Samuel Homiller
Challenges for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in Particle Physics
Oct 13, 2021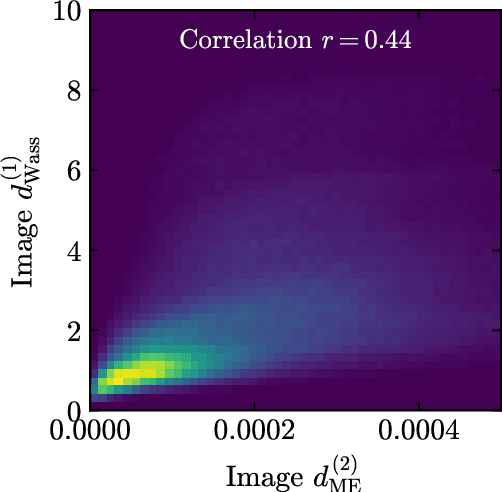
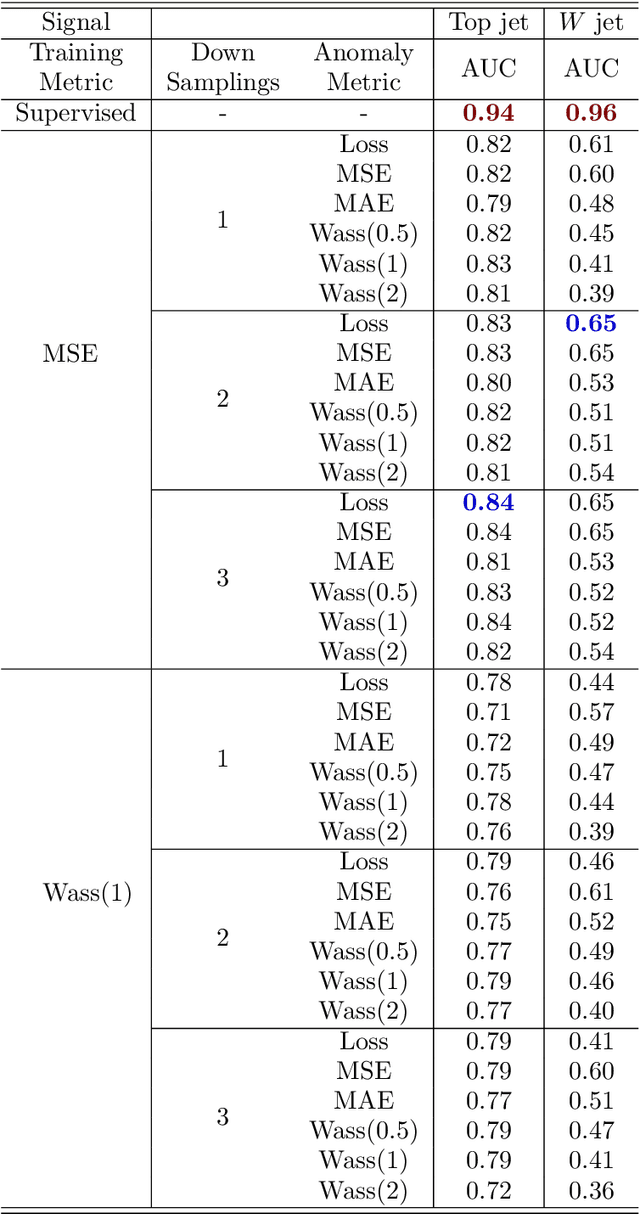
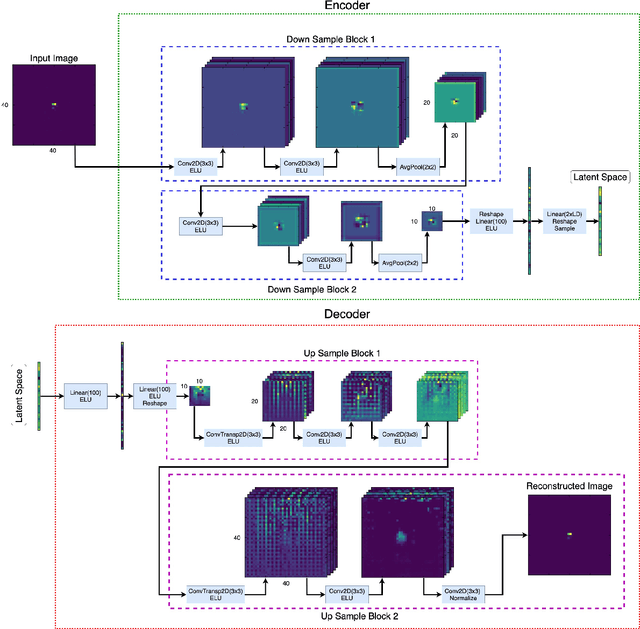
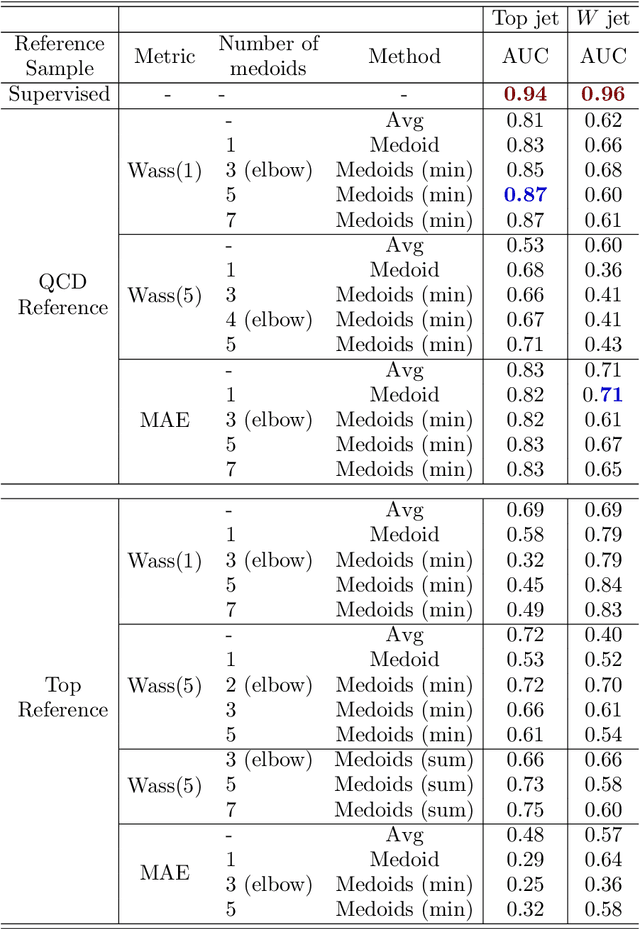
Abstract:Anomaly detection relies on designing a score to determine whether a particular event is uncharacteristic of a given background distribution. One way to define a score is to use autoencoders, which rely on the ability to reconstruct certain types of data (background) but not others (signals). In this paper, we study some challenges associated with variational autoencoders, such as the dependence on hyperparameters and the metric used, in the context of anomalous signal (top and $W$) jets in a QCD background. We find that the hyperparameter choices strongly affect the network performance and that the optimal parameters for one signal are non-optimal for another. In exploring the networks, we uncover a connection between the latent space of a variational autoencoder trained using mean-squared-error and the optimal transport distances within the dataset. We then show that optimal transport distances to representative events in the background dataset can be used directly for anomaly detection, with performance comparable to the autoencoders. Whether using autoencoders or optimal transport distances for anomaly detection, we find that the choices that best represent the background are not necessarily best for signal identification. These challenges with unsupervised anomaly detection bolster the case for additional exploration of semi-supervised or alternative approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge