J. L. Raheja
Real Time Fabric Defect Detection System on an Embedded DSP Platform
Sep 08, 2014



Abstract:In industrial fabric productions, automated real time systems are needed to find out the minor defects. It will save the cost by not transporting defected products and also would help in making compmay image of quality fabrics by sending out only undefected products. A real time fabric defect detection system (FDDS), implementd on an embedded DSP platform is presented here. Textural features of fabric image are extracted based on gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM). A sliding window technique is used for defect detection where window moves over the whole image computing a textural energy from the GLCM of the fabric image. The energy values are compared to a reference and the deviations beyond a threshold are reported as defects and also visually represented by a window. The implementation is carried out on a TI TMS320DM642 platform and programmed using code composer studio software. The real time output of this implementation was shown on a monitor.
Fingers' Angle Calculation using Level-Set Method
Jun 13, 2014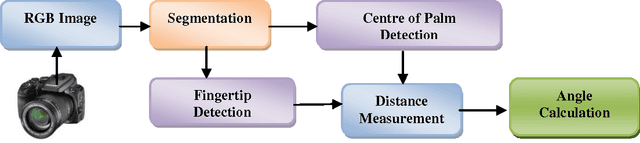


Abstract:In the current age, use of natural communication in human computer interaction is a known and well installed thought. Hand gesture recognition and gesture based applications has gained a significant amount of popularity amongst people all over the world. It has a number of applications ranging from security to entertainment. These applications generally are real time applications and need fast, accurate communication with machines. On the other end, gesture based communications have few limitations also like bent finger information is not provided in vision based techniques. In this paper, a novel method for fingertip detection and for angle calculation of both hands bent fingers is discussed. Angle calculation has been done before with sensor based gloves/devices. This study has been conducted in the context of natural computing for calculating angles without using any wired equipment, colors, marker or any device. The pre-processing and segmentation of the region of interest is performed in a HSV color space and a binary format respectively. Fingertips are detected using level-set method and angles were calculated using geometrical analysis. This technique requires no training for system to perform the task.
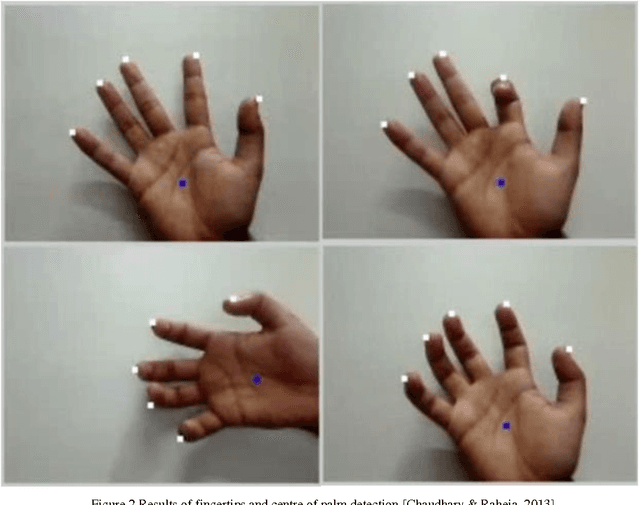
Tracking of Fingertips and Centres of Palm using KINECT
Apr 17, 2013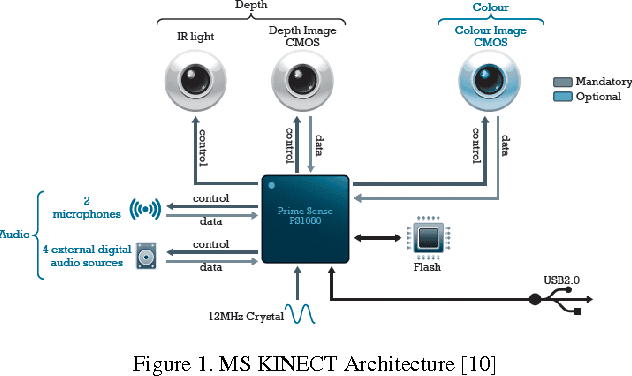
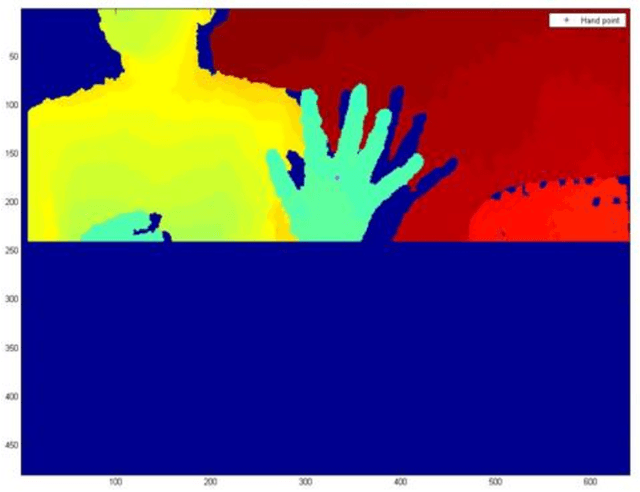
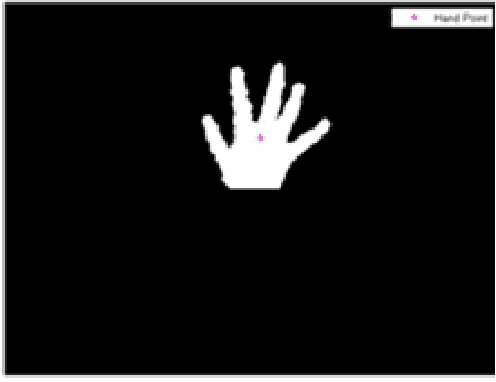
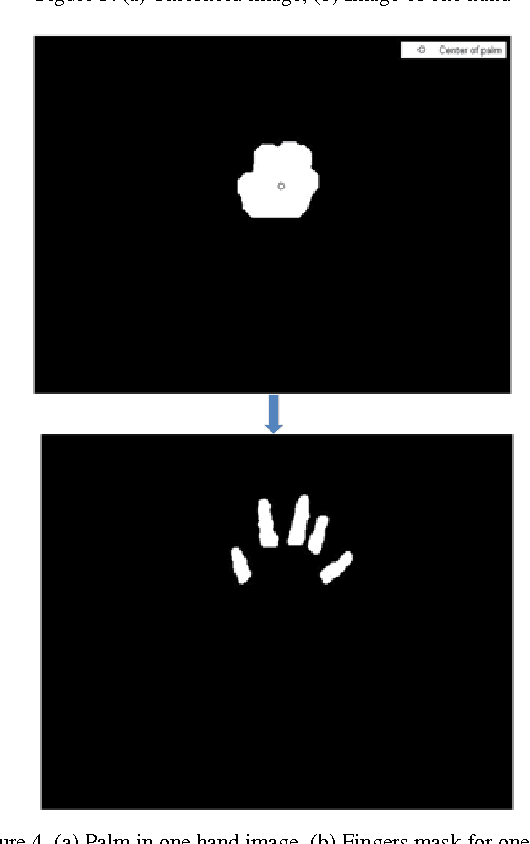
Abstract:Hand Gesture is a popular way to interact or control machines and it has been implemented in many applications. The geometry of hand is such that it is hard to construct in virtual environment and control the joints but the functionality and DOF encourage researchers to make a hand like instrument. This paper presents a novel method for fingertips detection and centres of palms detection distinctly for both hands using MS KINECT in 3D from the input image. KINECT facilitates us by providing the depth information of foreground objects. The hands were segmented using the depth vector and centres of palms were detected using distance transformation on inverse image. This result would be used to feed the inputs to the robotic hands to emulate human hands operation.
* 4 page
A Hash based Approach for Secure Keyless Steganography in Lossless RGB Images
Apr 17, 2013



Abstract:This paper proposes an improved steganography approach for hiding text messages in lossless RGB images. The objective of this work is to increase the security level and to improve the storage capacity with compression techniques. The security level is increased by randomly distributing the text message over the entire image instead of clustering within specific image portions. Storage capacity is increased by utilizing all the color channels for storing information and providing the source text message compression. The degradation of the images can be minimized by changing only one least significant bit per color channel for hiding the message, incurring a very little change in the original image. Using steganography alone with simple LSB has a potential problem that the secret message is easily detectable from the histogram analysis method. To improve the security as well as the image embedding capacity indirectly, a compression based scheme is introduced. Various tests have been done to check the storage capacity and message distribution. These testes show the superiority of the proposed approach with respect to other existing approaches.
* The paper is withdrawn due to license issue
Intelligent Approaches to interact with Machines using Hand Gesture Recognition in Natural way: A Survey
Mar 10, 2013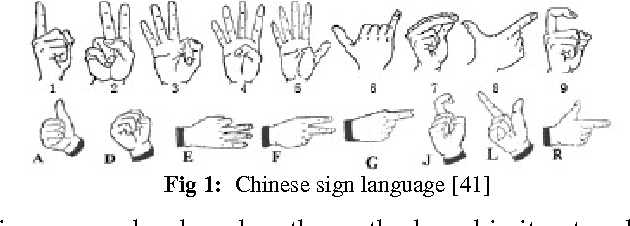
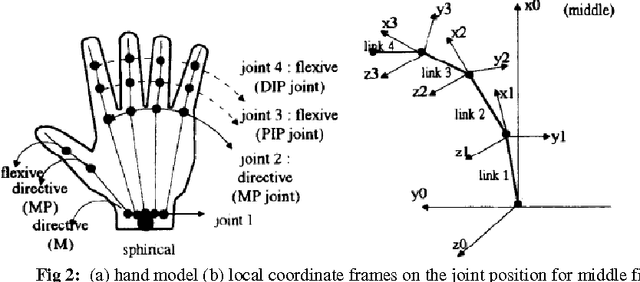
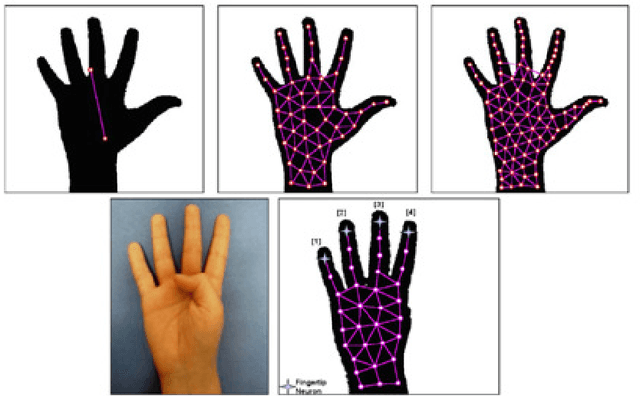
Abstract:Hand gestures recognition (HGR) is one of the main areas of research for the engineers, scientists and bioinformatics. HGR is the natural way of Human Machine interaction and today many researchers in the academia and industry are working on different application to make interactions more easy, natural and convenient without wearing any extra device. HGR can be applied from games control to vision enabled robot control, from virtual reality to smart home systems. In this paper we are discussing work done in the area of hand gesture recognition where focus is on the intelligent approaches including soft computing based methods like artificial neural network, fuzzy logic, genetic algorithms etc. The methods in the preprocessing of image for segmentation and hand image construction also taken into study. Most researchers used fingertips for hand detection in appearance based modeling. Finally the comparison of results given by different researchers is also presented.
Fingertip Detection: A Fast Method with Natural Hand
Dec 01, 2012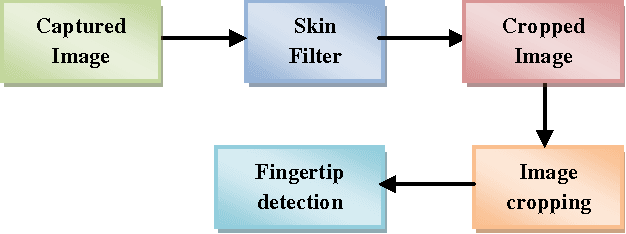



Abstract:Many vision based applications have used fingertips to track or manipulate gestures in their applications. Gesture identification is a natural way to pass the signals to the machine, as the human express its feelings most of the time with hand expressions. Here a novel time efficient algorithm has been described for fingertip detection. This method is invariant to hand direction and in preprocessing it cuts only hand part from the full image, hence further computation would be much faster than processing full image. Binary silhouette of the input image is generated using HSV color space based skin filter and hand cropping done based on intensity histogram of the hand image
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge