S. Kumar
Random Access Procedure over Non-Terrestrial Networks: From Theory to Practice
Jun 29, 2021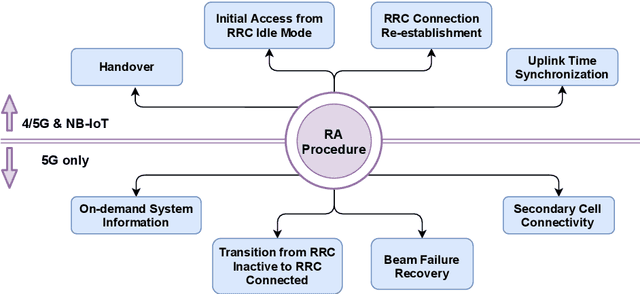
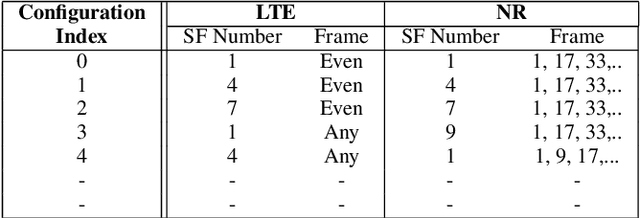
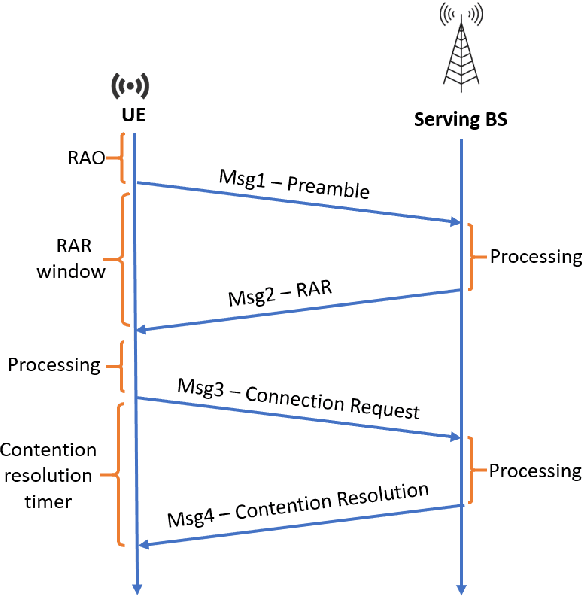
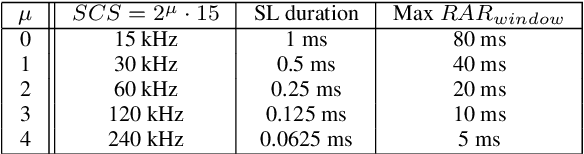
Abstract:Non-terrestrial Networks (NTNs) have become an appealing concept over the last few years and they are foreseen as a cornerstone for the next generations of mobile communication systems. Despite opening up new market opportunities and use cases for the future, the novel impairments caused by the signal propagation over the NTN channel compromises several procedures of the current cellular standards. One of the first and most important procedures impacted is the random access (RA) procedure, which is mainly utilized for achieving uplink synchronization among users in several standards, such as the fourth and fifth generation of mobile communication (4 & 5G) and narrowband internet of things (NB-IoT). In this work, we analyse the challenges imposed by the considerably increased delay in the communication link on the RA procedure and propose new solutions to overcome those challenges. A trade-off analysis of various solutions is provided taking into account also the already existing ones in the literature. In order to broaden the scope of applicability, we keep the analysis general targeting 4G, 5G and NB-IoT systems since the RA procedure is quasi-identical among these technologies. Last but not least, we go one step further and validate our techniques in an experimental setup, consisting of a user and a base station implemented in open air interface (OAI), and an NTN channel implemented in hardware that emulates the signal propagation delay. The laboratory test-bed built in this work, not only enables us to validate various solutions, but also plays a crucial role in identifying novel challenges not previously treated in the literature. Finally, an important key performance indicator (KPI) of the RA procedure over NTN is shown, which is the time that a single user requires to establish a connection with the base station.
A Hash based Approach for Secure Keyless Steganography in Lossless RGB Images
Apr 17, 2013



Abstract:This paper proposes an improved steganography approach for hiding text messages in lossless RGB images. The objective of this work is to increase the security level and to improve the storage capacity with compression techniques. The security level is increased by randomly distributing the text message over the entire image instead of clustering within specific image portions. Storage capacity is increased by utilizing all the color channels for storing information and providing the source text message compression. The degradation of the images can be minimized by changing only one least significant bit per color channel for hiding the message, incurring a very little change in the original image. Using steganography alone with simple LSB has a potential problem that the secret message is easily detectable from the histogram analysis method. To improve the security as well as the image embedding capacity indirectly, a compression based scheme is introduced. Various tests have been done to check the storage capacity and message distribution. These testes show the superiority of the proposed approach with respect to other existing approaches.
* The paper is withdrawn due to license issue
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge