Rupashree Dey
Contrastive Learning for OOD in Object detection
Aug 12, 2022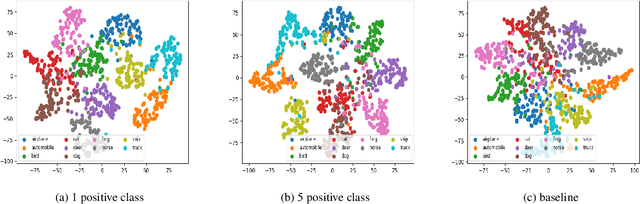
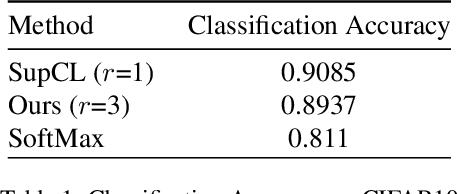
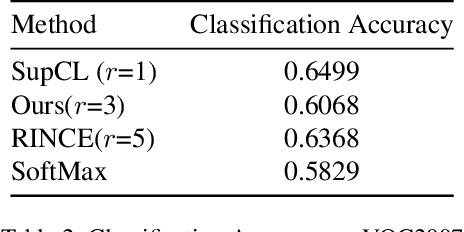
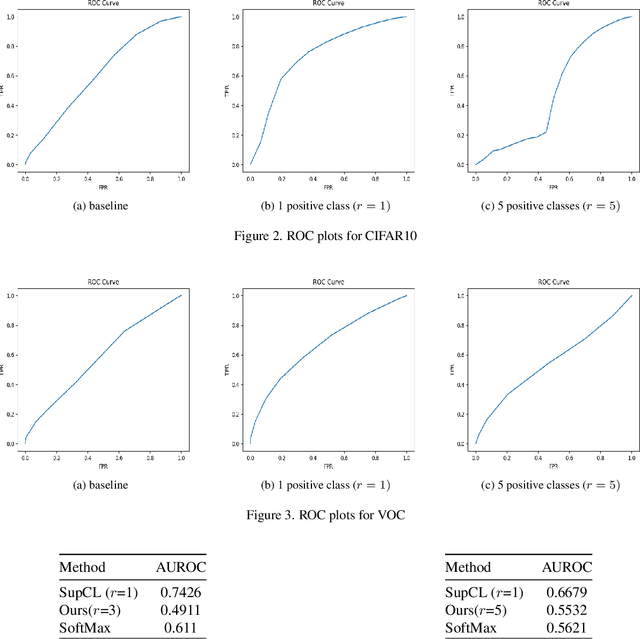
Abstract:Contrastive learning is commonly applied to self-supervised learning, and has been shown to outperform traditional approaches such as the triplet loss and N-pair loss. However, the requirement of large batch sizes and memory banks has made it difficult and slow to train. Recently, Supervised Contrasative approaches have been developed to overcome these problems. They focus more on learning a good representation for each class individually, or between a cluster of classes. In this work we attempt to rank classes based on similarity using a user-defined ranking, to learn an efficient representation between all classes. We observe how incorporating human bias into the learning process could improve learning representations in the parameter space. We show that our results are comparable to Supervised Contrastive Learning for image classification and object detection, and discuss it's shortcomings in OOD Detection
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge