the quadratic growth of dimensions complicates computation and estimation. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a new low-rank dynamic assortment model to transform this problem into a manageable scale. Then we propose an efficient algorithm that estimates the intrinsic subspaces and utilizes the upper confidence bound approach to address the exploration-exploitation trade-off in online decision making. Theoretically, we establish a regret bound of $\tilde{O}((d_1+d_2)r\sqrt{T})$, where $d_1, d_2$ represent the dimensions of the user and item features respectively, $r$ is the rank of the parameter matrix, and $T$ denotes the time horizon. This bound represents a substantial improvement over prior literature, made possible by leveraging the low-rank structure. Extensive simulations and an application to the Expedia hotel recommendation dataset further demonstrate the advantages of our proposed method.
RTB Formulation Using Point Process
Aug 17, 2023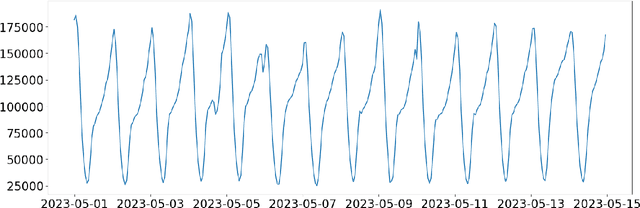
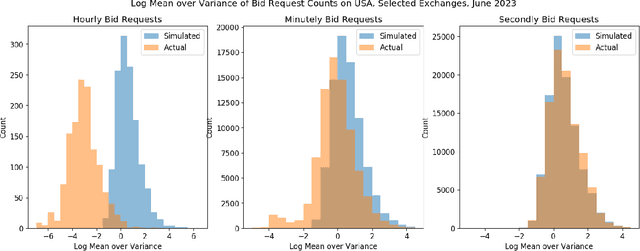
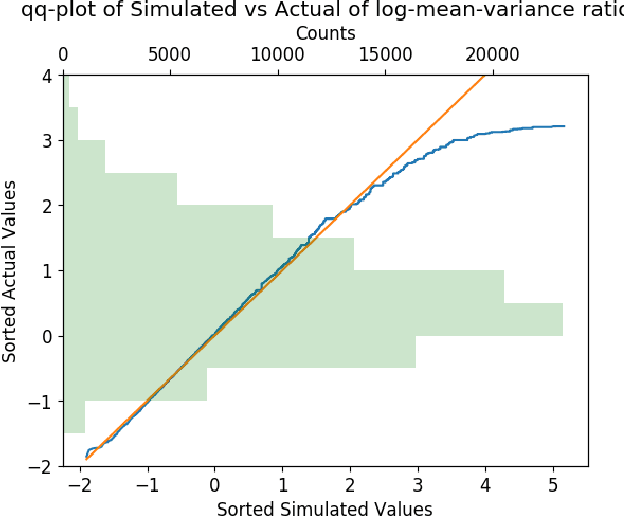
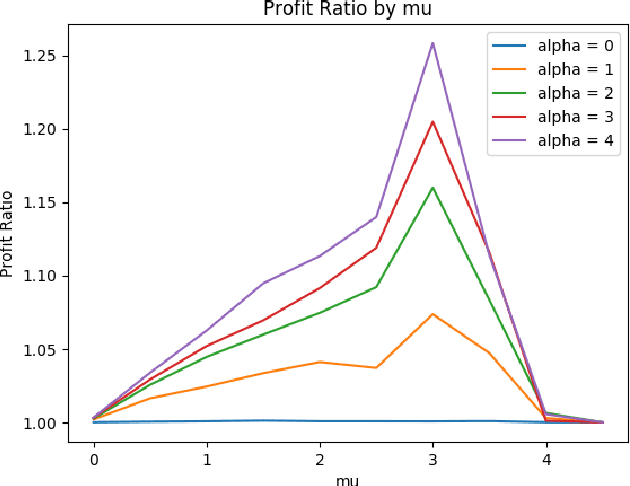
Abstract:We propose a general stochastic framework for modelling repeated auctions in the Real Time Bidding (RTB) ecosystem using point processes. The flexibility of the framework allows a variety of auction scenarios including configuration of information provided to player, determination of auction winner and quantification of utility gained from each auctions. We propose theoretical results on how this formulation of process can be approximated to a Poisson point process, which enables the analyzer to take advantage of well-established properties. Under this framework, we specify the player's optimal strategy under various scenarios. We also emphasize that it is critical to consider the joint distribution of utility and market condition instead of estimating the marginal distributions independently.
Addressing Distribution Shift in RTB Markets via Exponential Tilting
Aug 14, 2023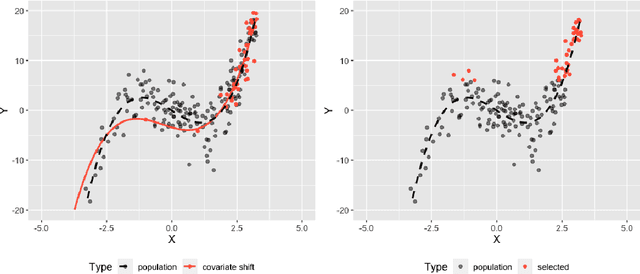
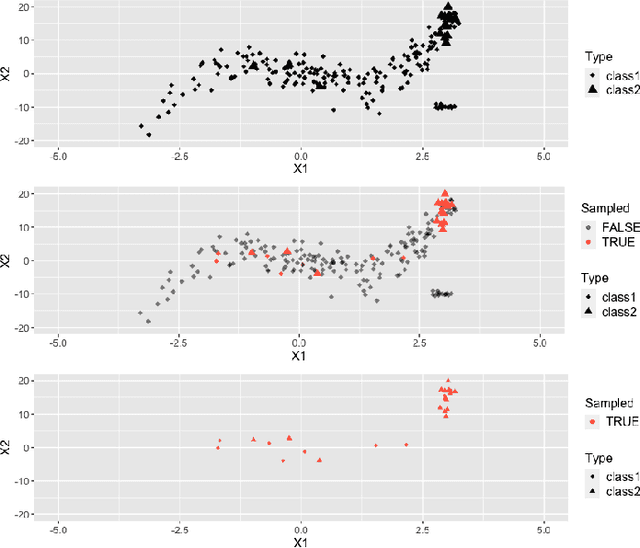
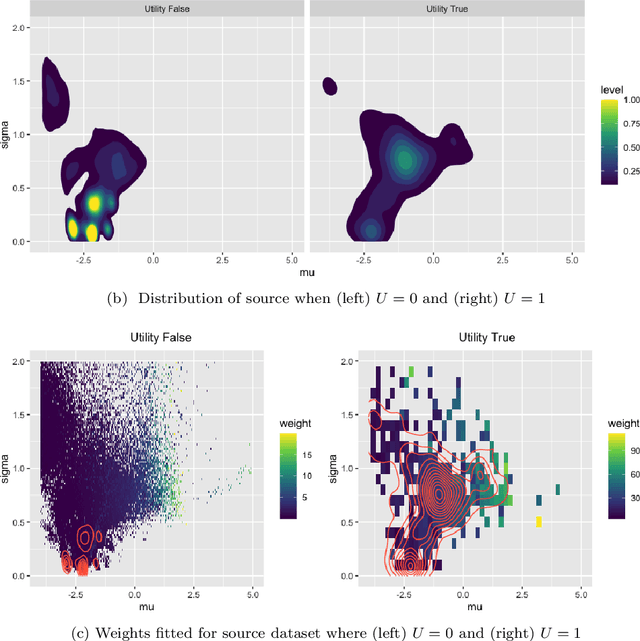
Abstract:Distribution shift in machine learning models can be a primary cause of performance degradation. This paper delves into the characteristics of these shifts, primarily motivated by Real-Time Bidding (RTB) market models. We emphasize the challenges posed by class imbalance and sample selection bias, both potent instigators of distribution shifts. This paper introduces the Exponential Tilt Reweighting Alignment (ExTRA) algorithm, as proposed by Marty et al. (2023), to address distribution shifts in data. The ExTRA method is designed to determine the importance weights on the source data, aiming to minimize the KL divergence between the weighted source and target datasets. A notable advantage of this method is its ability to operate using labeled source data and unlabeled target data. Through simulated real-world data, we investigate the nature of distribution shift and evaluate the applicacy of the proposed model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge