Sang Hyun Lee
Machine Learning-Aided Cooperative Localization under Dense Urban Environment
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:Future wireless network technology provides automobiles with the connectivity feature to consolidate the concept of vehicular networks that collaborate on conducting cooperative driving tasks. The full potential of connected vehicles, which promises road safety and quality driving experience, can be leveraged if machine learning models guarantee the robustness in performing core functions including localization and controls. Location awareness, in particular, lends itself to the deployment of location-specific services and the improvement of the operation performance. The localization entails direct communication to the network infrastructure, and the resulting centralized positioning solutions readily become intractable as the network scales up. As an alternative to the centralized solutions, this article addresses decentralized principle of vehicular localization reinforced by machine learning techniques in dense urban environments with frequent inaccessibility to reliable measurement. As such, the collaboration of multiple vehicles enhances the positioning performance of machine learning approaches. A virtual testbed is developed to validate this machine learning model for real-map vehicular networks. Numerical results demonstrate universal feasibility of cooperative localization, in particular, for dense urban area configurations.
Learning Autonomy in Management of Wireless Random Networks
Jun 15, 2021

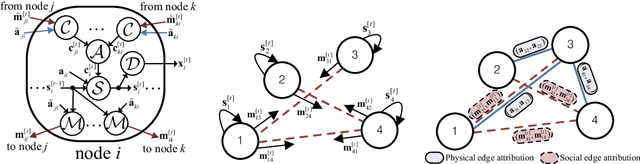

Abstract:This paper presents a machine learning strategy that tackles a distributed optimization task in a wireless network with an arbitrary number of randomly interconnected nodes. Individual nodes decide their optimal states with distributed coordination among other nodes through randomly varying backhaul links. This poses a technical challenge in distributed universal optimization policy robust to a random topology of the wireless network, which has not been properly addressed by conventional deep neural networks (DNNs) with rigid structural configurations. We develop a flexible DNN formalism termed distributed message-passing neural network (DMPNN) with forward and backward computations independent of the network topology. A key enabler of this approach is an iterative message-sharing strategy through arbitrarily connected backhaul links. The DMPNN provides a convergent solution for iterative coordination by learning numerous random backhaul interactions. The DMPNN is investigated for various configurations of the power control in wireless networks, and intensive numerical results prove its universality and viability over conventional optimization and DNN approaches.
A Deep Learning Approach to Universal Binary Visible Light Communication Transceiver
Oct 26, 2019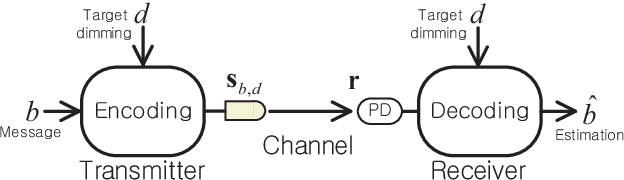



Abstract:This paper studies a deep learning (DL) framework for the design of binary modulated visible light communication (VLC) transceiver with universal dimming support. The dimming control for the optical binary signal boils down to a combinatorial codebook design so that the average Hamming weight of binary codewords matches with arbitrary dimming target. An unsupervised DL technique is employed for obtaining a neural network to replace the encoder-decoder pair that recovers the message from the optically transmitted signal. In such a task, a novel stochastic binarization method is developed to generate the set of binary codewords from continuous-valued neural network outputs. For universal support of arbitrary dimming target, the DL-based VLC transceiver is trained with multiple dimming constraints, which turns out to be a constrained training optimization that is very challenging to handle with existing DL methods. We develop a new training algorithm that addresses the dimming constraints through a dual formulation of the optimization. Based on the developed algorithm, the resulting VLC transceiver can be optimized via the end-to-end training procedure. Numerical results verify that the proposed codebook outperforms theoretically best constant weight codebooks under various VLC setups.
Deep Learning for Distributed Optimization: Applications to Wireless Resource Management
May 31, 2019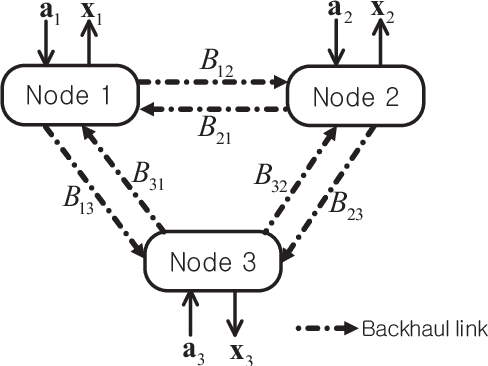
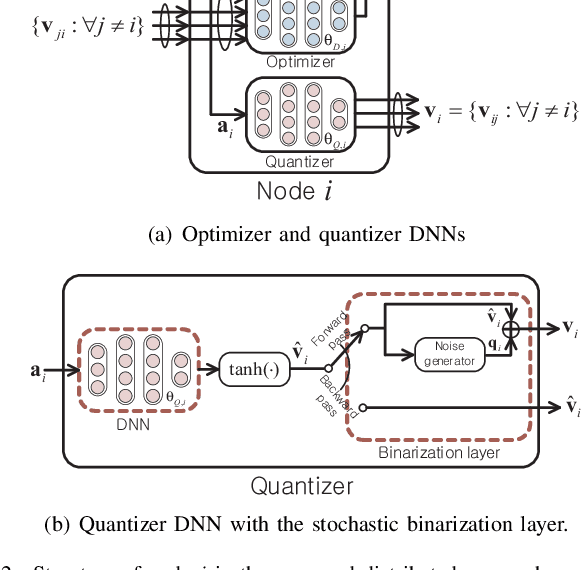
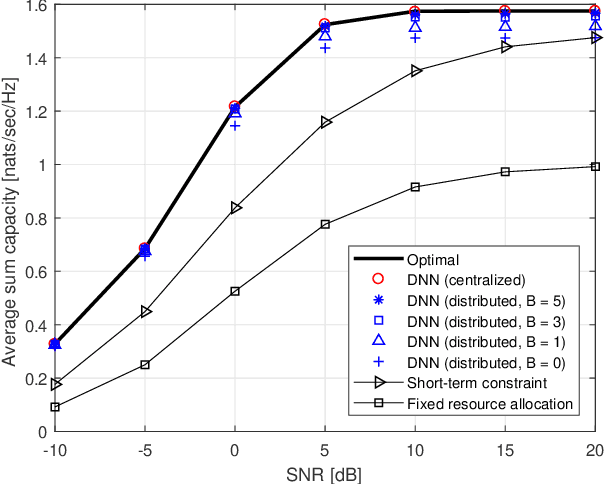
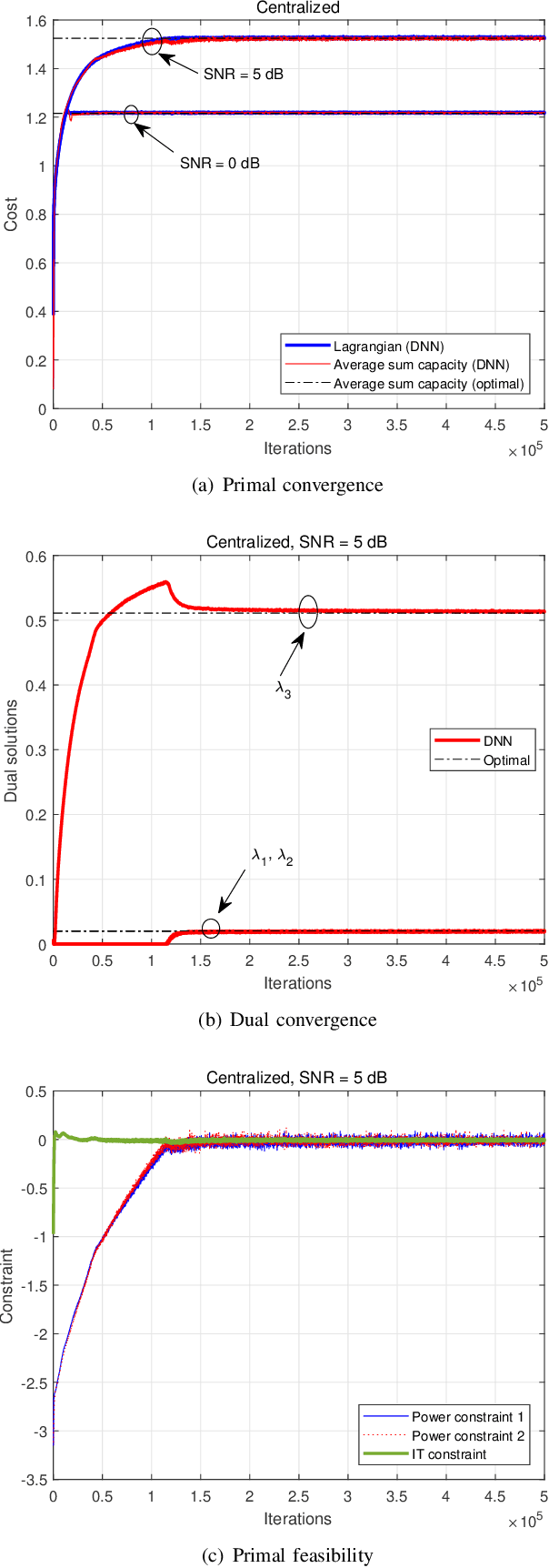
Abstract:This paper studies a deep learning (DL) framework to solve distributed non-convex constrained optimizations in wireless networks where multiple computing nodes, interconnected via backhaul links, desire to determine an efficient assignment of their states based on local observations. Two different configurations are considered: First, an infinite-capacity backhaul enables nodes to communicate in a lossless way, thereby obtaining the solution by centralized computations. Second, a practical finite-capacity backhaul leads to the deployment of distributed solvers equipped along with quantizers for communication through capacity-limited backhaul. The distributed nature and the nonconvexity of the optimizations render the identification of the solution unwieldy. To handle them, deep neural networks (DNNs) are introduced to approximate an unknown computation for the solution accurately. In consequence, the original problems are transformed to training tasks of the DNNs subject to non-convex constraints where existing DL libraries fail to extend straightforwardly. A constrained training strategy is developed based on the primal-dual method. For distributed implementation, a novel binarization technique at the output layer is developed for quantization at each node. Our proposed distributed DL framework is examined in various network configurations of wireless resource management. Numerical results verify the effectiveness of our proposed approach over existing optimization techniques.
Deep Learning Framework for Wireless Systems: Applications to Optical Wireless Communications
Dec 13, 2018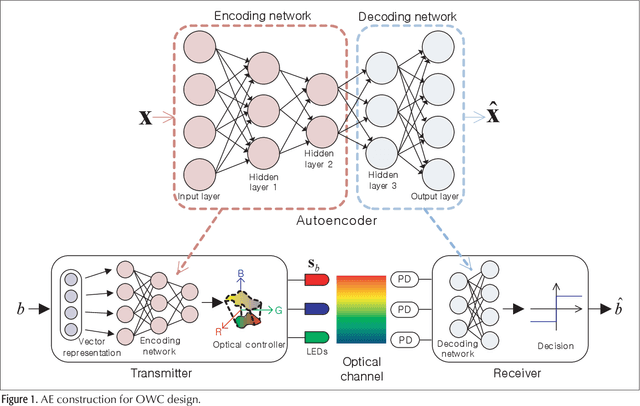
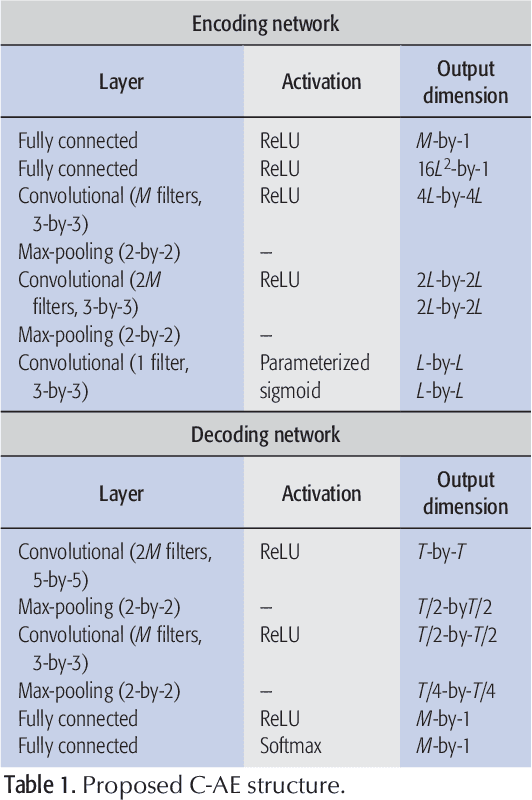
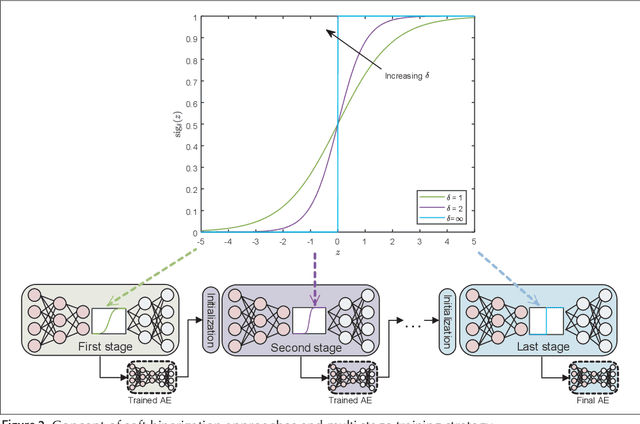
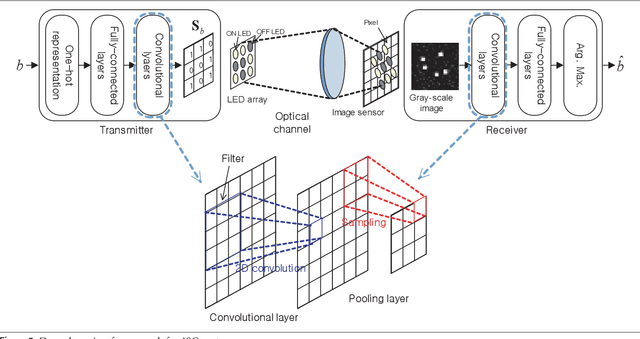
Abstract:Optical wireless communication (OWC) is a promising technology for future wireless communications owing to its potentials for cost-effective network deployment and high data rate. There are several implementation issues in the OWC which have not been encountered in radio frequency wireless communications. First, practical OWC transmitters need an illumination control on color, intensity, and luminance, etc., which poses complicated modulation design challenges. Furthermore, signal-dependent properties of optical channels raise non-trivial challenges both in modulation and demodulation of the optical signals. To tackle such difficulties, deep learning (DL) technologies can be applied for optical wireless transceiver design. This article addresses recent efforts on DL-based OWC system designs. A DL framework for emerging image sensor communication is proposed and its feasibility is verified by simulation. Finally, technical challenges and implementation issues for the DL-based optical wireless technology are discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge