Sebastian Dunzer
Recent Advances in Data-Driven Business Process Management
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:The rapid development of cutting-edge technologies, the increasing volume of data and also the availability and processability of new types of data sources has led to a paradigm shift in data-based management and decision-making. Since business processes are at the core of organizational work, these developments heavily impact BPM as a crucial success factor for organizations. In view of this emerging potential, data-driven business process management has become a relevant and vibrant research area. Given the complexity and interdisciplinarity of the research field, this position paper therefore presents research insights regarding data-driven BPM.
Machine learning in business process management: A systematic literature review
May 26, 2024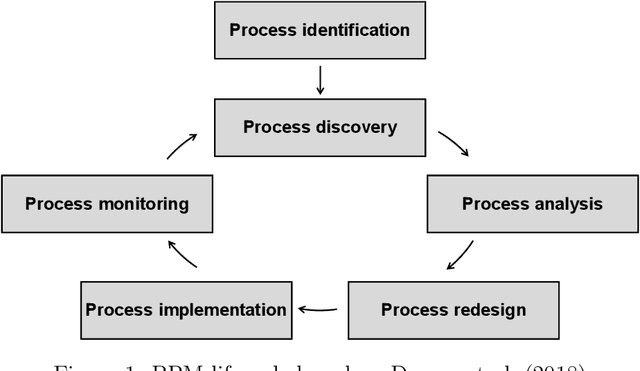
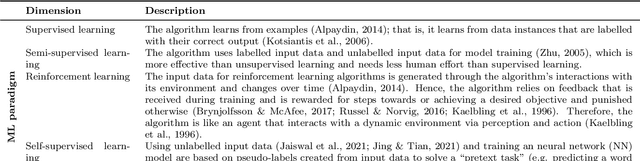
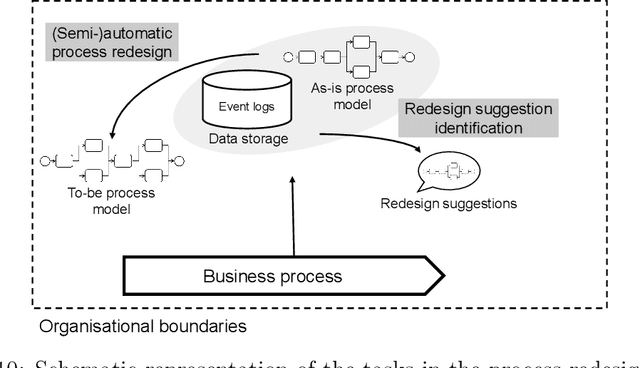
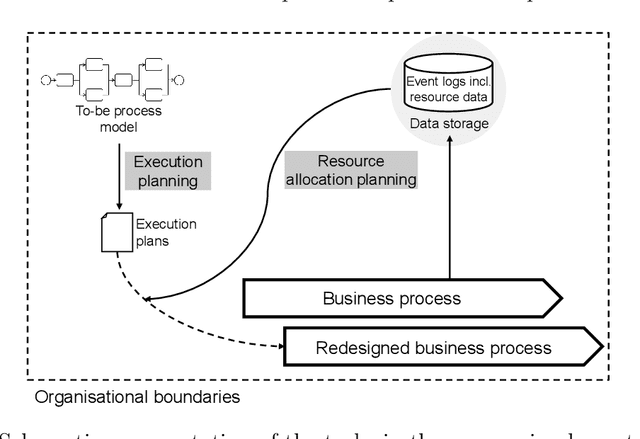
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) provides algorithms to create computer programs based on data without explicitly programming them. In business process management (BPM), ML applications are used to analyse and improve processes efficiently. Three frequent examples of using ML are providing decision support through predictions, discovering accurate process models, and improving resource allocation. This paper organises the body of knowledge on ML in BPM. We extract BPM tasks from different literature streams, summarise them under the phases of a process`s lifecycle, explain how ML helps perform these tasks and identify technical commonalities in ML implementations across tasks. This study is the first exhaustive review of how ML has been used in BPM. We hope that it can open the door for a new era of cumulative research by helping researchers to identify relevant preliminary work and then combine and further develop existing approaches in a focused fashion. Our paper helps managers and consultants to find ML applications that are relevant in the current project phase of a BPM initiative, like redesigning a business process. We also offer - as a synthesis of our review - a research agenda that spreads ten avenues for future research, including applying novel ML concepts like federated learning, addressing less regarded BPM lifecycle phases like process identification, and delivering ML applications with a focus on end-users.
Prescriptive Business Process Monitoring for Recommending Next Best Actions
Aug 19, 2020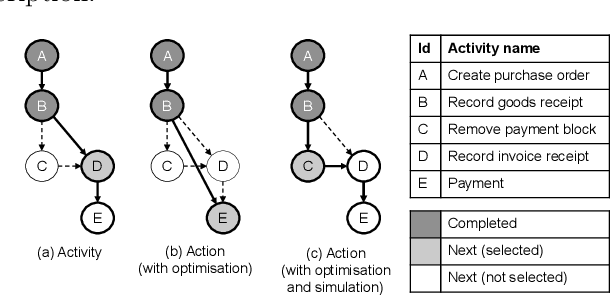
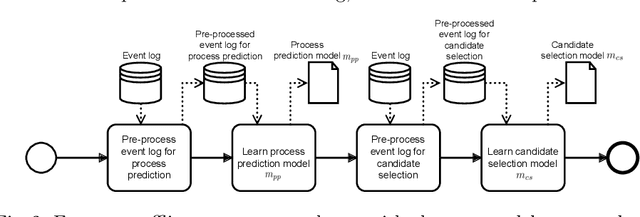
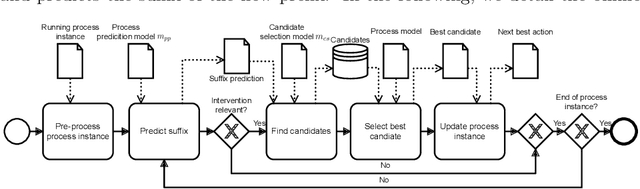
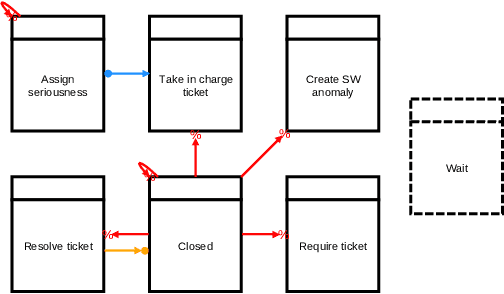
Abstract:Predictive business process monitoring (PBPM) techniques predict future process behaviour based on historical event log data to improve operational business processes. Concerning the next activity prediction, recent PBPM techniques use state-of-the-art deep neural networks (DNNs) to learn predictive models for producing more accurate predictions in running process instances. Even though organisations measure process performance by key performance indicators (KPIs), the DNN`s learning procedure is not directly affected by them. Therefore, the resulting next most likely activity predictions can be less beneficial in practice. Prescriptive business process monitoring (PrBPM) approaches assess predictions regarding their impact on the process performance (typically measured by KPIs) to prevent undesired process activities by raising alarms or recommending actions. However, none of these approaches recommends actual process activities as actions that are optimised according to a given KPI. We present a PrBPM technique that transforms the next most likely activities into the next best actions regarding a given KPI. Thereby, our technique uses business process simulation to ensure the control-flow conformance of the recommended actions. Based on our evaluation with two real-life event logs, we show that our technique`s next best actions can outperform next activity predictions regarding the optimisation of a KPI and the distance from the actual process instances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge