Sam B. Tran
Transparency strategy-based data augmentation for BI-RADS classification of mammograms
Mar 20, 2022
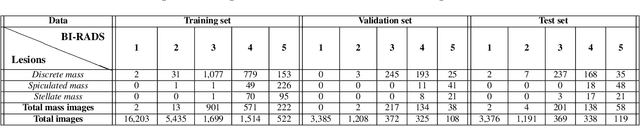
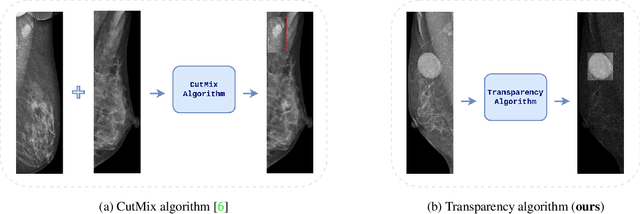
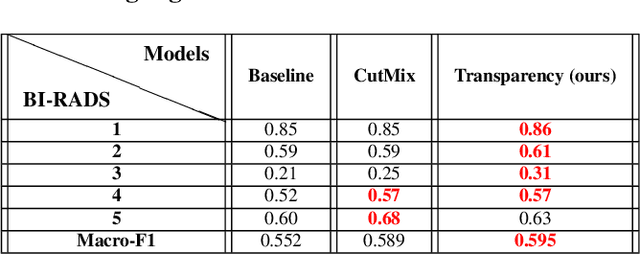
Abstract:Image augmentation techniques have been widely investigated to improve the performance of deep learning (DL) algorithms on mammography classification tasks. Recent methods have proved the efficiency of image augmentation on data deficiency or data imbalance issues. In this paper, we propose a novel transparency strategy to boost the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) scores of mammograms classifier. The proposed approach utilizes the Region of Interest (ROI) information to generate more high-risk training examples from original images. Our extensive experiments were conducted on our benchmark mammography dataset. The experiment results show that the proposed approach surpasses current state-of-the-art data augmentation techniques such as Upsampling or CutMix. The study highlights that the transparency method is more effective than other augmentation strategies for BI-RADS classification and can be widely applied for our computer vision tasks.
A novel multi-view deep learning approach for BI-RADS and density assessment of mammograms
Dec 08, 2021



Abstract:Advanced deep learning (DL) algorithms may predict the patient's risk of developing breast cancer based on the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) and density standards. Recent studies have suggested that the combination of multi-view analysis improved the overall breast exam classification. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-view DL approach for BI-RADS and density assessment of mammograms. The proposed approach first deploys deep convolutional networks for feature extraction on each view separately. The extracted features are then stacked and fed into a Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM) classifier to predict BI-RADS and density scores. We conduct extensive experiments on both the internal mammography dataset and the public dataset Digital Database for Screening Mammography (DDSM). The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms the single-view classification approach on two benchmark datasets by huge margins (5% on the internal dataset and 10% on the DDSM dataset). These results highlight the vital role of combining multi-view information to improve the performance of breast cancer risk prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge