Sara Latifi
Session-aware Recommendation: A Surprising Quest for the State-of-the-art
Nov 06, 2020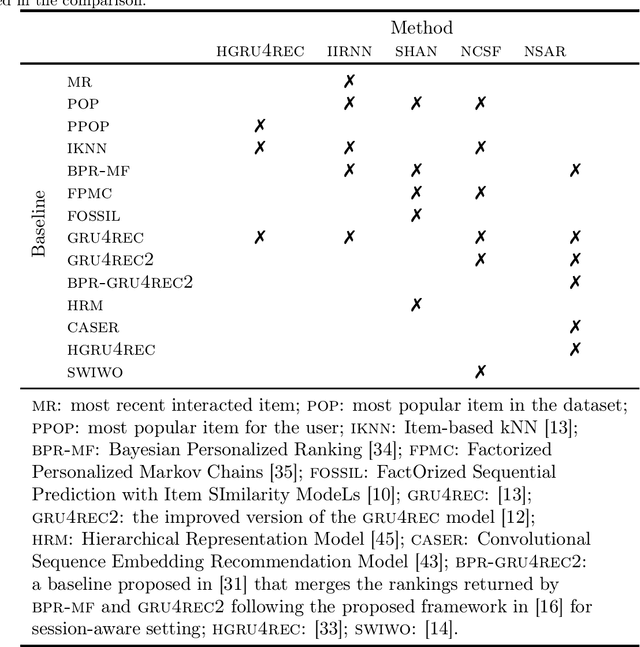
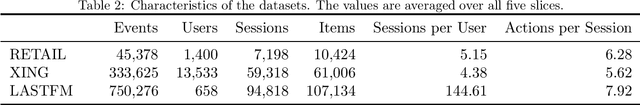
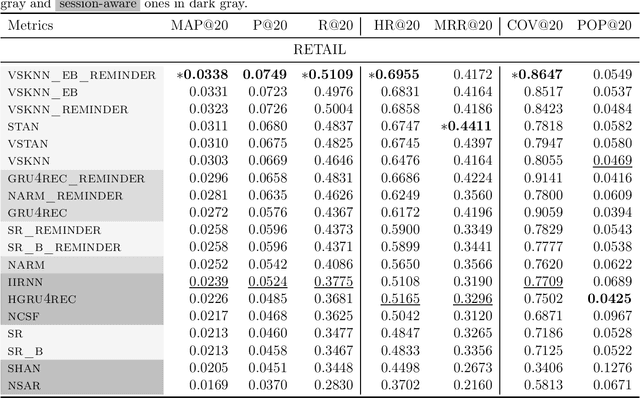
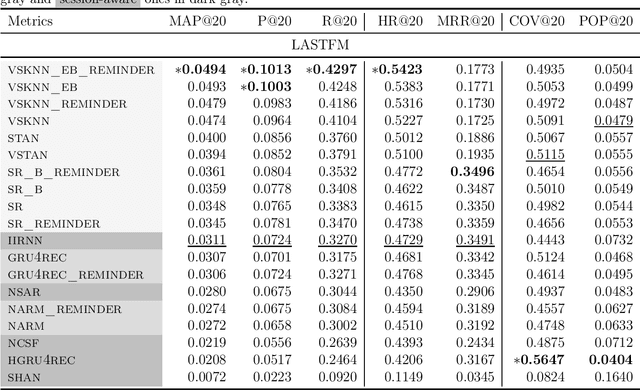
Abstract:Recommender systems are designed to help users in situations of information overload. In recent years, we observed increased interest in session-based recommendation scenarios, where the problem is to make item suggestions to users based only on interactions observed in an ongoing session. However, in cases where interactions from previous user sessions are available, the recommendations can be personalized according to the users' long-term preferences, a process called session-aware recommendation. Today, research in this area is scattered and many existing works only compare session-aware with session-based models. This makes it challenging to understand what represents the state-of-the-art. To close this research gap, we benchmarked recent session-aware algorithms against each other and against a number of session-based recommendation algorithms and trivial extensions thereof. Our comparison, to some surprise, revealed that (i) item simple techniques based on nearest neighbors consistently outperform recent neural techniques and that (ii) session-aware models were mostly not better than approaches that do not use long-term preference information. Our work therefore not only points to potential methodological issues where new methods are compared to weak baselines, but also indicates that there remains a huge potential for more sophisticated session-aware recommendation algorithms.
Empirical Analysis of Session-Based Recommendation Algorithms
Oct 28, 2019
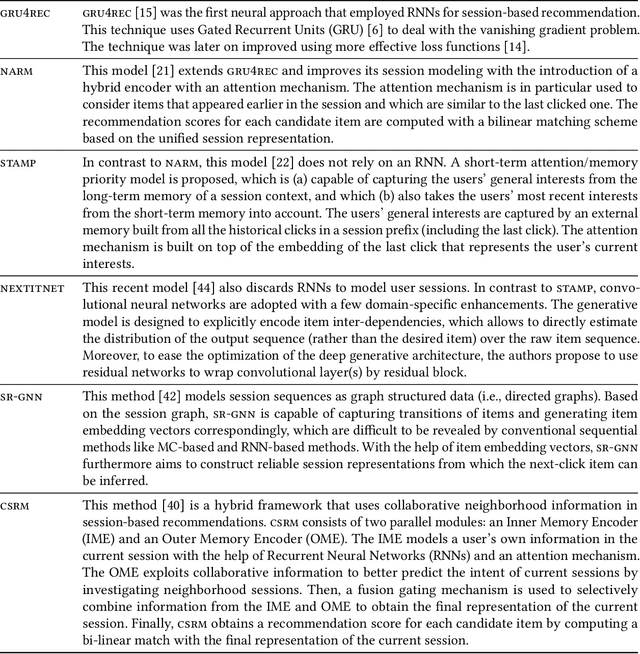
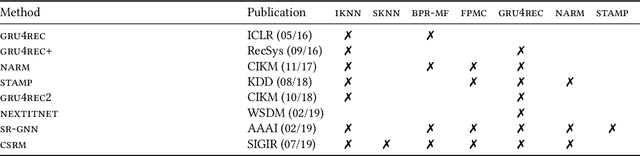
Abstract:Recommender systems are tools that support online users by pointing them to potential items of interest in situations of information overload. In recent years, the class of session-based recommendation algorithms received more attention in the research literature. These algorithms base their recommendations solely on the observed interactions with the user in an ongoing session and do not require the existence of long-term preference profiles. Most recently, a number of deep learning based ("neural") approaches to session-based recommendations were proposed. However, previous research indicates that today's complex neural recommendation methods are not always better than comparably simple algorithms in terms of prediction accuracy. With this work, our goal is to shed light on the state-of-the-art in the area of session-based recommendation and on the progress that is made with neural approaches. For this purpose, we compare twelve algorithmic approaches, among them six recent neural methods, under identical conditions on various datasets. We find that the progress in terms of prediction accuracy that is achieved with neural methods is still limited. In most cases, our experiments show that simple heuristic methods based on nearest-neighbors schemes are preferable over conceptually and computationally more complex methods. Observations from a user study furthermore indicate that recommendations based on heuristic methods were also well accepted by the study participants. To support future progress and reproducibility in this area, we publicly share the session-rec evaluation framework that was used in our research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge