S. M. Kamruzzaman
The Most Advantageous Bangla Keyboard Layout Using Data Mining Technique
Sep 26, 2010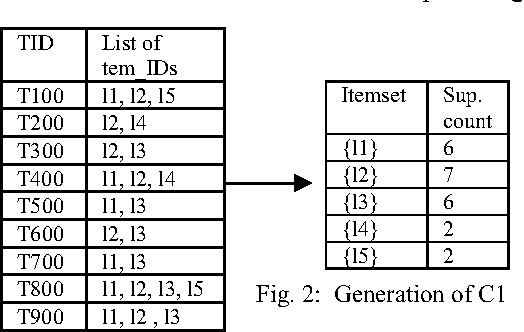
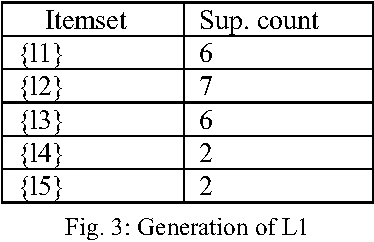
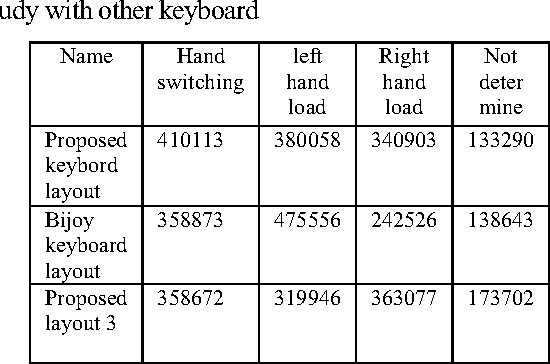
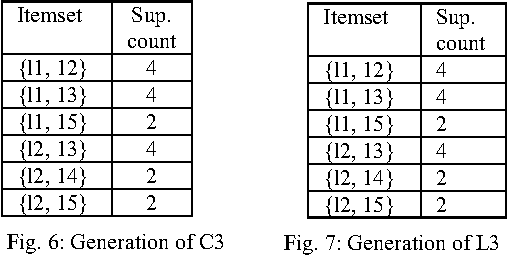
Abstract:Bangla alphabet has a large number of letters, for this it is complicated to type faster using Bangla keyboard. The proposed keyboard will maximize the speed of operator as they can type with both hands parallel. Association rule of data mining to distribute the Bangla characters in the keyboard is used here. The frequencies of data consisting of monograph, digraph and trigraph are analyzed, which are derived from data wire-house, and then used association rule of data mining to distribute the Bangla characters in the layout. Experimental results on several data show the effectiveness of the proposed approach with better performance. This paper presents an optimal Bangla Keyboard Layout, which distributes the load equally on both hands so that maximizing the ease and minimizing the effort.
* 10 Pages, International Journal
Web Page Categorization Using Artificial Neural Networks
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:Web page categorization is one of the challenging tasks in the world of ever increasing web technologies. There are many ways of categorization of web pages based on different approach and features. This paper proposes a new dimension in the way of categorization of web pages using artificial neural network (ANN) through extracting the features automatically. Here eight major categories of web pages have been selected for categorization; these are business & economy, education, government, entertainment, sports, news & media, job search, and science. The whole process of the proposed system is done in three successive stages. In the first stage, the features are automatically extracted through analyzing the source of the web pages. The second stage includes fixing the input values of the neural network; all the values remain between 0 and 1. The variations in those values affect the output. Finally the third stage determines the class of a certain web page out of eight predefined classes. This stage is done using back propagation algorithm of artificial neural network. The proposed concept will facilitate web mining, retrievals of information from the web and also the search engines.
* 4 Pages, International Conference
REx: An Efficient Rule Generator
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:This paper describes an efficient algorithm REx for generating symbolic rules from artificial neural network (ANN). Classification rules are sought in many areas from automatic knowledge acquisition to data mining and ANN rule extraction. This is because classification rules possess some attractive features. They are explicit, understandable and verifiable by domain experts, and can be modified, extended and passed on as modular knowledge. REx exploits the first order information in the data and finds shortest sufficient conditions for a rule of a class that can differentiate it from patterns of other classes. It can generate concise and perfect rules in the sense that the error rate of the rules is not worse than the inconsistency rate found in the original data. An important feature of rule extraction algorithm, REx, is its recursive nature. They are concise, comprehensible, order insensitive and do not involve any weight values. Extensive experimental studies on several benchmark classification problems, such as breast cancer, iris, season, and golf-playing, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach with good generalization ability.
* 4 Pages, International Conference
Rule Extraction using Artificial Neural Networks
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:Artificial neural networks have been successfully applied to a variety of business application problems involving classification and regression. Although backpropagation neural networks generally predict better than decision trees do for pattern classification problems, they are often regarded as black boxes, i.e., their predictions are not as interpretable as those of decision trees. In many applications, it is desirable to extract knowledge from trained neural networks so that the users can gain a better understanding of the solution. This paper presents an efficient algorithm to extract rules from artificial neural networks. We use two-phase training algorithm for backpropagation learning. In the first phase, the number of hidden nodes of the network is determined automatically in a constructive fashion by adding nodes one after another based on the performance of the network on training data. In the second phase, the number of relevant input units of the network is determined using pruning algorithm. The pruning process attempts to eliminate as many connections as possible from the network. Relevant and irrelevant attributes of the data are distinguished during the training process. Those that are relevant will be kept and others will be automatically discarded. From the simplified networks having small number of connections and nodes we may easily able to extract symbolic rules using the proposed algorithm. Extensive experimental results on several benchmarks problems in neural networks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach with good generalization ability.
* 14 Pages, International Conference
Pattern Classification using Simplified Neural Networks
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:In recent years, many neural network models have been proposed for pattern classification, function approximation and regression problems. This paper presents an approach for classifying patterns from simplified NNs. Although the predictive accuracy of ANNs is often higher than that of other methods or human experts, it is often said that ANNs are practically "black boxes", due to the complexity of the networks. In this paper, we have an attempted to open up these black boxes by reducing the complexity of the network. The factor makes this possible is the pruning algorithm. By eliminating redundant weights, redundant input and hidden units are identified and removed from the network. Using the pruning algorithm, we have been able to prune networks such that only a few input units, hidden units and connections left yield a simplified network. Experimental results on several benchmarks problems in neural networks show the effectiveness of the proposed approach with good generalization ability.
* 7 Pages, International Conference
Optimal Bangla Keyboard Layout using Data Mining Technique
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:This paper presents an optimal Bangla Keyboard Layout, which distributes the load equally on both hands so that maximizing the ease and minimizing the effort. Bangla alphabet has a large number of letters, for this it is difficult to type faster using Bangla keyboard. Our proposed keyboard will maximize the speed of operator as they can type with both hands parallel. Here we use the association rule of data mining to distribute the Bangla characters in the keyboard. First, we analyze the frequencies of data consisting of monograph, digraph and trigraph, which are derived from data wire-house, and then used association rule of data mining to distribute the Bangla characters in the layout. Experimental results on several data show the effectiveness of the proposed approach with better performance.
* 9 Pages, International Conference
Extracting Symbolic Rules for Medical Diagnosis Problem
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:Neural networks (NNs) have been successfully applied to solve a variety of application problems involving classification and function approximation. Although backpropagation NNs generally predict better than decision trees do for pattern classification problems, they are often regarded as black boxes, i.e., their predictions cannot be explained as those of decision trees. In many applications, it is desirable to extract knowledge from trained NNs for the users to gain a better understanding of how the networks solve the problems. An algorithm is proposed and implemented to extract symbolic rules for medical diagnosis problem. Empirical study on three benchmarks classification problems, such as breast cancer, diabetes, and lenses demonstrates that the proposed algorithm generates high quality rules from NNs comparable with other methods in terms of number of rules, average number of conditions for a rule, and predictive accuracy.
* 6 Pages, International Conference
Text Classification using Association Rule with a Hybrid Concept of Naive Bayes Classifier and Genetic Algorithm
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:Text classification is the automated assignment of natural language texts to predefined categories based on their content. Text classification is the primary requirement of text retrieval systems, which retrieve texts in response to a user query, and text understanding systems, which transform text in some way such as producing summaries, answering questions or extracting data. Now a day the demand of text classification is increasing tremendously. Keeping this demand into consideration, new and updated techniques are being developed for the purpose of automated text classification. This paper presents a new algorithm for text classification. Instead of using words, word relation i.e. association rules is used to derive feature set from pre-classified text documents. The concept of Naive Bayes Classifier is then used on derived features and finally a concept of Genetic Algorithm has been added for final classification. A system based on the proposed algorithm has been implemented and tested. The experimental results show that the proposed system works as a successful text classifier.
* 6 Pages, International Conference
Rotation Invariant Face Detection Using Wavelet, PCA and Radial Basis Function Networks
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel method for human face detection with its orientation by using wavelet, principle component analysis (PCA) and redial basis networks. The input image is analyzed by two-dimensional wavelet and a two-dimensional stationary wavelet. The common goals concern are the image clearance and simplification, which are parts of de-noising or compression. We applied an effective procedure to reduce the dimension of the input vectors using PCA. Radial Basis Function (RBF) neural network is then used as a function approximation network to detect where either the input image is contained a face or not and if there is a face exists then tell about its orientation. We will show how RBF can perform well then back-propagation algorithm and give some solution for better regularization of the RBF (GRNN) network. Compared with traditional RBF networks, the proposed network demonstrates better capability of approximation to underlying functions, faster learning speed, better size of network, and high robustness to outliers.
* 5 Pages, International Conference
Speaker Identification using MFCC-Domain Support Vector Machine
Sep 25, 2010



Abstract:Speech recognition and speaker identification are important for authentication and verification in security purpose, but they are difficult to achieve. Speaker identification methods can be divided into text-independent and text-dependent. This paper presents a technique of text-dependent speaker identification using MFCC-domain support vector machine (SVM). In this work, melfrequency cepstrum coefficients (MFCCs) and their statistical distribution properties are used as features, which will be inputs to the neural network. This work firstly used sequential minimum optimization (SMO) learning technique for SVM that improve performance over traditional techniques Chunking, Osuna. The cepstrum coefficients representing the speaker characteristics of a speech segment are computed by nonlinear filter bank analysis and discrete cosine transform. The speaker identification ability and convergence speed of the SVMs are investigated for different combinations of features. Extensive experimental results on several samples show the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
* 5 Pages, International Journal
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge