Sebastien Deschamps
Frugal Satellite Image Change Detection with Deep-Net Inversion
Sep 26, 2023

Abstract:Change detection in satellite imagery seeks to find occurrences of targeted changes in a given scene taken at different instants. This task has several applications ranging from land-cover mapping, to anthropogenic activity monitory as well as climate change and natural hazard damage assessment. However, change detection is highly challenging due to the acquisition conditions and also to the subjectivity of changes. In this paper, we devise a novel algorithm for change detection based on active learning. The proposed method is based on a question and answer model that probes an oracle (user) about the relevance of changes only on a small set of critical images (referred to as virtual exemplars), and according to oracle's responses updates deep neural network (DNN) classifiers. The main contribution resides in a novel adversarial model that allows learning the most representative, diverse and uncertain virtual exemplars (as inverted preimages of the trained DNNs) that challenge (the most) the trained DNNs, and this leads to a better re-estimate of these networks in the subsequent iterations of active learning. Experiments show the out-performance of our proposed deep-net inversion against the related work.
Adversarial Virtual Exemplar Learning for Label-Frugal Satellite Image Change Detection
Dec 28, 2022

Abstract:Satellite image change detection aims at finding occurrences of targeted changes in a given scene taken at different instants. This task is highly challenging due to the acquisition conditions and also to the subjectivity of changes. In this paper, we investigate satellite image change detection using active learning. Our method is interactive and relies on a question and answer model which asks the oracle (user) questions about the most informative display (dubbed as virtual exemplars), and according to the user's responses, updates change detections. The main contribution of our method consists in a novel adversarial model that allows frugally probing the oracle with only the most representative, diverse and uncertain virtual exemplars. The latter are learned to challenge the most the trained change decision criteria which ultimately leads to a better re-estimate of these criteria in the following iterations of active learning. Conducted experiments show the out-performance of our proposed adversarial display model against other display strategies as well as the related work.
Frugal Reinforcement-based Active Learning
Dec 09, 2022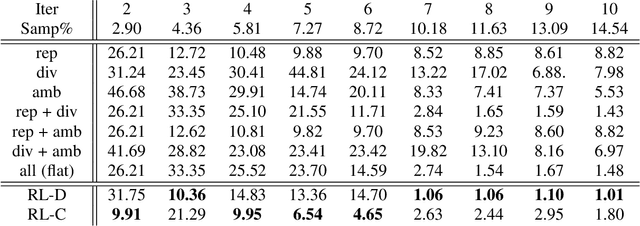

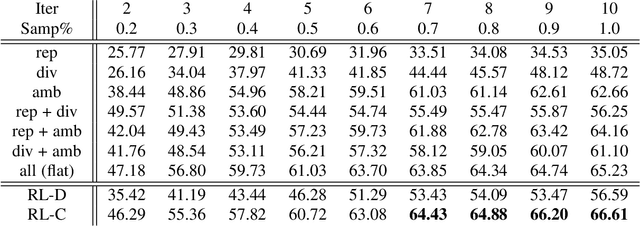

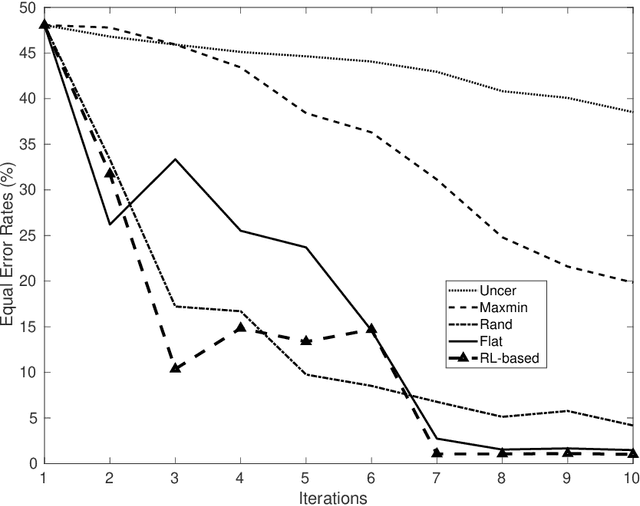
Abstract:Most of the existing learning models, particularly deep neural networks, are reliant on large datasets whose hand-labeling is expensive and time demanding. A current trend is to make the learning of these models frugal and less dependent on large collections of labeled data. Among the existing solutions, deep active learning is currently witnessing a major interest and its purpose is to train deep networks using as few labeled samples as possible. However, the success of active learning is highly dependent on how critical are these samples when training models. In this paper, we devise a novel active learning approach for label-efficient training. The proposed method is iterative and aims at minimizing a constrained objective function that mixes diversity, representativity and uncertainty criteria. The proposed approach is probabilistic and unifies all these criteria in a single objective function whose solution models the probability of relevance of samples (i.e., how critical) when learning a decision function. We also introduce a novel weighting mechanism based on reinforcement learning, which adaptively balances these criteria at each training iteration, using a particular stateless Q-learning model. Extensive experiments conducted on staple image classification data, including Object-DOTA, show the effectiveness of our proposed model w.r.t. several baselines including random, uncertainty and flat as well as other work.
Reinforcement-based frugal learning for satellite image change detection
Mar 22, 2022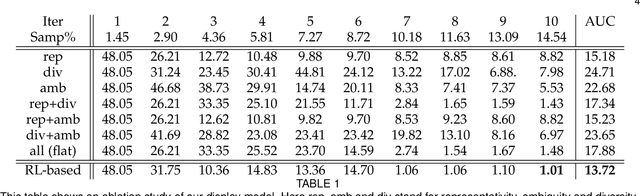
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel interactive satellite image change detection algorithm based on active learning. The proposed approach is iterative and asks the user (oracle) questions about the targeted changes and according to the oracle's responses updates change detections. We consider a probabilistic framework which assigns to each unlabeled sample a relevance measure modeling how critical is that sample when training change detection functions. These relevance measures are obtained by minimizing an objective function mixing diversity, representativity and uncertainty. These criteria when combined allow exploring different data modes and also refining change detections. To further explore the potential of this objective function, we consider a reinforcement learning approach that finds the best combination of diversity, representativity and uncertainty, through active learning iterations, leading to better generalization as corroborated through experiments in interactive satellite image change detection.
Frugal Learning of Virtual Exemplars for Label-Efficient Satellite Image Change Detection
Mar 22, 2022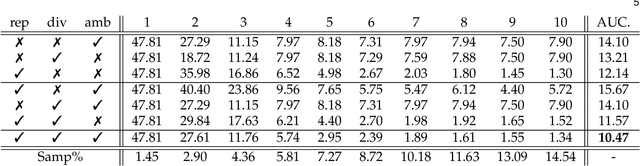
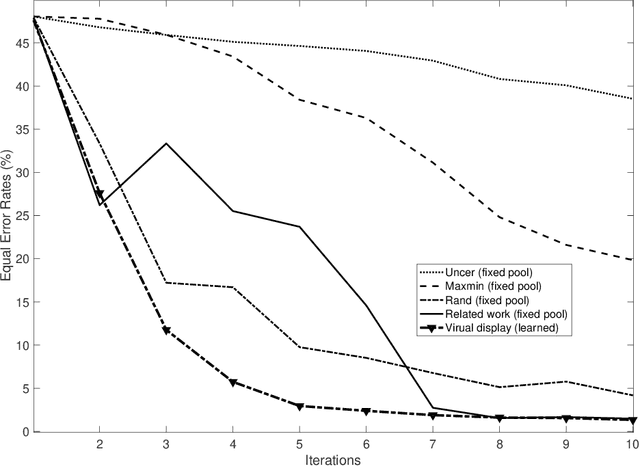
Abstract:In this paper, we devise a novel interactive satellite image change detection algorithm based on active learning. The proposed framework is iterative and relies on a question and answer model which asks the oracle (user) questions about the most informative display (subset of critical images), and according to the user's responses, updates change detections. The contribution of our framework resides in a novel display model which selects the most representative and diverse virtual exemplars that adversely challenge the learned change detection functions, thereby leading to highly discriminating functions in the subsequent iterations of active learning. Extensive experiments, conducted on the challenging task of interactive satellite image change detection, show the superiority of the proposed virtual display model against the related work.
Active learning for interactive satellite image change detection
Oct 08, 2021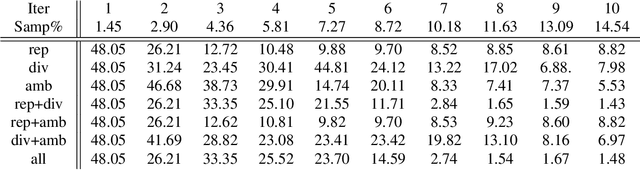
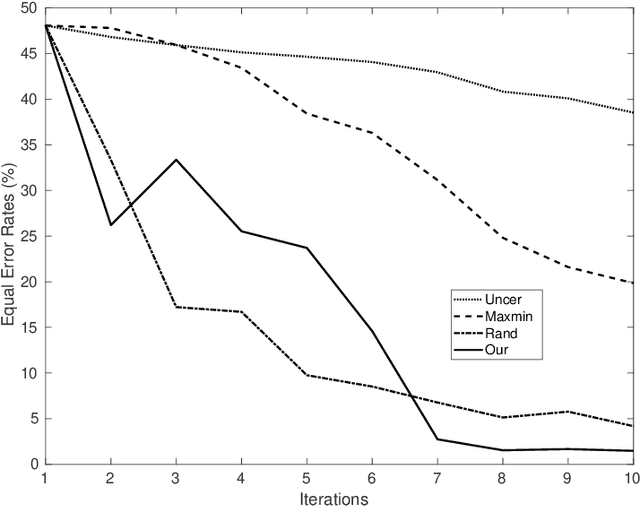
Abstract:We introduce in this paper a novel active learning algorithm for satellite image change detection. The proposed solution is interactive and based on a question and answer model, which asks an oracle (annotator) the most informative questions about the relevance of sampled satellite image pairs, and according to the oracle's responses, updates a decision function iteratively. We investigate a novel framework which models the probability that samples are relevant; this probability is obtained by minimizing an objective function capturing representativity, diversity and ambiguity. Only data with a high probability according to these criteria are selected and displayed to the oracle for further annotation. Extensive experiments on the task of satellite image change detection after natural hazards (namely tornadoes) show the relevance of the proposed method against the related work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge