Ruxandra Barbulescu
INESC-ID, Rua Alves Redol 9, 1000-029 Lisboa
Matching the Neuronal Representations of V1 is Necessary to Improve Robustness in CNNs with V1-like Front-ends
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:While some convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved great success in object recognition, they struggle to identify objects in images corrupted with different types of common noise patterns. Recently, it was shown that simulating computations in early visual areas at the front of CNNs leads to improvements in robustness to image corruptions. Here, we further explore this result and show that the neuronal representations that emerge from precisely matching the distribution of RF properties found in primate V1 is key for this improvement in robustness. We built two variants of a model with a front-end modeling the primate primary visual cortex (V1): one sampling RF properties uniformly and the other sampling from empirical biological distributions. The model with the biological sampling has a considerably higher robustness to image corruptions that the uniform variant (relative difference of 8.72%). While similar neuronal sub-populations across the two variants have similar response properties and learn similar downstream weights, the impact on downstream processing is strikingly different. This result sheds light on the origin of the improvements in robustness observed in some biologically-inspired models, pointing to the need of precisely mimicking the neuronal representations found in the primate brain.
Modelling Neuronal Behaviour with Time Series Regression: Recurrent Neural Networks on C. Elegans Data
Jul 01, 2021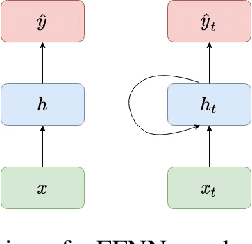
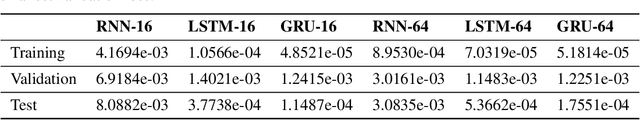
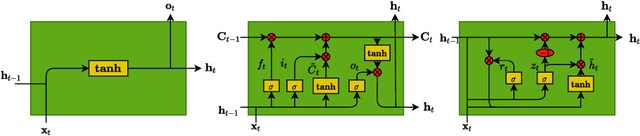
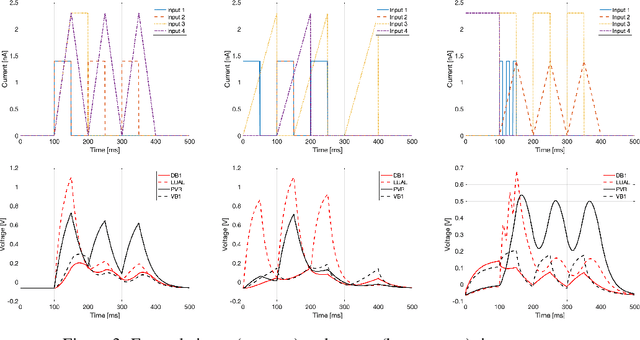
Abstract:Given the inner complexity of the human nervous system, insight into the dynamics of brain activity can be gained from understanding smaller and simpler organisms, such as the nematode C. Elegans. The behavioural and structural biology of these organisms is well-known, making them prime candidates for benchmarking modelling and simulation techniques. In these complex neuronal collections, classical, white-box modelling techniques based on intrinsic structural or behavioural information are either unable to capture the profound nonlinearities of the neuronal response to different stimuli or generate extremely complex models, which are computationally intractable. In this paper we show how the nervous system of C. Elegans can be modelled and simulated with data-driven models using different neural network architectures. Specifically, we target the use of state of the art recurrent neural networks architectures such as LSTMs and GRUs and compare these architectures in terms of their properties and their accuracy as well as the complexity of the resulting models. We show that GRU models with a hidden layer size of 4 units are able to accurately reproduce with high accuracy the system's response to very different stimuli.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge