Saja AL-Tawalbeh
Towards the Characterization of Representations Learned via Capsule-based Network Architectures
May 09, 2023Abstract:Capsule Networks (CapsNets) have been re-introduced as a more compact and interpretable alternative to standard deep neural networks. While recent efforts have proved their compression capabilities, to date, their interpretability properties have not been fully assessed. Here, we conduct a systematic and principled study towards assessing the interpretability of these types of networks. Moreover, we pay special attention towards analyzing the level to which part-whole relationships are indeed encoded within the learned representation. Our analysis in the MNIST, SVHN, PASCAL-part and CelebA datasets suggest that the representations encoded in CapsNets might not be as disentangled nor strictly related to parts-whole relationships as is commonly stated in the literature.
A Benchmark Arabic Dataset for Commonsense Explanation
Dec 18, 2020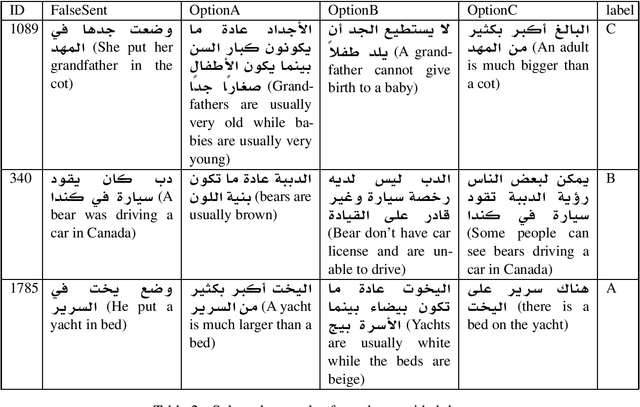
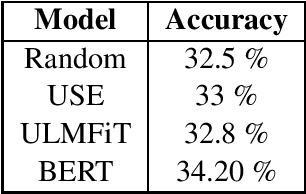
Abstract:Language comprehension and commonsense knowledge validation by machines are challenging tasks that are still under researched and evaluated for Arabic text. In this paper, we present a benchmark Arabic dataset for commonsense explanation. The dataset consists of Arabic sentences that does not make sense along with three choices to select among them the one that explains why the sentence is false. Furthermore, this paper presents baseline results to assist and encourage the future evaluation of research in this field. The dataset is distributed under the Creative Commons CC-BY-SA 4.0 license and can be found on GitHub
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge