S. Edwin Raja
UNCA: A Neutrosophic-Based Framework for Robust Clustering and Enhanced Data Interpretation
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Accurately representing the complex linkages and inherent uncertainties included in huge datasets is still a major difficulty in the field of data clustering. We address these issues with our proposed Unified Neutrosophic Clustering Algorithm (UNCA), which combines a multifaceted strategy with Neutrosophic logic to improve clustering performance. UNCA starts with a full-fledged similarity examination via a {\lambda}-cutting matrix that filters meaningful relationships between each two points of data. Then, we initialize centroids for Neutrosophic K-Means clustering, where the membership values are based on their degrees of truth, indeterminacy and falsity. The algorithm then integrates with a dynamic network visualization and MST (Minimum Spanning Tree) so that a visual interpretation of the relationships between the clusters can be clearly represented. UNCA employs SingleValued Neutrosophic Sets (SVNSs) to refine cluster assignments, and after fuzzifying similarity measures, guarantees a precise clustering result. The final step involves solidifying the clustering results through defuzzification methods, offering definitive cluster assignments. According to the performance evaluation results, UNCA outperforms conventional approaches in several metrics: it achieved a Silhouette Score of 0.89 on the Iris Dataset, a Davies-Bouldin Index of 0.59 on the Wine Dataset, an Adjusted Rand Index (ARI) of 0.76 on the Digits Dataset, and a Normalized Mutual Information (NMI) of 0.80 on the Customer Segmentation Dataset. These results demonstrate how UNCA enhances interpretability and resilience in addition to improving clustering accuracy when contrasted with Fuzzy C-Means (FCM), Neutrosophic C-Means (NCM), as well as Kernel Neutrosophic C-Means (KNCM). This makes UNCA a useful tool for complex data processing tasks
Optimizing Disease Prediction with Artificial Intelligence Driven Feature Selection and Attention Networks
Jul 31, 2024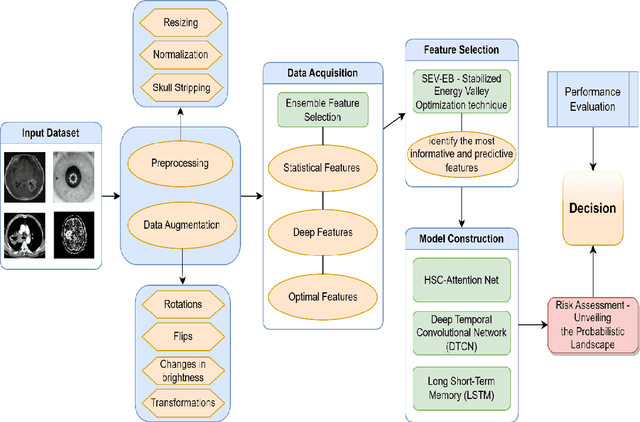
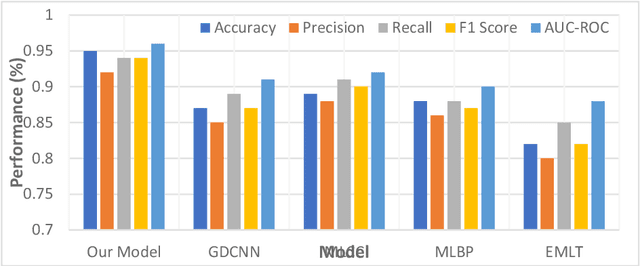
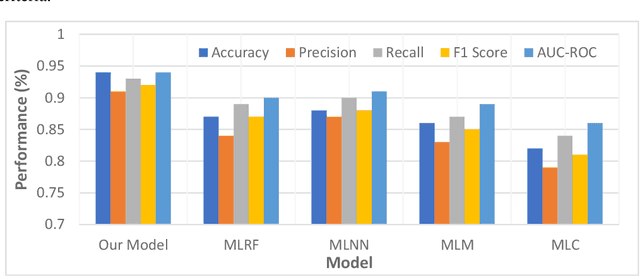
Abstract:The rapid integration of machine learning methodologies in healthcare has ignited innovative strategies for disease prediction, particularly with the vast repositories of Electronic Health Records (EHR) data. This article delves into the realm of multi-disease prediction, presenting a comprehensive study that introduces a pioneering ensemble feature selection model. This model, designed to optimize learning systems, combines statistical, deep, and optimally selected features through the innovative Stabilized Energy Valley Optimization with Enhanced Bounds (SEV-EB) algorithm. The objective is to achieve unparalleled accuracy and stability in predicting various disorders. This work proposes an advanced ensemble model that synergistically integrates statistical, deep, and optimally selected features. This combination aims to enhance the predictive power of the model by capturing diverse aspects of the health data. At the heart of the proposed model lies the SEV-EB algorithm, a novel approach to optimal feature selection. The algorithm introduces enhanced bounds and stabilization techniques, contributing to the robustness and accuracy of the overall prediction model. To further elevate the predictive capabilities, an HSC-AttentionNet is introduced. This network architecture combines deep temporal convolution capabilities with LSTM, allowing the model to capture both short-term patterns and long-term dependencies in health data. Rigorous evaluations showcase the remarkable performance of the proposed model. Achieving a 95% accuracy and 94% F1-score in predicting various disorders, the model surpasses traditional methods, signifying a significant advancement in disease prediction accuracy. The implications of this research extend beyond the confines of academia.
* 16 Pages, 4 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge